Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) and Erectile Dysfunction
Some sexually transmitted diseases can cause erectile dysfunction, especially those that lead to prostate inflammation. Infections like gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C can damage the prostate, blood vessels, or nerves, making it harder to get and keep an erection. Prostatitis from these infections can block blood flow to the penis and cause symptoms such as painful urination or ejaculation. The good news is that many cases improve with timely treatment. Bacterial infections usually respond well to antibiotics, while viral infections require long-term care to manage their effects. If erection problems continue even after treatment, lifestyle changes, counseling, or medical therapy may help. Prevention is also key. Practicing safe sex, getting vaccinated, testing regularly, and openly communicating with your partner can lower your risk. In short, some STDs can cause ED, but both conditions are manageable with early medical care and healthy habits.
Can stds cause erectile dysfunction? Yes, sexually transmitted diseases can cause erectile dysfunction. But can all STDs cause ED? No, not all STDs have the potential to cause ED. Some STDs, like gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, hepatitis, and HIV, can cause ED. These diseases not only affect a person physically but can also have long-lasting effects on their mental state. Communicating with your partner and seeking professional help is always a good idea.
Let us now read this article to understand what the common STDs causing ED are, how they cause ED, treatment options, and preventive measures for the same.
Common STDs And Their Effects Causing ED
Some common STDs, along with their effects, causing erectile dysfunction are
Chlamydia
It is caused by a bacterium, Chlamydia trachomatis. This STD is very easy to treat and cure. Chlamydia can cause pain during urination, testicular pain, and infection of the rectum and prostate [1], all of which can interfere with sexual function and cause ED. [2]
Gonorrhea
It is caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Patients who suffer from gonorrhea may have pain in their testicles, rectum, epididymis, and prostate. These patients may notice whitish discharge from the penis in the early stages and yellowish-greenish discharge in the later stages. According to a patient education material by Colorado State University, gonorrhea, if left untreated, can cause erectile dysfunction [3].
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
HIV leads to the inflammation of the entire bodily system and damages blood vessels. Poor blood flow will lead to poor erections. People suffering from HIV face reduced sexual interest and arousal. In a survey that involved filling out an anonymous self-questionnaire, 40 percent of men reported loss of sexual interest [4].
Hepatitis
Both hepatitis B [5] and hepatitis C [6] are associated with loss of erectile function and thereby cause erectile dysfunction.
Syphilis
This STD progresses in 3 stages: primary, secondary, and tertiary. Every stage has its own symptoms. If not treated, syphilis in the tertiary or late stages can cause erectile dysfunction [7].
How Can STDs Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
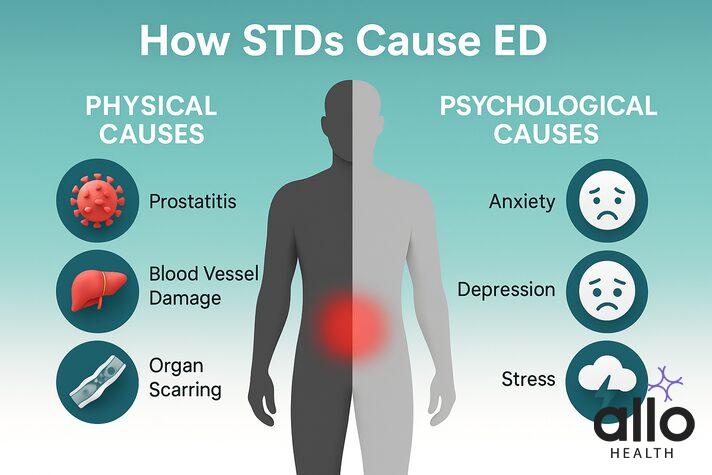
Some STDs can cause erectile dysfunction directly, while others can cause it by indirect means. There are two types of mechanisms by which STDs can cause ED. They are physical and psychological. They may cause an infection, inflammation, hormonal disturbances, damage to reproductive organs, and other systemic conditions in the body [8]. All of these, when untreated, can cause erectile dysfunction.
Prostatitis
Prostatitis refers to inflammation of the prostate gland and the surrounding area. This condition can damage the nerves and blood flow to the penis, which is important for achieving and maintaining an erection. Prostatitis can have multiple causes; sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are one of them [9]. Among these, chlamydia is one of the most common STDs associated with prostatitis [10].
Damage to the reproductive organ tract
STDs like gonorrhea, if untreated, can cause pain, scarring in the pathway that carries sperm, problems with fertility, and erectile dysfunction [11].
Underlying diseases
Some STDs, like HIV, hepatitis B, and C, exist along with a lot of other diseases and systemic conditions. These STIs are associated with cardiovascular diseases, chronic inflammation, and mental health conditions [12].
