UTIs and Erectile Dysfunction: What’s the Relationship?
Written by Dr. Sharon Kumar

With a strong academic background in dentistry and clinical exposure, Dr. Sharon who has studied at PDM Dental College, brings a valuable blend of medical knowledge and communication skills to health content writing. She is passionate about creating clear, compassionate, and evidence-based content on topics such as general wellness, sexual health, oral care, and patient education. Her goal is to make complex medical information easy to understand, relatable, and genuinely helpful for readers seeking clarity on their health concerns. Dr. Sharon believes in the power of well-researched, empathetic content to educate and empower people to make better health decisions. Whether it’s writing about preventive care or breaking down myths in sexual wellness, her content always balances science with sensitivity.
•
August 28, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.

Quick Read
While urinary tract infections (UTIs) do not directly cause erectile dysfunction (ED), there is a notable link between the two. UTIs, especially when involving the prostate, can lead to inflammation and discomfort that affect blood flow and nerve signals essential for erections. Both conditions share common risk factors like diabetes, high blood pressure, and metabolic syndrome, which increase the chances of experiencing sexual dysfunction. If you have symptoms of a UTI along with erectile problems, it’s important to seek medical advice early for proper diagnosis and treatment to improve overall urinary and sexual health.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) and erectile dysfunction (ED) are common health issues that affect many men, especially in India. While these problems might seem unrelated, many men wonder: Does UTI cause erectile dysfunction? Understanding this connection is important because both conditions can affect quality of life and may share underlying causes. Although a UTI does not directly cause ED, research shows a strong link between them. Discomfort, inflammation, and shared health risks like diabetes can contribute to sexual difficulties during or after a UTI. Knowing how these conditions relate helps men seek the right treatment early and avoid complications. This article explains the relationship between UTIs and erectile dysfunction, explores why they often occur together, and offers advice on managing both for better health.
Allo asks
Do you think urinary tract infections (UTIs) can affect sexual performance and cause erectile dysfunction (ED)?
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections in Men
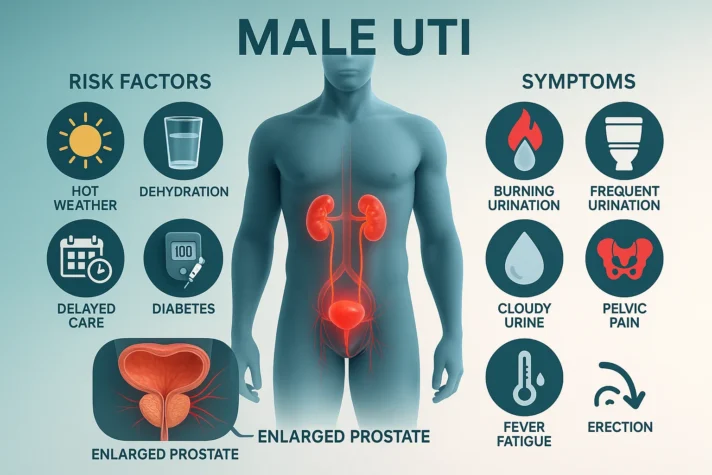
Urinary tract infections occur when harmful bacteria, such as Escherichia coli [1], enter the urinary tract. The infection can affect the urethra, bladder, or prostate gland. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body, the bladder stores urine, and the prostate gland produces fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Poor hygiene, diabetes, and benign prostatic hyperplasia increase UTI risks. Men face higher UTI rates due to several factors.
- Hot weather
- Inadequate water intake
- Delayed medical care
- Diabetes affects millions and makes UTI treatment more challenging.
Common UTI Symptoms
- Men with UTIs experience
- Burning during urination
- Frequent urges to pee
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain [2]
- Fever
- Feel tired
- Prostate infections- The enlarged prostate blocks urine flow and creates pressure. This inflammation affects nearby blood vessels and nerves that control sexual function.
