Lisinopril vs Losartan: Erectile Dysfunction Effects Compared
Written by Dr. Sharon Kumar

With a strong academic background in dentistry and clinical exposure, Dr. Sharon who has studied at PDM Dental College, brings a valuable blend of medical knowledge and communication skills to health content writing. She is passionate about creating clear, compassionate, and evidence-based content on topics such as general wellness, sexual health, oral care, and patient education. Her goal is to make complex medical information easy to understand, relatable, and genuinely helpful for readers seeking clarity on their health concerns. Dr. Sharon believes in the power of well-researched, empathetic content to educate and empower people to make better health decisions. Whether it’s writing about preventive care or breaking down myths in sexual wellness, her content always balances science with sensitivity.
•
July 25, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.

Quick Read
Losartan is often the better option when erectile dysfunction is a concern. It has a more favorable effect on sexual health and may even improve erectile function in some men. Lisinopril, while effective for blood pressure, can sometimes cause temporary ED when first started, though this usually improves over time. If you're starting treatment and worried about sexual side effects, losartan may be the preferred choice, especially in the beginning.
Doctors commonly prescribe lisinopril and losartan to manage high blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart attacks, stroke, and other cardiovascular issues. While both are effective antihypertensive medications, they belong to different drug classes and work in slightly different ways. One question many patients ask is how these medications affect sexual health specifically, whether they can cause erectile dysfunction (ED). If you’re searching for answers about lisinopril vs losartan erectile dysfunction, you're not alone. In this article, we explore how each medication may impact erectile function and what that means for your treatment and quality of life.
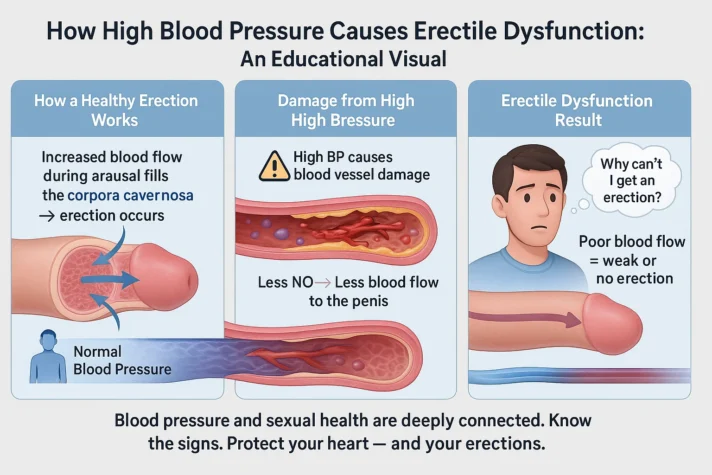
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) and Blood Flow: How are they related?
Erectile dysfunction means a man has trouble getting or keeping an erection for sex. It's a common issue, especially among older men, and can result from many different causes that affect quality of life and intercourse events. High blood pressure can lead to ED by damaging blood vessels, making it harder for penile blood to flow to the penis. The penis has empty spaces called the corpora cavernosa. When a man is aroused, blood flows into these empty compartments, causing a firm erection. So, now the picture gets a lot clearer about how blood plays such an important role in an erection and orgasmic ability.
What is Lisinopril?
Lisinopril is a type of drug called an ACE inhibitor. These antihypertensive therapy agents are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for blood pressure control. It works by blocking the angiotensin-converting enzyme that narrows blood vessels, helping blood flow more easily and reducing blood pressure.
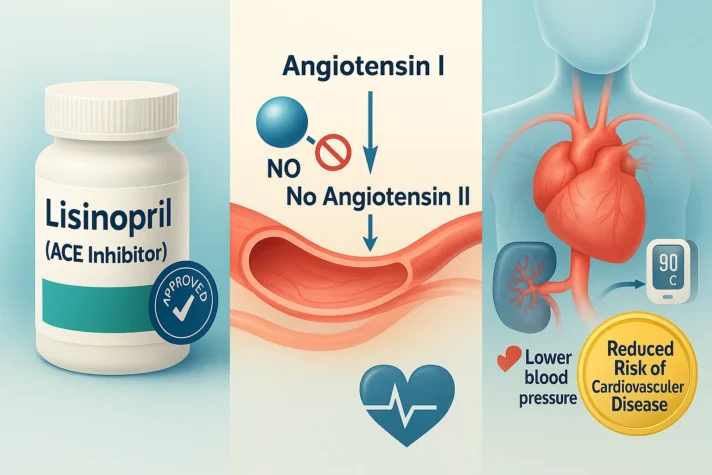
- Common Uses: It is prescribed to manage hypertension (high blood pressure) and heart failure, and also to protect kidney function, especially in people with diabetes. This medication helps reduce cardiac risk and prevent cardiovascular disease.