Damage to the blood vessels
STDs like syphilis can damage the endothelium (lining of blood vessels), which plays an important role in achieving erections [13].
Treatments For STDs causing Erectile Dysfunction
You might be wondering about the quality of life with an STD. It is not good, but that does not mean that it can not be improved. Treatment options for STDs causing EDs may involve treatment for the underlying STD, managing ED, or a combination of both.
Treating the underlying STD
Different STDs have different lines of treatment. But in this section, our main focus is to cover the STDs that are responsible for causing ED.
In most cases, treating sexually transmitted infections can improve and cure erectile dysfunction.
- For bacterial infections: STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis that are caused by bacteria are often treated with antibiotics. [14]
- Viral infections: Some viral infections, like HIV and hepatitis, may not be curable, but with antiviral therapy and long-term medical care, their impact on sexual health can be reduced. [14]
- In some cases, additional tests or follow-up care may be necessary to ensure the infection is fully resolved or well-controlled.
- In cases where sexually transmitted infections involve psychological impacts, counseling and therapy sessions by a healthcare professional play a major role.
“Do not self-medicate and rely on medicines by yourself. Treatment and duration should always be decided by a healthcare professional.”
Managing erectile dysfunction
In some cases, even after the STD has been treated, the symptoms of erectile dysfunction persist. In such cases, a proper treatment therapy for ED is followed.
The line of treatment for erectile dysfunction includes the following [15]-
- Counseling is especially helpful when anxiety, embarrassment, or relationship stress is involved.
- Lifestyle changes, such as improving diet, sleep, and physical activity, can support both sexual health and overall well-being.
- Medical options like phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5 inhibitors), penile prosthesis, vacuum erection devices, penile injection therapy may be considered in severe cases.
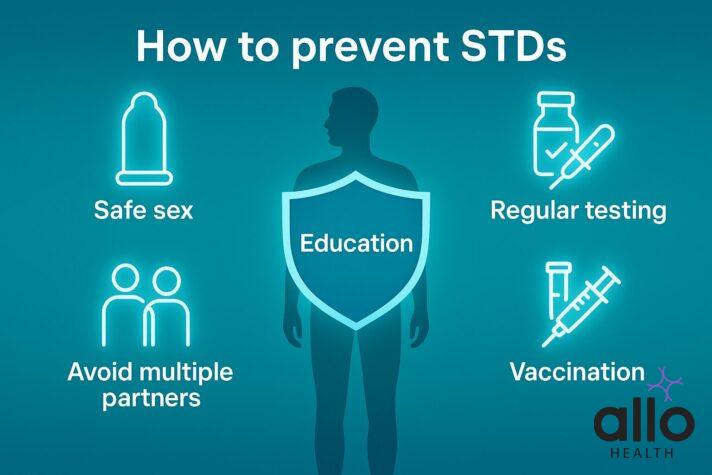
How Can We Prevent Stds?
Anyone who is sexually active can get an STD. The good news? STDs are preventable, and you can try some measures to keep you and your partner STD-free [16].
Practice safe sex
By practicing safe sex, we always mean to use contraceptives. Use condoms every time you have sex. Condom use can reduce the risk of infection in both partners.
Avoid multiple partners
Always prefer staying in a long-term sexual relationship with one person or fewer people. Having sex with multiple partners can increase the risk of developing an STD.
Get vaccinated
Some STDs, like warts or human papillomavirus infections, can be prevented by getting the HPV vaccine.
Open communication
There is nothing to be shy about. Communicate with your partner about your safety, desires, the importance of safe sex, and regular testing.
Regular testing
Anyone who is sexually active should get an STD test done, and there is nothing to be ashamed about. Because there are a lot of STDs that do not have any symptoms but can pose serious risks.
Conclusion
Some STDs, like gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, hepatitis, and HIV, can cause ED. These infections may lead to prostatitis, damage blood vessels, or create stress and anxiety, all of which can affect erections. Prostate inflammation can block proper blood flow to the penis, making it hard to get or keep an erection, and symptoms like painful urination or ejaculation may also occur.
The good news is that many cases improve once the infection is treated. Bacterial STDs usually respond well to antibiotic treatment, while viral infections need long-term care to reduce their impact. If ED continues even after treatment, counseling, lifestyle changes, and treatment options can help. The best way to protect yourself from getting sexually transmitted infection is through practicing safe sex, using condoms, getting proper vaccination, regular testing, and open communication with your partner.
In short, some STDs can cause ED, but with early diagnosis, proper treatment, and preventive steps, both your health and sexual well-being can be managed and protected.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."