Aspirin and Erectile Dysfunction: What’s the Connection?

If you're looking for a specific aspirin dosage to treat erectile dysfunction, here's the straight answer: there isn't an officially recommended dose because aspirin isn't a proven ED treatment. While some small studies tested 100 mg daily and showed modest improvements in men with blood flow-related ED, larger research suggests aspirin might actually increase ED risk by 22-38%. The science is genuinely mixed and conflicting. Rather than experimenting with aspirin (which can cause serious bleeding and drug interactions), stick with what actually works: FDA-approved medications like Viagra and Cialis help 60-80% of men safely and effectively.
Aspirin dosage for erectile dysfunction is a question many men are curious about, especially since aspirin is already a familiar household medicine for pain relief and heart health.
The truth is, the science is mixed. While some small studies suggest low-dose aspirin might boost blood flow and support erectile dysfunction, larger population studies raise concerns about possible risks of aspirin for erectile dysfunction.
In this article, we’ll unpack how aspirin works in the body, what the research says about its potential role in ED.
How Aspirin Works and Why Some Think it Can Work for ED?
Aspirin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) most people know as a common pain reliever and fever reducer. Doctors also prescribe it in low doses to help reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack in people with heart disease(cardiovascular disease).
In simple terms, aspirin helps the heart by improving blood flow, lowering inflammation, and preventing clots from forming (antiplatelet effect).
As erections depend heavily on steady blood circulation, this has led many to wonder- could aspirin work for erectile dysfunction?
The idea makes sense, especially for vasculogenic erectile dysfunction (erectile dysfunction caused by poor blood flow to the penis). But the truth is, research on aspirin and erectile dysfunction is limited and mixed.
Let’s dive deeper.
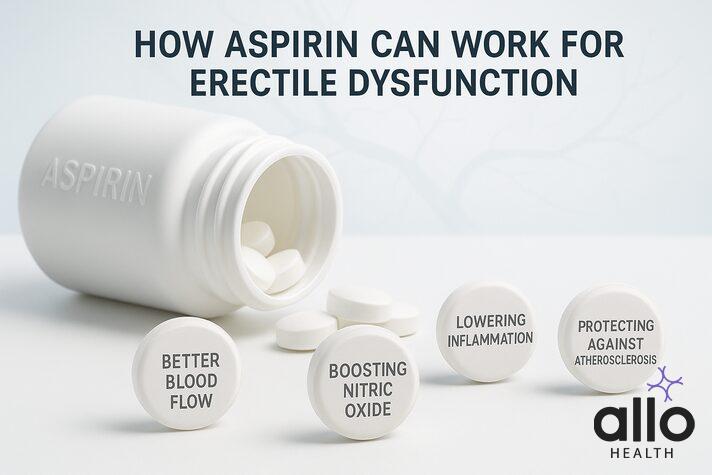
How Aspirin Can Work For Erectile Dysfunction
An analysis of two trials[1] (214 men) found that aspirin improved erectile function (by about 5 points on the International Index of Erectile Function scale).
In another study[2](randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study), men with vasculogenic erectile dysfunction who took 100 mg of aspirin daily for 6 weeks improved more than the placebo group, with 88% able to have sex successfully compared to 59% on placebo.
Researchers[3] believe aspirin could support erectile function through several heart-and-blood-vessel-related pathways:
1. Better Blood Flow
Aspirin prevents platelets from clumping together(platelet aggregation), which reduces clotting and helps blood flow more smoothly.
This is important because larger, stickier platelets can release chemicals like thromboxane B2, which narrows the blood vessels and makes it harder for blood to reach the penis.
2. Boosting Nitric Oxide
Aspirin may also stimulate the release of nitric oxide(through the NO pathway) and have a protective role against endothelial dysfunction, the process that inhibits the inner lining of blood vessels from releasing nitric oxide.
Nitric oxide relaxes the smooth muscles in penile blood vessels, allowing more blood to enter and create a firm erection.
3. Lowering Inflammation
Chronic inflammation damages blood vessels over time. By reducing the inflammation, aspirin may help protect healthy circulation, which is essential for normal penile erections.
4. Protecting Against Atherosclerosis
Aspirin can slow down the buildup of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis) in the arteries of the penis. This could, in theory, delay age-related erectile problems.
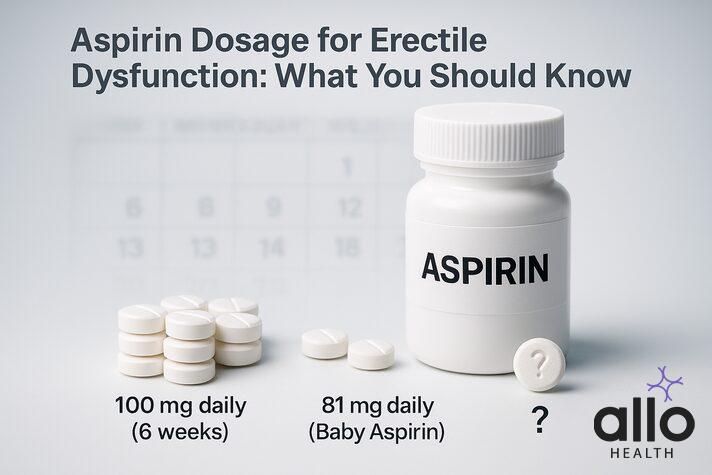
Aspirin Dosage for Erectile Dysfunction: What You Should Know
There is currently no officially approved dosage of aspirin for erectile dysfunction. Different clinical studies have tested different amounts, and the evidence is still too limited to recommend aspirin as a standard ED treatment.
The most commonly studied dose is 100 mg daily for 6 weeks, which showed some improvement in erectile function compared to placebo in small clinical trials. Some sources also mention 81 mg daily (often called “baby aspirin”) as a possible dose, since it’s already widely used for heart health.
That said, it’s important to remember: aspirin is not a proven or approved treatment for ED, and it can carry risks. Always talk to your doctor before considering aspirin for this purpose, especially if you have other medical conditions or take other medications.
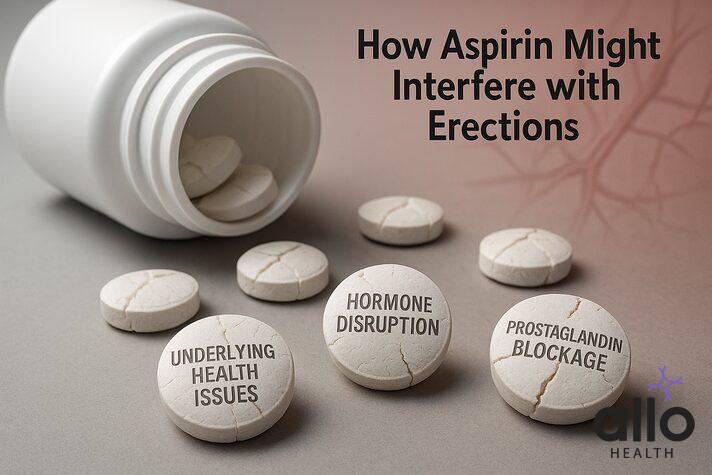
Contradiction: How Aspirin May Not Help With ED
While some studies suggest aspirin could help with ED, other research raises important concerns.
Some studies paint a different picture. For example, a 2011 study[4] found that regular users of NSAIDs (including aspirin) had a 22–38% higher risk of erectile dysfunction.
More recently, a 2024 genetic study[5](Mendelian randomization) linked aspirin use to a much higher chance of ED (odds ratio ~20).
How Aspirin Might Interfere with Erections
Scientists have proposed a few possible ways aspirin could be harmful:
a) Prostaglandin Blockage:
Aspirin reduces prostaglandins E2 and I2, natural chemicals that help blood vessels relax, which is essential for erections.
b) Hormone Disruption:
Long-term NSAID use may interfere with hormones involved in sexual function.
c) Underlying Health Issues:
Men who take aspirin often already have cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, or other vascular disorders, conditions that themselves increase ED risk, which may confuse the data.
Erectile dysfunction can be a sign of underlying health issues like diabetes or heart disease. Instead of just reaching for aspirin, it’s important to find the root cause, that’s where real, lasting treatment begins.
Risks and Side Effects of Taking Aspirin
Common Side Effects of Aspirin
- Stomach upset, burning, constipation,
- Changes in appetite,
- Dizziness, tremors, nervousness, restlessness,
- Skin rashes,
- Urinary problems.
Serious Risks Of Aspirin
- Bleeding problems (including gastrointestinal bleeding)
- Stomach irritation and ulcers
- Interactions with other medicines (like blood thinners)
- Rare but serious Reye’s syndrome (mostly in children and teens)
This is why aspirin should never be used for ED without medical supervision. A doctor can weigh the potential benefits against the risks for each individual.
Should You Take Aspirin for Erectile Dysfunction?
The short answer is no, you should not take aspirin for erectile dysfunction unless your doctor specifically recommends it.
The research so far is limited. The studies that suggest aspirin might help with ED are small and not strong enough to prove it works.
These studies mainly looked at men with vasculogenic ED (ED caused by poor blood flow) who also had high mean platelet volume- a blood marker linked to larger, stickier platelets. This means the results may not apply to all men with ED.
On the other hand, larger studies have shown no clear benefit, and more high-quality research is still needed.
So while aspirin is a common household medicine, it should not be self-prescribed as a treatment for ED. At best, it may support certain underlying conditions that contribute to ED, but it is not a proven or standalone solution, and in some cases, it could even be risky.

