Do Muscle Relaxers Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Written by Dr. Deepali Anand

Dr. Deepali is a medical writer and healthcare professional with a background in clinical surgery and patient care. Having transitioned from active clinical practice to medical communications, she specializes in bridging the gap between complex clinical data and patient education. Dr. Deepali is dedicated to creating evidence-based content that is grounded in scientific rigor and empathy, ensuring that sensitive topics like sexual wellness and mental health are accessible and empowering for every reader.
•
September 23, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.

Quick Read
Yes, muscle relaxers can cause erectile dysfunction in some men, though it doesn't happen to everyone who takes these medications. These drugs work on your brain and nervous system, which can interfere with the nerve signals and blood flow needed for normal erections. The good news is that this type of ED is usually reversible - sexual function typically improves when you stop the medication or reduce the dose. If you're experiencing ED while taking muscle relaxers, don't stop the medication on your own; instead, talk to your healthcare provider who can adjust your treatment or explore other options while keeping your overall health in mind.
Can muscle relaxers cause ED? The short answer is yes, in some men, these medications can play a role in erectile dysfunction. Muscle relaxers are often prescribed for back pain, spasms, or injuries, but because they act on the brain and nervous system, their effects can sometimes spill over into sexual health.
While not everyone who takes them will experience erectile problems, it’s natural to wonder if your medication could be the reason behind changes in erections or libido.
In this article, we’ll break down how muscle relaxers may affect erections, factors that influence your risk, and what you can do if you notice ED while on these medications.
Can Muscle Relaxers Cause ED?
Yes, muscle relaxers can sometimes cause or contribute to erectile dysfunction. The risk depends on factors like the type of medication, dosage, and individual health differences.
This can happen because muscle relaxers affect the central nervous system, interfere with how nerve signals travel, and may also influence blood vessels. These changes can make it harder to get or maintain an erection.
But it’s important to distinguish between a temporary drop in erections or libido after taking a muscle relaxer and ongoing erectile dysfunction. Not everyone who takes muscle relaxers experiences erectile problems, but it can occur in some men.
According to Allo Health, nearly 1 in 2 men experience erectile dysfunction, which is based on our internal clinical data of more than 2.5 lakh patients who have visited our clinics.
Allo asks
Have you ever noticed changes in your erections after starting a muscle relaxer?
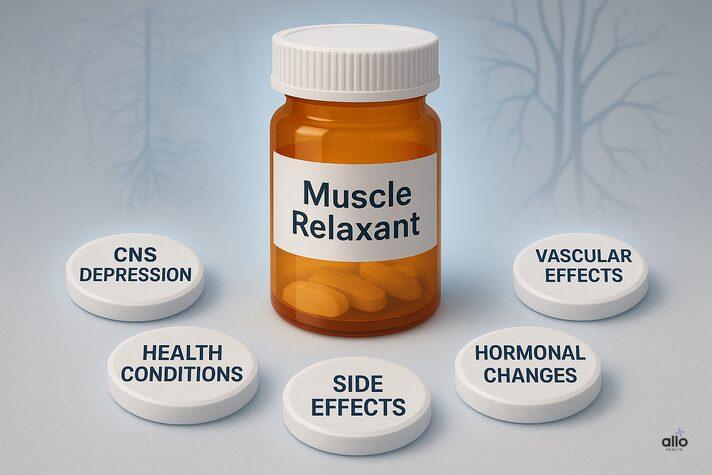
How Do Muscle Relaxers Cause ED?
Muscle relaxers work mainly on the brain and nervous system, not just on the muscles. Because of this, their side effects can spill over into other areas of the body, including sexual function. They may contribute to erectile dysfunction through several pathways:
1. Depression of the Central Nervous System
- Most muscle relaxers slow down the central nervous system, creating sedative effects.[1]
- This slowdown can interfere with the neural signals needed to achieve and maintain an erection.
- Some, such as benzodiazepine-based relaxants, may also reduce sexual interest and overall libido.
2. Interference with Nerve Signals
- Certain drugs, like baclofen, act on GABA-B receptors, which are involved in erection and ejaculation.[2]
- This interference can directly disrupt normal sexual responses.
3. Vascular Effects
- Certain drugs, like baclofen, act on GABA-B receptors, which are involved in erection and ejaculation.[3]
- This interference can directly disrupt normal sexual responses.
4. Hormonal Changes
- A few relaxants, especially those related to opioids or antidepressants, may affect hormone levels.
- For example, opioids can reduce testosterone production, leading to loss of libido and erection problems.[4]
5. Underlying Health Conditions
- The very conditions for which muscle relaxers are prescribed, such as chronic back pain, nerve injury, or spasticity, can also contribute to ED.
- This makes it tricky to know whether ED is due to the drug itself or the underlying health issue.