- Mechanism: Lisinopril works by inhibiting an enzyme that causes blood vessels to constrict (narrow down). This leads to widened vessels, improving blood flow and lowering blood pressure. Current rules say ACE inhibitors should be the first choice for many patients with high blood pressure.
What is Losartan?
Losartan is part of a class of drugs called angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), also known as angiotensin receptor blockers. Like ACE inhibitors, ARBs affect the renin-angiotensin system. This system blocks the enzyme that narrows blood vessels. But ARBs work in a slightly different way. Losartan blocks the action of angiotensin II, a hormone that narrows blood vessels, thus helping to lower blood pressure. The effects of ARBs have been extensively studied in hypertensive patients.
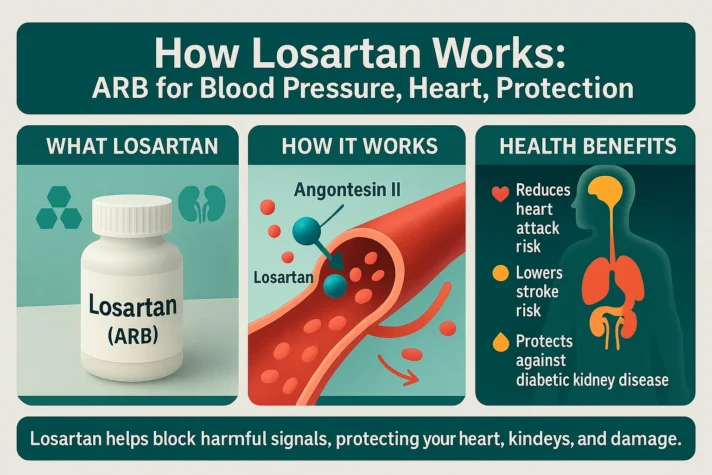
- Common Uses: Losartan is used to treat hypertension and reduce the risk of stroke in people with high blood pressure. It is also prescribed for diabetic kidney disease and helps prevent heart attacks.
- Mechanism: Losartan works by blocking angiotensin II receptors in blood vessels, preventing narrowing and allowing blood to flow more easily, thereby reducing blood pressure and providing beneficial effects for cardiovascular health.
Erectile Dysfunction and Blood Pressure Medications
Both lisinopril and losartan work on the renin-angiotensin system. But they affect erectile function very differently. Studies examining different classes of erectile function have shown varying results.
In many cases, switching from one medication like lisinopril to another like losartan can make a real difference, especially if you're experiencing erectile dysfunction.”
High blood pressure itself can cause erectile dysfunction. Blood pressure medicine can make sexual function better or worse, depending on the drug. Let's find out about their effects on erectile function.
Lisinopril and Erectile Dysfunction
In most cases, lisinopril does not cause erectile dysfunction. However, like other medications, it may have some common side effects that affect sexual activity in certain patients. Some research says losartan may improve erectile function in men with high blood pressure. It helps blood flow and stops damage to blood vessels. Lisinopril works by widening blood vessels. This may help erectile function in men with ED caused by high blood pressure.
- ED Side Effects: While ED is not typically associated with lisinopril, some men may experience a temporary decline in sexual activity when they first start taking the medication. These initial symptoms usually go away within the first month as the body adjusts to the medication. With respect to erectile function, most patients experience neutral effects over time.
- Research Findings: A study from the American Journal of Medicine and Science suggests that ACE inhibitors, including lisinopril, have neutral effects on sexual function overall. In some cases, the medication may even help improve it by improving blood flow. More studies are needed to fully understand the long-term effects.
Losartan and Erectile Dysfunction
Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker or ARB. It has a neutral or good effect on erectile function. This is better than ACE inhibitors like lisinopril. ARBs tend to have fewer negative effects. Some studies say losartan may improve sexual satisfaction and activity in men with high blood pressure and ED.
- Effect on ED: In studies, losartan has been associated with improved erectile function, particularly in men with both hypertension and ED. One study showed men taking losartan had better erections compared to those in the placebo arm. They could get and keep erections more easily.
- Positive Impact: ARBs like losartan are considered to have fewer sexual side effects than other blood pressure medications, such as beta-blockers or diuretics, which are often linked to ED. Beta blockers or diuretics slow down your heart rate and reduce the force of your heartbeat, potentially creating negative effects on sexual function.
Additionally, ARBs like losartan are sometimes even used off-label to help treat ED and improve quality of life in patients with sexual dysfunction.
