Gonorrhea and Erectile Dysfunction: Link Between and Effects on Sexual Health
Written by Dr. Pranitha Bangera

Dr. Pranitha Bangera is a gold-medalist healthcare professional with an elite foundation in clinical training and patient care. A researcher at heart, she specializes in creating high-impact, research-driven medical content that empowers readers through accessible patient education. Dr. Bangera focuses on the intersection of digital health and clinical communication, specifically within the fields of sexual health and mental well-being. Her work is dedicated to making complex medical innovations understandable and trustworthy for a global audience.
•
October 6, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Quick Read
Yes, gonorrhea can contribute to erectile dysfunction, but usually through complications like prostatitis, male accessory gland infections, or psychological stress rather than the infection itself. These complications affect the pathways of erections, like healthy blood flow and arousal signals. The key takeaway is that both gonorrhea and ED are treatable with timely diagnosis, antibiotics, and healthy lifestyle choices. If symptoms such as painful urination, discharge, or erection problems appear, it’s important to see your doctor early. Practicing safe sex and regular STI testing are the best ways to prevent long-term issues with sexual health.
Many men worry about the effects of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhea on their sexual health. One common concern is: Can gonorrhea cause erectile dysfunction? The short answer is: yes, in some cases. Gonorrhea itself doesn’t usually cause ED directly, but if the infection spreads to surrounding areas, it can trigger complications due to inflammation. Inflammation can interfere with blood flow, cause pain, and make it harder to get or maintain an erection. With early diagnosis, proper treatment, and healthy lifestyle choices, both gonorrhea and erectile dysfunction (ED) are usually treatable. Let’s break this down: what gonorrhea is, can gonorrhea cause erectile dysfunction, and if yes, then how it can be treated.
Allo asks
If you had gonorrhea symptoms and ED, what would you do first?
What is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is an infection of the genitals caused by a bacterium called Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It spreads through sexual activity (vaginal, anal, or oral sex) with an infected partner. It most commonly affects the genitals in both sexes, but can also infect the urethra, rectum, mouth, throat, and eyes. Anyone can get it, but it’s especially common among people aged 15–24. [1]
Common Symptoms of Gonorrhea in Men:
- Painful urination
- White, yellow, or green discharge from the penis
- Pain in the testicles
- Swelling near the scrotum
Sometimes, gonorrhea shows no obvious signs, making regular testing important for anyone sexually active.
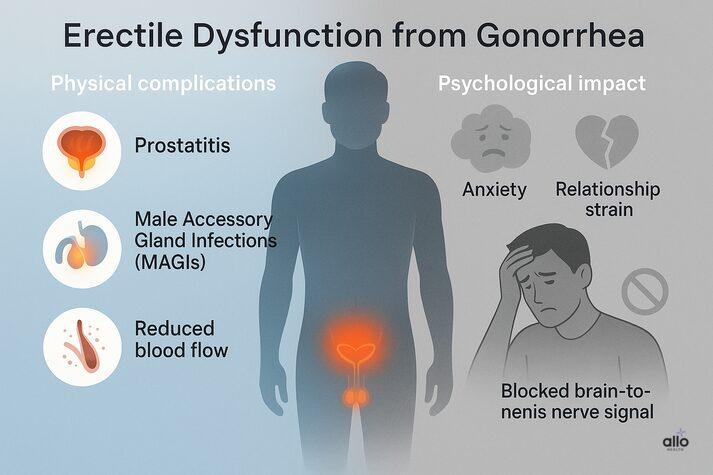
Can Gonorrhea Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Yes, gonorrhea can cause erectile dysfunction, but not directly because of the infection. The complications caused by the infection can make erections difficult. [2] These complications are:
- Prostate Inflammation (Prostatitis)
- Male Accessory Gland Infections (MAGIs)
- Psychological Issues
Let’s look at each in detail.
Prostate Inflammation (Prostatitis)
When gonorrhea isn’t treated quickly, the bacteria can move beyond the urethra and infect nearby organs. One of the organs infected is the prostate gland. This condition is called prostatitis. The prostate plays an important role in semen production, but it’s also closely connected to the nerves and blood vessels that control erections. [3] When gonorrhea causes the prostate to become inflamed:
- The swelling compresses delicate nerves that send signals between the brain and penis, which causes these signals to be blocked or weakened. Because of this, the body may struggle to trigger or maintain an erection.
- Inflammation can also restrict the smooth circulation of blood into the penis. Healthy blood flow is essential for firm erections, which means any disruption makes it harder for the penis to stay rigid during sexual activity.