6. Other Common Side Effects
Common side effects include drowsiness, tiredness, dizziness, dry mouth, low blood pressure, trouble urinating, confusion, or memory problems. These side effects can lower sexual desire and performance. They do this even if they do not directly affect erections.
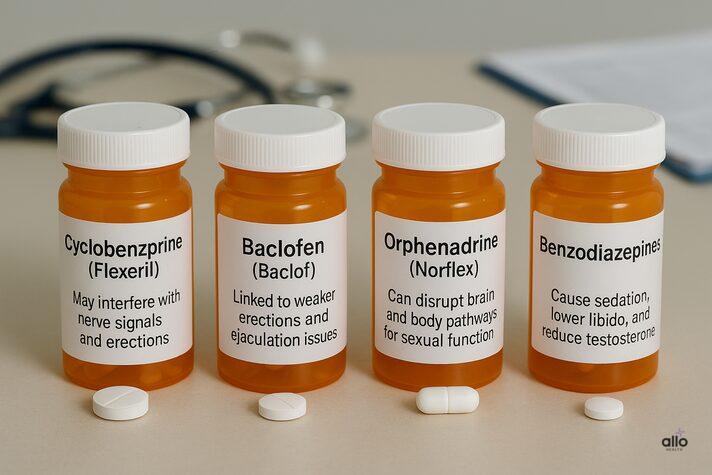
Some Muscle Relaxants & Their Sexual Side Effects
Cyclobenzaprine(Flexeril)(Flexabenz)
Cyclobenzaprine is one of the most commonly linked muscle relaxants with sexual dysfunction.[5] It is structurally similar to certain antidepressants, and antidepressants themselves are well-known to cause erectile dysfunction.
By affecting nerve activity in the central nervous system, cyclobenzaprine may interfere with the signals necessary for achieving and maintaining an erection.
Baclofen(Baclof)
Research[6] shows that intrathecal (spinal) use of baclofen can reduce the quality of erections and sometimes cause ejaculation difficulties. These sexual side effects are often dose-dependent and may improve once the dose is lowered or the medication is stopped.
Orphenadrine (Norflex)(Acetofen)
Orphenadrine is another muscle relaxer that can cause erectile dysfunction.[7] It affects both the brain and body pathways involved in sexual function, which can impact erections.
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines, used for anxiety and muscle spasms, can lead to ED and other sexual problems.[8] They make you feel sedated, which lowers arousal and interest in sex. With long-term use, they may also reduce testosterone, further affecting sexual health.
Drug
Effect on Body
Sexual Side Effects
Cyclobenzaprine
Slows nerve activity (CNS)
Trouble getting/keeping erections
Baclofen
Acts on nerves (GABA-B)
Weaker erections, ejaculation issues
Orphenadrine
Affects brain + body signals
Can cause erection problems
Benzodiazepines
Sedative, lowers testosterone
ED, low desire, poor performance
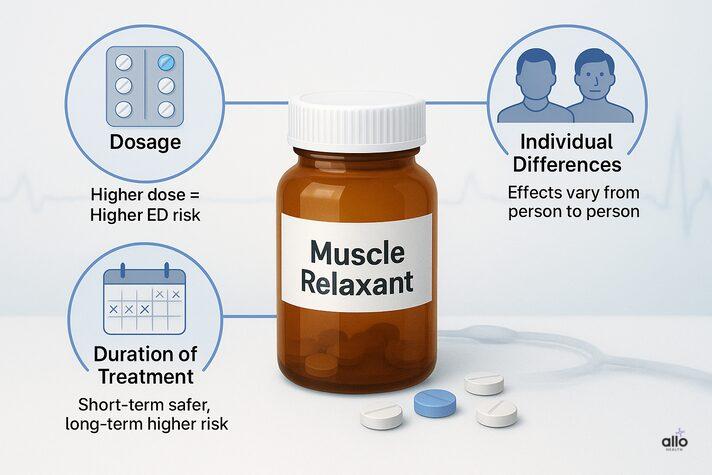
Factors Influencing ED Caused by Muscle Relaxants
1. Dosage of Muscle Relaxant
Sexual side effects from muscle relaxers are often dose-related. Higher doses make erectile dysfunction more likely and sometimes more severe. Even low or standard doses can cause problems in certain individuals, as shown in case reports.
2. Individual Differences
Not everyone reacts the same way. Some people may never notice sexual side effects, while others may develop ED even on regular therapeutic doses.
3. Duration of Treatment
Most muscle relaxers are meant for short-term use (2-3 weeks). Using them longer may increase the risk of ED and other side effects.
Many times, it’s not just the muscle relaxer itself- the pain, stress, or other medications you’re taking can also affect sexual function. That’s why a full evaluation is important before jumping to conclusions.