The Link Between UTIs and Sexual Function
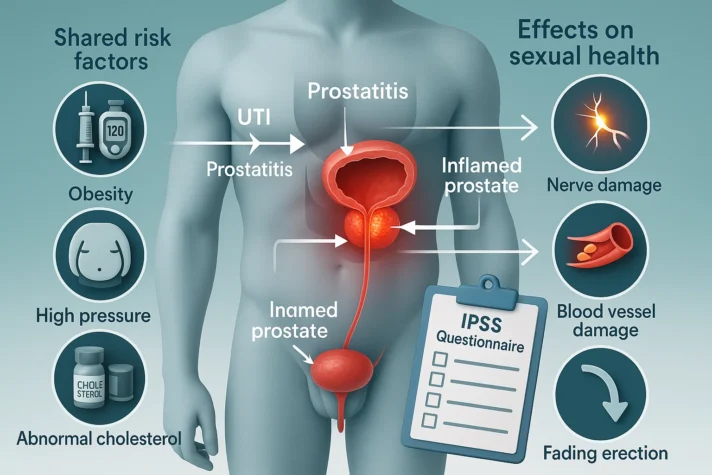
Does UTI cause erectile dysfunction? The answer lies in understanding shared risk factors. Diabetes mellitus [3] affects millions of Indians and increases both UTI and ED risks. High blood sugar damages nerves and blood vessels throughout the body. Metabolic syndrome [4] is a group of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels that occur together and increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Metabolic syndrome combines obesity, high blood pressure, and insulin resistance. This condition affects both urinary and sexual health. Men with metabolic syndrome face higher rates of benign prostatic enlargement. UTIs often spread to the prostate, causing prostatitis [5]. Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland, often causing pain, urinary problems, and sometimes flu-like symptoms. The swollen prostate presses against the urethra and affects blood flow. Inflammation or swelling releases chemicals that damage nearby tissues. Chronic/Constant prostatitis creates ongoing pain in the pelvic region. This constant discomfort reduces sexual desire and makes erections difficult. The International Prostate Symptom Score helps doctors measure these problems. The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) is a simple questionnaire used by doctors to assess the severity of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) [6], often caused by prostate problems. It asks about symptoms like difficulty urinating, frequency, urgency, and the impact on daily life.
Impact on Quality of Life due to UTI and ED
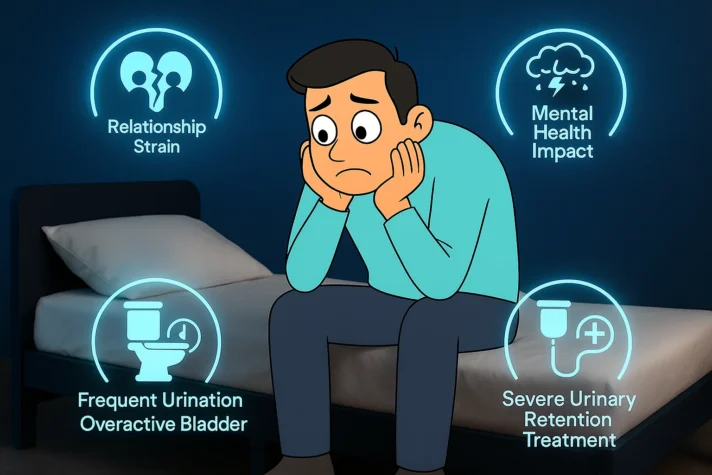
Both UTIs and ED reduce quality of life. Men avoid intimate relationships due to fear of pain or performance failure. This affects marriages and mental health. Affecting mental health can further cause ED. Frequent urination can disturb sleep and daily routines. Men with an overactive bladder often organize their day to stay near a bathroom. This ongoing concern can lower confidence and affect mood. Urinary retention or having trouble emptying the bladder can become a medical emergency. Severe cases require catheter insertion or surgical interventions. Early treatment prevents these complications.