- Prostatitis can cause pelvic pain, painful urination, or discomfort during ejaculation. These symptoms not only interfere physically but also add psychological stress, which can cause erectile dysfunction.
Male Accessory Gland Infections (MAGIs)
The bacteria can also spread into other parts of the male reproductive system. These include the epididymis (a coiled tube at the back of the testicles where sperm are stored) and the seminal vesicles (small glands that produce the fluid in semen). [4] Infections in these areas are grouped under the term Male Accessory Gland Infections (MAGIs). This can cause:
- Pain and Swelling: Infections in these areas can cause significant pelvic or testicular pain and make sexual activity uncomfortable.
- Scarring and Blockages: Chronic inflammation may leave behind scar tissue. This can block the natural path that sperm and semen travel through, affecting both fertility and ejaculation. Disrupted ejaculation can weaken sexual confidence and performance.
- Interfere with Blood Flow and Nerve Signals: Just like with prostatitis, the swelling from MAGIs can interfere with surrounding blood vessels and nerve endings and reduce healthy blood flow.
Psychological Issues
Sexual health isn’t just about the body. The mind plays a huge role, too. When someone is diagnosed with gonorrhea, it often brings an emotional weight that can’t be ignored. Feelings of anxiety, embarrassment, or guilt are common, and all of these can directly influence erectile function. This can happen even in STIs like herpes, where the ED mainly occurs due to emotional stress. Here’s how it happens:
- Worrying about whether you might pass the infection to a partner, or whether your partner might react negatively, can create a mental block. This causes performance anxiety, which makes it harder to get an erection.
- Many men blame themselves after an STI diagnosis. That guilt and shame can decrease confidence in intimate situations and lower sexual desire.
- STIs can put a strain on intimacy and trust within a relationship. Tension or arguments with a partner may make it harder to relax, and erections often depend on feeling safe and connected.
- Even if gonorrhea is successfully treated, the memory of having had an STI may linger. Some men remain anxious about their sexual health, and this anxiety itself can cause ED. This is called psychogenic erectile dysfunction.
Can Leaving Gonorrhea Untreated Worsen ED?
Yes, leaving gonorrhea untreated can cause medical conditions that can affect sexual performance. [5]Some of the most common issues include:
- Urethritis: Painful swelling of the urethra that makes urination and sexual activity uncomfortable.
- Epididymitis: Swelling at the back of the testicles, which can affect fertility and cause ongoing pelvic pain that makes erections difficult.
- Orchitis: Severe inflammation of the testicles that may cause pain during arousal or ejaculation.
When to See a Doctor
- If you notice symptoms of gonorrhea (painful urination, discharge, testicular pain).
- If you have difficulty getting or keeping an erection that continues even after treatment.
- If you have a history of untreated STIs and ongoing urinary or pelvic issues.
Your doctor may suggest ED medications, run further tests, or refer you to a specialist if needed.
If you’ve noticed symptoms like painful urination, discharge, or ongoing erection problems, don’t ignore them. Getting checked early by your doctor can prevent long-term damage.
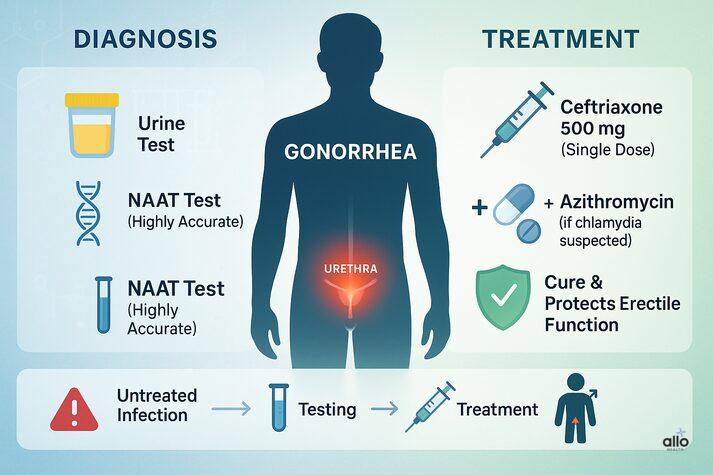
Diagnosis and Treatment of Gonorrhea (and Its Effect on ED)
If you’re experiencing erection problems and suspect an STI, getting tested is the first step. Diagnosis is usually straightforward and may include:
- Urine sample: Often checked for both gonorrhea and symptoms of chlamydia, since the two infections can cause ED and are commonly screened together.