Safer & Proven Alternatives for ED
The best path forward for ED is a personalized plan, combining healthy lifestyle changes, evidence-based treatments, and guidance from a qualified professional.
Talking with your doctor can help you find what’s safest, most effective, and right for you[6].
1. FDA-Approved Medications
The most trusted treatments for ED are prescription ED pills known as PDE5 inhibitors, like Viagra(sildenafil citrate), Cialis, and Levitra.
Backed by decades of research, these phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors work for 60–80% of men, helping improve the body’s natural ability to get and keep an erection.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
Regular exercise boosts blood circulation, maintaining a healthy weight eases strain on blood vessels, quitting smoking restores blood flow, and managing stress keeps your mind and body in sync.
These changes not only help with ED but also improve overall health.
3. Natural Supports
Some natural options, such as L-arginine supplements for ED, have shown modest benefits in studies.
They aren’t quick fixes, but they may offer gentle support when paired with healthier habits or medical treatment.
Always use supplements cautiously and ideally, under a doctor’s guidance.

When to Talk to a Doctor
- Red flag symptoms: Sudden ED with chest pain, shortness of breath, or fatigue may signal heart disease or diabetes.
- Don’t self-medicate: Taking aspirin without guidance can cause bleeding, drug interactions, or hide serious conditions.
- See a professional: Doctors handle ED all the time. They can find the root cause and suggest safe, effective treatments tailored to you.
Bottom Line
The link between aspirin and erectile dysfunction is still unclear. As the research on aspirin for erectile dysfunction is limited and conflicting, there’s no clear recommendation on how much aspirin to take for erectile dysfunction yet.
For now, the most reliable treatments remain FDA-approved medications like Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra, which work for most men. Aspirin should only be used under a doctor’s guidance as part of overall heart health and not as a main treatment for ED.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."