Diagnosis of UTI and ED
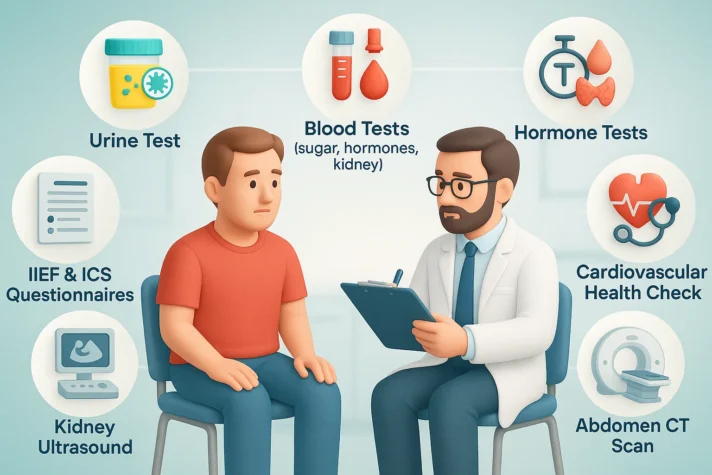
- Your primary care physician will perform a physical examination and review symptoms.
- Urine tests [7] identify bacteria and check for infection signs.
- Blood tests [8] measure blood sugar, hormone levels, and kidney function.
- The International Index of Erectile Function questionnaire [8] measures how severe ED is. The ICS sex questionnaire evaluates broader sexual health issues. These tools help doctors understand the full picture.
- Some men need additional tests, like a kidney ultrasound or a CT scan [9] of your abdomen.
- These imaging tests [10] check for structural problems. Blood and imaging tests rule out serious conditions.
- Doctors may measure testosterone levels and check for thyroid disorders.
- Cardiovascular health assessment, or Heart health assessment, includes checking blood pressure and heart function. All these factors affect both urinary and sexual health.
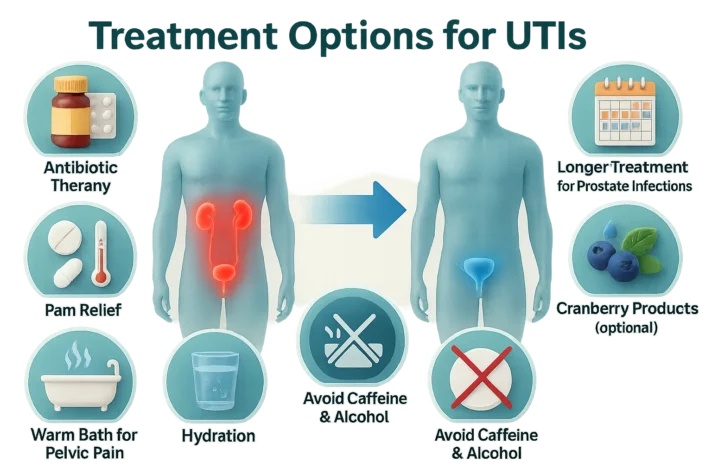
Treatment Options for UTIs
Antibiotic Therapy for UTI
- Doctors prescribe specific antibiotics based on urine sample results.
- Taking the full course of antibiotics prevents antibiotic resistance.
- Most UTIs clear within days of proper treatment.
- Doctors prescribe longer antibiotic courses for men with recurrent UTIs
- Prostate infections require 4-6 weeks of treatment.
- Following medical advice helps prevent complications.
Supportive Care for UTI
- Drinking plenty of water helps wash bacteria out of the urinary tract.
- Some men feel cranberry products help, but studies are not clear.
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol while treating the infection can help you get better faster. Painkillers can ease discomfort, and warm baths may reduce pelvic pain.
- These simple steps work well alongside medical treatment.