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT): A highly accurate test that confirms whether the gonorrhea bacteria are present.
Your primary healthcare provider may recommend these tests if you have ED symptoms alongside signs of an STI, such as painful urination or unusual discharge.
Treatment of Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection, and the good news is that it can be cured with antibiotics. According to CDC guidelines[6]:
- A single dose of 500 mg ceftriaxone (given as a muscle injection) is the standard treatment.
- In some cases, it is combined with a dose of azithromycin, especially if chlamydia infection is also suspected.
Getting treated early usually clears the infection and helps prevent permanent damage to the prostate, urethra, and other reproductive organs.
Restoring Erectile Function After Gonorrhea
If ED continues even after the infection is treated, it may be linked to complications such as prostatitis or other medical conditions. In that case, additional ED treatments may be recommended, including:
- ED medicines like PDE5 inhibitors (such as Viagra®, Cialis®) to improve blood flow.
- Regular exercise, a balanced diet, better sleep, and quitting smoking.
- Managing underlying medical conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart disease.
- Correcting poor lifestyle choices (alcohol misuse, lack of activity, stress) that weaken erections.
- Psychotherapy to manage ED resulting from psychological factors associated with the disease.
With a combination of proper STI treatment and ED management, most men are able to restore normal sexual function and return to healthy sexual activity.
How to Prevent Gonorrhea and Protect Yourself from ED
Preventing gonorrhea doesn’t just protect you from infection but also lowers your risk of complications that could interfere with erections. Here are some practical steps:
- Practice safe sex: Using condoms consistently during vaginal, anal, and oral sex greatly reduces the chance of infection.
- Get tested regularly: Many people with gonorrhea show no symptoms. [7] Routine STI testing helps catch infections early before they cause lasting damage.
- Encourage partner testing and treatment: If you’ve been diagnosed with gonorrhea, any partner you’ve had sexual contact with should also be tested and treated. This can prevent reinfection.
- Make healthy lifestyle choices: Strengthening your immune system with exercise, a balanced diet, and good sleep habits lowers the risk of infection-related complications. Avoiding poor lifestyle choices such as heavy smoking or alcohol use also supports better erections overall.
Bottom Line
Gonorrhea doesn’t usually cause erectile dysfunction directly, but when left untreated, it can lead to complications that interfere with blood flow, nerve function, and overall sexual health. The good news is that both gonorrhea and ED are highly treatable when addressed early. If you notice symptoms like painful urination, discharge, or difficulty maintaining erections, don’t ignore them and see your primary healthcare provider for testing and treatment. With timely care, lifestyle improvements, and open communication with partners, most men are able to fully recover and return to healthy sexual activity. Taking proactive steps like practicing safe sex and getting regular STI screenings is the best way to protect yourself from gonorrhea and reduce the risk of erectile dysfunction in the future.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Can gonorrhea really cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes. While gonorrhea doesn’t directly damage the ability to have erections, it can lead to complications like prostatitis or epididymitis. These conditions affect blood flow, nerves, and cause pain, all of which can result in ED.
Is ED from gonorrhea permanent?
Usually not. In most cases, once gonorrhea is treated with antibiotics, erectile function returns to normal. If ED lingers, it may be due to lasting complications or other medical conditions, which a doctor can help diagnose.
How long does it take for ED to improve after gonorrhea treatment?
Improvement can be quick once the infection and inflammation settle, often within weeks. If symptoms of ED remain for longer, it’s important to follow up with your healthcare provider.
Can antibiotics for gonorrhea fix erectile dysfunction, too?
Antibiotics clear the infection, which often helps resolve ED caused by gonorrhea. However, they cannot repair tissue scarring or nerve damage that has already happened, so additional ED treatments may be needed.
Can safe sex prevent gonorrhea and ED?
Yes. Using condoms consistently during sexual activity and getting tested regularly are the most effective ways to prevent gonorrhea and the complications like ED that can follow.
Sources
- 1.
CDC’s STI surveillance data, in 2023, 48.2% of reported cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis were among adolescents and young adults aged 15–24
- 2.
Long-term consequences of sexually transmitted infections on men’s sexual function
- 3.
STIs (including gonorrhea) can cause prostatitis.
- 4.
Male accessory gland infection
- 5.
Complications from gonorrhea
- 6.
Recommended regimen for uncomplicated gonococcal infections
- 7.
Asymptomatic gonorrhea in the male