Is Erectile Dysfunction Caused By Muscle Relaxants Reversible?
In most cases, yes. Erectile dysfunction caused by muscle relaxers is usually reversible. Research and case reports show that sexual function often improves once the medication is stopped or the dose is reduced. This suggests the effects are pharmacological, meaning they don’t cause permanent damage.
That said, it’s important to get ED checked by a doctor before making any changes on your own. Erectile dysfunction can have many different causes, and muscle relaxers may only be part of the bigger picture, or not the cause at all.
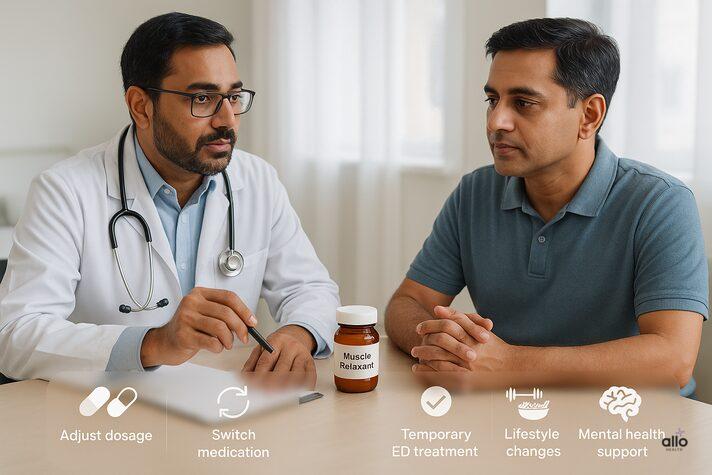

What to Do If You Notice ED While Taking Muscle Relaxers
If you have erectile dysfunction while taking muscle relaxers, do not panic. Do not stop the medicine suddenly. The first step is to talk to your healthcare provider. They can:
- Adjust the dosage to the lowest effective level.
- Switch you to another muscle relaxer with fewer sexual side effects.
- Provide temporary ED treatment if the relaxer is needed only for the short term.
- Check for underlying conditions causing ED(like pain, nerve issues, or other health problems) that may be affecting both muscles and erections.
- Prescribe safe ED medications (such as sildenafil) if appropriate.
You can also support your sexual health through:
- Lifestyle changes like regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and good sleep.
- Mental health care, since anxiety and depression can make ED worse.
Bottom Line
Do muscle relaxers cause ED? Yes, they can in some cases. While not everyone will experience problems, muscle relaxers may interfere with erections through their effects on the nervous system, blood flow, or hormones.
Always talk to your healthcare provider about possible side effects and pay attention to any changes in sexual function when starting these medications.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Can you take Viagra with a muscle relaxer?
Yes, in most cases Viagra (sildenafil) can be taken with a muscle relaxer, but you should always check with your doctor first. Some muscle relaxants lower blood pressure, and combining them with Viagra may increase this effect. Your doctor can confirm if it’s safe for you.
What drug gives you erectile dysfunction?
Several types of medications can cause erectile dysfunction, including certain muscle relaxers, antidepressants, blood pressure medicines, and opioids. Not everyone experiences this side effect, and in many cases ED improves once the medication is adjusted or switched.
Can stiff muscles cause ED?
Stiff or tight muscles themselves don’t directly cause ED, but the underlying conditions that cause muscle stiffness — such as back injuries, nerve damage, or chronic pain — can make sexual performance more difficult. Muscle relaxers are often prescribed for these issues, which can blur the cause.
Is ED from muscle relaxers permanent?
No, erectile dysfunction caused by muscle relaxers is usually temporary. Most men regain normal sexual function once the medication is reduced, switched, or stopped. If ED continues, it may be due to another health condition, which is why a doctor’s evaluation is important.
How do I know if my ED is from muscle relaxers or another cause?
The best way to know is by speaking with your healthcare provider. They may adjust your dose, change your medication, or run tests to rule out other causes like diabetes, heart disease, or stress. Don’t try to stop or change medication on your own.
Sources
- 1.
Side Effects of Muscle Relaxers
- 2.
Sexual Dysfunction Associated With Intrathecal Baclofen Use: A Report of Two Cases
- 3.
Co-Prescription of Strong CYP1A2 Inhibitors and the Risk of Tizanidine-Associated Hypotension: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- 4.
Opioids and endocrine dysfunction
- 5.
Painful Ejaculation with Cyclobenzaprine: A Case Report and Literature Review
- 6.
Sexual Dysfunction Associated With Intrathecal Baclofen Use: A Report of Two Cases
- 7.
Orphenadrine (oral route)
- 8.
Benzodiazepines related sexual dysfunctions: A critical review on pharmacology and mechanism of action