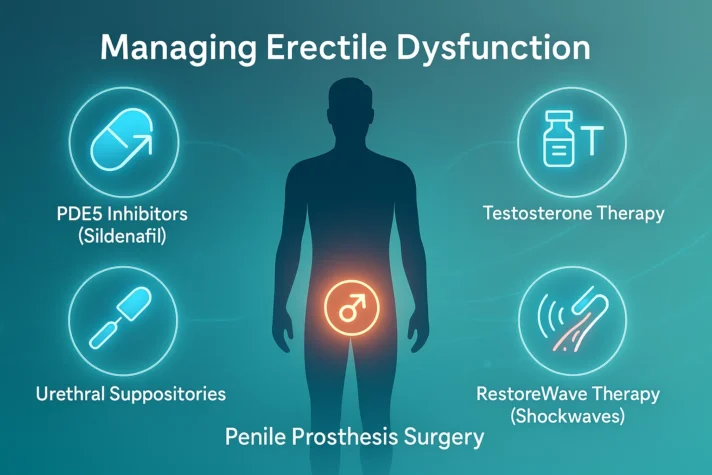
Managing Erectile Dysfunction
Medical Treatments
- Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors like sildenafil work well for many men.
- These medications improve blood flow to the penis.
- They work best when underlying health problems are controlled.
- Testosterone therapy helps men with low hormone levels.
- Doctors must check for prostate cancer first.
- Hormone treatment requires regular monitoring for safety.
Alternative Approaches
- RestoreWave therapy uses sound waves to improve blood flow.
- This treatment shows promise for men who cannot take ED medications.
- Several sessions may be needed for the best results.
- Urethral suppositories put medicine directly into the penis. Some men prefer this method over pills.
- Penile prosthesis surgery remains an option for severe cases.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Health
Diet and Exercise
- Regular physical activity improves both urinary and sexual health. Exercise enhances blood flow and reduces inflammation. Even 30 minutes of walking daily helps.
- A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables supports overall health. Reducing salt intake helps control blood pressure. Keeping a healthy waist size prevents metabolic problems.
Habits
- Quitting smoking improves blood vessel function within weeks.
- Alcohol limits should be followed to prevent nerve damage.
- Good sleep habits support hormone production.
- Stress management techniques like meditation help with both conditions.
- Regular medical checkups catch problems early.
- Pelvic floor muscle exercises may strengthen the area, like yoga.

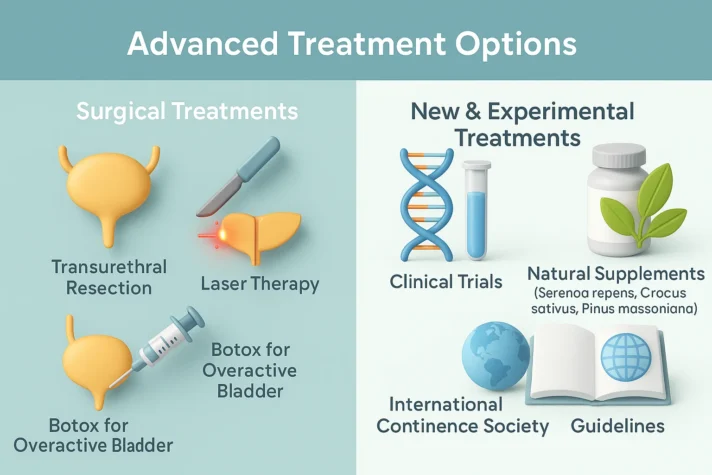
Advanced Treatment Options
Surgical Treatments
- Men with severe prostate enlargement may need surgery. One common surgery is transurethral resection, which removes extra prostate tissue.
- Laser therapy is another option that is less invasive than traditional surgery.
- Some men with nerve problems after spinal cord injuries may have trouble controlling their bladder.
- Botox injections can help with an overactive bladder in these cases.
New and Experimental Treatments
- Research is ongoing to find new ways to treat these problems.
- Clinical trials test new ideas and treatments.
- Some natural supplements, such as Serenoa repens, Crocus sativus, and Pinus massoniana, are great options.
- The International Continence Society sets guidelines for new treatments.
