Zinc and Erectile Function: Is This Trace Element Essential for Men’s Health?

Zinc plays an important role in testosterone production and nitric oxide (NO) synthesis, both essential for sexual health. Low zinc levels can contribute to erectile dysfunction (ED), so getting enough can help improve erectile function. The recommended daily intake for men is 11 mg, but for ED treatment, doses of 15-30 mg daily are often suggested, especially for those with zinc deficiency or low testosterone. Studies show that 12 mg daily for 12 weeks can improve erectile function in some men. However, avoid exceeding 40 mg daily to prevent toxicity, which can cause nausea and interfere with copper absorption. Zinc helps produce nitric oxide (NO), which relaxes the penis's muscles, allowing blood to flow in and cause an erection. Sources like oysters, red meat, poultry, and beans are rich in zinc. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting zinc supplements for ED to ensure proper dosage.
Many men wonder how much zinc for erectile dysfunction they should take to improve their sexual health. Zinc is an essential mineral that plays an important role in testosterone production, nitric oxide synthesis, and overall sexual function.
Research shows that zinc deficiency can contribute to erectile dysfunction. So, proper intake may help restore normal sexual performance.
This comprehensive guide examines how much zinc is needed for erectile dysfunction, the scientific evidence behind zinc and erectile dysfunction, including optimal dosages, clinical studies, and safety considerations. We’ll explore how zinc affects male sexual health, what the research says about supplementation, and how to incorporate zinc into an ED treatment plan.
Whether you’re dealing with zinc deficiency or looking to optimize your sexual health, understanding the relationship between zinc and erectile function can help you make informed decisions about supplementation and treatment options.
The Role of Zinc in Male Sexual Health
Zinc is a vital element that supports numerous body functions. It plays a major role in testosterone production, which directly affects sexual desire (libido) and erectile function. Research shows that men with low zinc levels often have reduced testosterone levels.
This mineral also supports the immune system and helps with DNA synthesis.
For sexual health, zinc helps produce nitric oxide, which improves blood flow to the penis. The better the blood flow better the erection. Without enough zinc, men may experience reduced sexual performance.
Studies say that zinc deficiency can lead to sexual dysfunction. Men with zinc deficiencies show lower testosterone levels compared to those with normal intake. Zinc supplementation is linked to improvements in testosterone production and overall sexual function.[1]

How Much Zinc for Erectile Dysfunction: The Recommended Dosage
The standard daily zinc intake for adult men is 11 mg per day. Research suggests doses of 15-30 mg daily may benefit those with zinc deficiency or low testosterone.
For erectile dysfunction treatment, most studies use a zinc dosage for erectile dysfunction ranging from 12-30 mg daily.
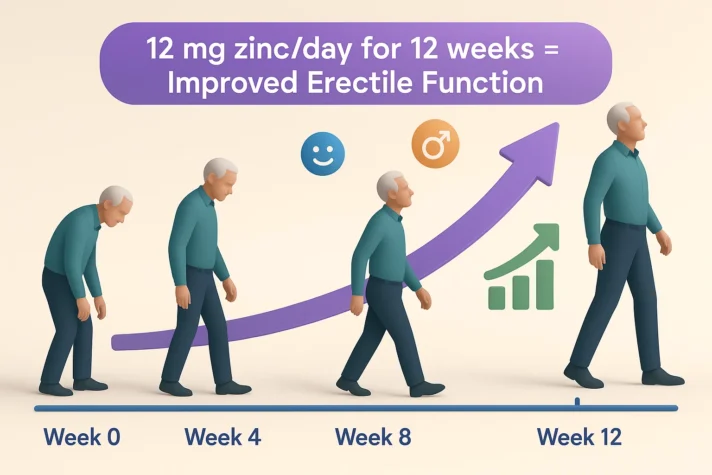
A study on elderly men used 12 mg daily for 12 weeks and showed significant improvements in erectile function scores.[2]
Zinc can be a powerful tool for men dealing with ED, but more is not always better. Crossing 40 mg a day can lead to toxicity and interfere with copper absorption.”