Key Differences Between Lisinopril and Losartan
Both lisinopril and losartan are effective at lowering blood pressure, but they can have different effects on sexual health and sexual dysfunction management:
Medication
Impact on ED
Key Features
Lisinopril (ACE Inhibitor)
Generally neutral; may cause temporary ED in some men
Inhibits angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which helps relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
Losartan (ARB)
May improve ED or have neutral effects; some studies show benefits to sexual function
Blocks angiotensin II, leading to vasodilation and lower blood pressure; linked with better sexual function.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Lisinopril and Losartan
While both lisinopril and losartan are effective for managing high blood pressure, choosing the right antihypertensive treatment for your health, especially if you are concerned about ED, depends on several factors:
- Personal Health History: If you are already experiencing erectile dysfunction or other sexual health issues, losartan may be a better choice as it's less likely to cause sexual side effects and may provide beneficial effects for sexual activity.
- Other Medications: If you're on other medications, such as antidepressants, or have other health conditions like diabetes or heart disease, these could also affect ED. Your doctor may recommend different antihypertensive agents if they think another drug might better suit your overall health needs and reduce cardiac risk.
- How Your Body Responds: Each person responds differently to medications. Some men may find that lisinopril doesn't cause any sexual side effects, while others may feel some temporary decline in sexual function at first. The common side effects usually resolve after a few weeks.
- Lifestyle Factors: Things like smoking, alcohol, lack of exercise, poor diet, stress, and sleep apnea can also contribute to ED, and may need to be addressed alongside medication for the best results. Lifestyle changes often help blood pressure medicine work better.
What to Do If You Experience ED
If you are taking lisinopril or losartan and begin to experience erectile dysfunction, the first thing to do is talk to your doctor. Many things can cause ED, not just medicine. Proper ED treatment needs professional help. Your healthcare provider will be able to:
- Determine whether your blood pressure medication is contributing to your ED
- Adjust your dosage or suggest alternative medications, such as switching from lisinopril to losartan, or vice versa
- Explore other treatment options, including erectile dysfunction medications like Viagra, Cialis, or Levitra
- Consider other antihypertensive drugs like calcium antagonists if the current treatment isn't suitable
Note: Never stop or change your blood pressure medication without consulting your doctor, as it can lead to serious health risks, including cardiovascular disease and heart attacks.
Conclusion: Lisinopril vs. Losartan for Erectile Dysfunction
Both lisinopril and losartan work well to control high blood pressure. Losartan tends to have better effects on sexual health:
- It often has neutral effects or even beneficial effects on erectile function
- ARBs generally provide better outcomes with respect to erectile function
Lisinopril may cause temporary sexual side effects, such as erectile dysfunction:
- These issues usually go away after a few weeks of use
- Most patients experience neutral effects over time
If you experience ED while taking either medicine:
- Talk to your doctor; they can help find out the cause and adjust your antihypertensive treatment if needed
- Consider lifestyle changes alongside medication adjustments
ED can also be triggered by:
- Stress or anxiety
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Heart disease, cardiovascular disease, or other medical conditions
- Other medications that may interact with your antihypertensive therapy
Understanding the different effects of various classes on erectile function can help you and your healthcare provider make the best decision for your blood pressure control while maintaining your quality of life and sexual health.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only. If your medicine causes erectile dysfunction or other side effects, talk to your doctor. They can give you advice on your health and recommend appropriate antihypertensive agents based on current guidelines. AI answers may have mistakes. Always trust professional advice for your health, especially for high blood pressure and sexual problems.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Is losartan better than lisinopril for ED?
Yes, in many cases. Losartan (an ARB) may improve erectile function in men with high blood pressure and ED, making it a preferred choice if sexual health is a concern.
Can I switch from lisinopril to losartan if I experience ED?
Yes, but only under your doctor’s supervision. Never change or stop your blood pressure medication on your own.
Are there other blood pressure medications that don’t affect sexual function?
Yes. In addition to ARBs like losartan, some calcium channel blockers may have minimal impact on sexual health. Your doctor can help choose the best option for you.
Are ARBs safer than beta blockers for sexual health?
Yes. ARBs like losartan are generally considered to have fewer negative sexual side effects compared to beta blockers or diuretics.
How long do ED side effects last after starting lisinopril?
If you do experience ED from lisinopril, the symptoms typically fade within the first few weeks as your body adjusts.
Can I take Viagra with lisinopril or losartan?
In most cases, yes, but only if your doctor says it's safe. Always consult your healthcare provider before combining ED meds with blood pressure drugs.