- Patients should talk to their doctors before trying experimental options because not all treatments work for everyone.
Prevention Strategies for UTI and Troubles with Sexual Health
- Good hygiene practices prevent many UTIs.
- Urinating after sexual activity helps flush bacteria. Men should drink adequate water daily, especially in India's hot climate.
- Managing diabetes keeps blood sugar levels stable.
- Regular checkups detect problems early. Treating benign prostatic enlargement stops urine retention.
- Controlling cardiovascular/heart disease maintains good blood flow.
- Regular exercise and a healthy diet support vascular health.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive drinking protects nerves.
- Mental health care addresses psychological causes of ED. Open communication with partners reduces relationship stress. Regular medical check-ups help find problems early.
“It’s common for men with urinary infections to experience temporary sexual difficulties, but with proper treatment, most can expect full recovery.”

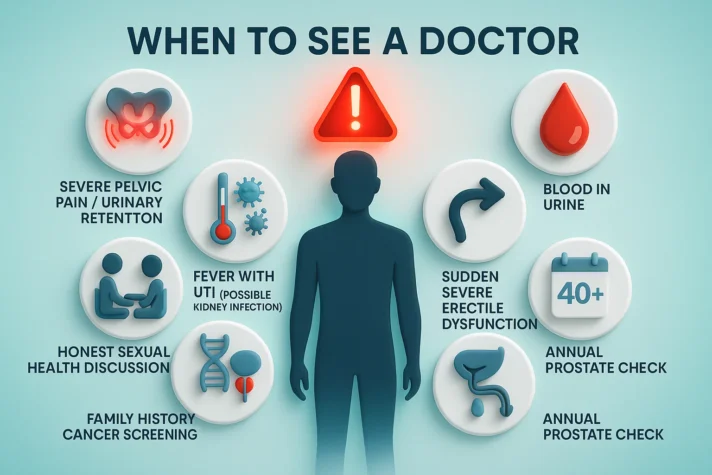
When to See a Doctor
- Seek immediate medical attention for severe pelvic pain or inability to urinate.
- Fever with UTI symptoms may indicate a kidney infection.
- Blood in urine always requires evaluation.
- Sudden onset of severe erectile dysfunction needs prompt assessment.
- Chest pain during sexual activity requires emergency care.
- These symptoms may indicate serious underlying problems.
- Men over 40 should discuss prostate health during annual visits.
“The prostate plays an important role in both urinary and sexual health, so inflammation there can affect more than one area.”
- Those with diabetes need more frequent monitoring.
- A family history of prostate cancer requires earlier screening.
- Honest discussion about sexual health helps doctors provide better care.
- Many treatment options exist for both UTIs and ED. Early intervention prevents complications and improves outcomes.
Conclusion
While urinary tract infections do not directly cause erectile dysfunction, the two conditions are closely linked through shared risk factors like diabetes, prostate issues, and inflammation. Recognizing this connection is important for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Managing both UTI and ED together, along with addressing underlying health problems, can improve overall well-being and quality of life. If you experience symptoms of either condition, consulting a healthcare professional early can help prevent complications and support better sexual and urinary health.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
What lifestyle changes help prevent UTIs and ED?
Drinking plenty of water, managing diabetes, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight are key steps.
Are there any natural remedies for UTIs and erectile dysfunction?
Some supplements show promise, but you should always discuss these with your doctor before trying them.
How does an enlarged prostate affect urinary and sexual health?
It can block urine flow and reduce blood flow, leading to symptoms in both areas.
Can recurrent UTIs increase the risk of long-term erectile dysfunction?
Repeated infections, especially involving the prostate, may increase risks if left untreated.
What diagnostic tests are needed for UTIs and ED?
Urine tests, blood sugar checks, hormone levels, and sometimes imaging tests help doctors identify the cause.
When is surgery needed for prostate-related urinary or sexual problems?
Surgery is usually a last resort for severe prostate enlargement causing persistent symptoms.