Note– Never exceed 40 mg daily to avoid toxicity. Excessive zinc can cause nausea, diarrhea, and interfere with copper and iron absorption. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation, especially for managing ED.
Zinc Deficiency and Low Testosterone
Research shows zinc deficiency is linked to hypogonadism (low testosterone). Hypogonadism is a condition in which the body does not produce enough sexual hormones, like testosterone, in case of males. Young men with low zinc levels experienced low testosterone. When they were supplemented with zinc, their testosterone levels improved.
This supports the theory that zinc is vital for maintaining testosterone levels. Low testosterone is a major contributor to erectile dysfunction, making zinc supplementation potentially beneficial for affected men.[3]
Zinc’s Effect on Sexual Function
Animal studies have found that giving zinc to male rats helped improve their sexual performance. The rats that got a moderate amount of zinc (about 5 mg a day) showed more frequent erections and mating activity. But when the dose was too high, it lowered their interest in sex. This shows that zinc can help with sexual health, but only in the right amount.
These studies highlight the importance of finding the right balance. Too little zinc causes deficiency, while too much can harm sexual function.[4]
Zinc and Nitric Oxide Production
Zinc helps your body make a substance called nitric oxide (NO), which is important for getting an erection. Nitric oxide helps relax the muscles in the penis, allowing more blood to flow in. This results in a perfect erection.
Studies show zinc supports the activation of nitric oxide synthases (nNOS and eNOS). These enzymes are responsible for NO production. By stabilizing these enzymes, zinc helps maintain proper erectile function and smooth muscle relaxation.[5]
Zinc’s Protective Effects
Research on rats with lead-induced erectile dysfunction showed that zinc supplementation helped reverse the harmful effects. Lead exposure had reduced their testosterone levels and caused oxidative stress, which means too many harmful molecules (called free radicals) were building up in the body. This can damage cells and tissues, including those needed for erections.
Zinc helped bring back healthy testosterone levels and improved NO signaling. NO signaling is the process where the body releases nitric oxide (NO), a chemical that relaxes blood vessels and increases blood flow to the penis, which is key for getting an erection.
Zinc also boosts antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes act like the body’s cleanup crew, reducing oxidative damage by removing the harmful free radicals. This helps protect cells and supports better erectile function.[6]
Zinc and Erectile Dysfunction: Clinical Evidence
A study on elderly men with vitamin D deficiency found that zinc supplementation (12 mg daily) improved erectile function.
These men showed significant increases in International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) scores after 12 weeks. The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) is a questionnaire used to assess male sexual function, particularly in the context of erectile dysfunction (ED).
This shows that zinc, when combined with other nutrients like vitamin D, can have therapeutic effects on erectile dysfunction in aging men. So, Zinc is a good supplement for ED.[7]
Zinc Supplementation Forms and Absorption
Different zinc forms are available, including zinc gluconate and zinc sulfate.
Zinc comes in several different forms, and each type is absorbed by the body slightly differently. The most common forms found in supplements include:
| Zinc Form | Key Uses | Absorption & Tolerance | Notes |
| Zinc Gluconate | Common in supplements, lozenges, and cold remedies | Gentle on the stomach, well tolerated | Affordable and widely available, but not the most absorbable |
| Zinc Sulfate | Often used to treat zinc deficiency, testosterone support | Decent absorption; may cause nausea if taken without food | Commonly prescribed for confirmed deficiency cases |
| Zinc Picolinate | General supplementation, testosterone, and immune health | Highly absorbable; good bioavailability | Often recommended for better absorption |
| Zinc Citrate | General supplementation | Well absorbed; easy on the stomach | Good option for people with sensitive digestion |
| Zinc Acetate | Found in cold lozenges | Decent absorption | May be used for faster zinc delivery in immune-support products |
Healthcare providers may recommend specific forms based on individual needs and tolerance levels.
Zinc from animal sources is more easily absorbed than from plant sources. If you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, you may need higher zinc intake or supplementation to meet your needs.
Taking zinc with food can reduce stomach upset but may slightly decrease absorption. Taking it on an empty stomach improves absorption but may cause nausea in some people.
Zinc-Rich Foods for Better Sexual Health
Including zinc-rich foods in your diet can help maintain adequate levels. The best dietary sources include:

- Oysters (highest zinc content)
- Red meat (lamb, pork)
- Poultry (chicken)
- Seafood (crab, shrimp, lobster)
- Beans (chickpeas, lentils, black beans)
- Nuts and seeds (pumpkin seeds, cashews)
- Whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice)
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
Monitoring your dietary intake and conducting a blood zinc level test can help determine if you’re getting adequate amounts. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey shows dietary trace metal intake varies significantly among different populations.
What We’ve Seen at Allo Health
In over 250,000+ consultations at Allo Health, we’ve found that:
- 62% of men under 35 with ED also had low testosterone or stress-linked symptoms, both of which are influenced by zinc levels.
- Only 1 in 5 diabetic patients with ED improved without addressing diet and micronutrients like zinc, highlighting how important nutrition is for recovery.
- Among patients taking zinc supplements for ED, those who also focused on stress management and lifestyle saw the best long-term results.
- 38% of ED patients had never considered checking their zinc levels or diet until it was discussed during their first consultation.
- 24% of men with performance anxiety showed measurable improvement in erectile quality after adding zinc + therapy to their treatment plan.
Comprehensive Approach to Erectile Dysfunction
Taking zinc supplements can help with erectile problems, but it works best when combined with other healthy habits and treatments. That’s because ED (erectile dysfunction) can happen due to many reasons, like stress, heart health issues, hormone imbalances, or an unhealthy lifestyle.
Today, ED treatment can include a mix of options from natural supplements like zinc to advanced medical therapies, and even online consultations for easy access to expert care.
Here’s how zinc helps support sexual health:
- Boosts testosterone levels if you’re low on zinc
- Helps your body make nitric oxide, which improves blood flow to the penis
- Reduces oxidative stress, which can damage blood vessels
- Supports better blood circulation, especially to the penis
- Improves the health of the inner lining of penile arteries (called the endothelium)
- Helps with healing and repairing tissues in the body
Additional Considerations for Sexual Health
While zinc is important for sexual health, other things also play a big role in how well your body performs sexually.
- Prostate health matters, and zinc helps keep the prostate working properly, which supports sexual performance.
- Your mental health and brain function also affect your sex life. Stress, anxiety, or a low mood can lead to problems like ED.
- Metabolic problems, like high blood sugar or cholesterol, can reduce blood flow and hormone balance. Fixing these can improve erections.
- Healthy blood flow is key. If your blood vessels aren’t working well, especially the ones leading to the penis, getting or keeping an erection can be hard. Zinc helps, but full vascular support is important for lasting results. [8]
Track Your Zinc & Sexual Health for 7 Days
Start a simple journal where you record:
- Zinc intake (from food or supplements)
- Morning erections
- Sleep quality
- Stress or anxiety levels
- Energy or libido
Take this journal to your doctor. It helps identify patterns like low zinc or high stress that might be affecting your erections.
Safety and Side Effects
For most men, zinc supplements are safe when taken in the right amount. But like any supplement, it can cause a few mild side effects for some people, such as:
- Nausea
- Stomach discomfort
- A metallic taste in the mouth
Taking too much zinc for a long time isn’t a good idea. High doses can block your body from absorbing copper, which you also need for good health. It may even weaken your immune system over time.
Watch out for signs of zinc overdose, such as:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
If you notice any of these, cut back on the zinc and talk to your doctor to stay safe.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."