OCD and Erectile Dysfunction: Mental Health and Sexual Function

OCD and erectile dysfunction are closely connected- constant anxiety, intrusive thoughts, and compulsive behaviors from OCD can disrupt sexual arousal and make it difficult to maintain an erection. Additionally, medications commonly used to treat OCD, particularly SSRIs, can cause sexual side effects in 30–50% of patients. The good news is that both conditions can be treated together through therapy like ERP and cognitive behavioral sex therapy, medication adjustments, and open communication with your doctor. When OCD symptoms improve with proper treatment, sexual health typically improves as well. Remember, recovery involves both mind and body working together.
OCD and erectile dysfunction often overlap in ways many people don’t expect. If you’re wondering how obsessive thoughts, anxiety, or medication for OCD might be affecting your sexual performance, you’re not alone. OCD can trigger constant stress and mental tension that disrupts sexual arousal and makes it difficult to get or keep an erection. In some cases, even the medications used to treat OCD, like SSRIs, can add to the problem.
This article explains exactly how OCD can lead to erectile dysfunction, what role anxiety and medication play, and how both conditions can be treated together. You’ll also find practical, natural coping tips to manage OCD-related ED, improve confidence, and restore healthy sexual function.
The Connection Between OCD and Erectile Dysfunction
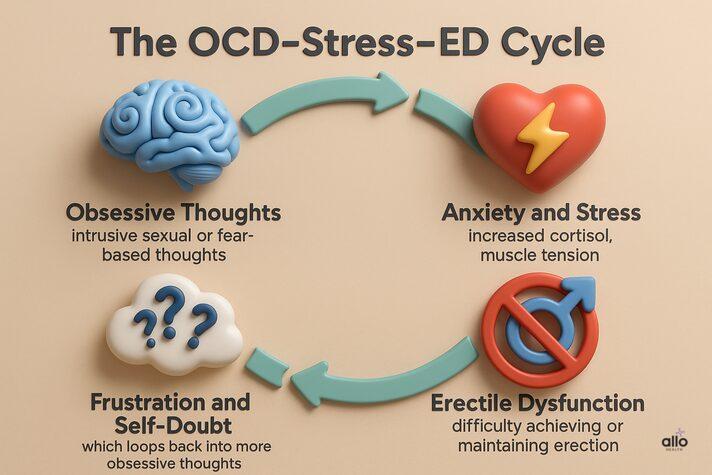
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a long-term mental health condition that causes recurring cycles of stress, anxiety, obsessive thoughts, and compulsive actions. These repeated patterns can take a toll on both mental and physical health, including sexual response.
But what’s the link between OCD and erectile dysfunction? People with OCD experience constant anxiety and mental tension, which can interfere with sexual desire, arousal, and performance. The body stays in a state of stress, making it harder to relax, something that’s essential for a healthy erection.
Research[1] shows that around 25% of men with OCD report reduced sexual arousal, 12% experience premature ejaculation, and about 6% struggle with erectile dysfunction.
Interestingly, this relationship is two-way. OCD can directly lead to ED through anxiety and obsessive thinking, while the stress of having ED can worsen OCD symptoms, creating a difficult cycle.
According to Allo Health, every 1 in 2 patients has ED, which is based on our internal clinical data of more than 2.5 Lakh patients who come to our clinic.
Let’s understand this more deeply.
How OCD Contributes To Erectile Dysfunction
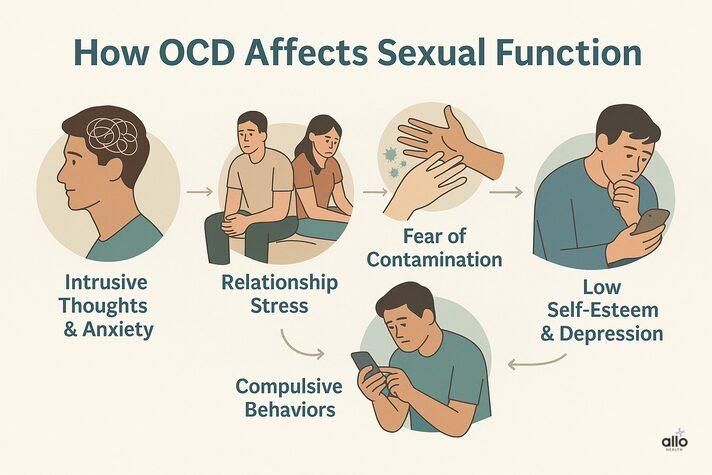
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder can affect sexual health in several ways. The constant cycle of obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors can make it hard to relax, enjoy intimacy, and maintain an erection. Here’s how OCD can impact sexual function:
1. Intrusive Thoughts and Performance Anxiety
During sexual activity, men with OCD may experience unwanted or intrusive thoughts that trigger anxiety. These thoughts can involve fears about performance, sexual orientation, infections, or relationship issues.
When the mind is overloaded with anxiety, it creates mental pressure and distraction, making it difficult to get or keep an erection.
2. Relationship OCD and Stress
People with relationship-focused OCD often experience obsessive doubts about their partner or the relationship itself. They may constantly question emotional connection or seek reassurance about love and attraction.
This hyper-awareness and stress take the focus away from physical sensations and pleasure. Over time, it can lead to avoidance of intimacy and a decline in sexual desire or arousal.
3. Fear of Contamination
Some individuals with OCD have a fear of germs, bodily fluids, or disease transmission. This fear can make sexual contact feel unsafe or “dirty,” leading to avoidance of intimacy or difficulty relaxing during sex, both of which can cause erection problems.
4. Compulsive Behavior
Compulsive-repetitive behaviors linked with OCD often harm sexual confidence and performance. Common examples include:
- Avoiding sexual situations altogether (the most common compulsion)
- Repeatedly seeking reassurance from partners about attraction or satisfaction
- Checking the genitals to “verify” sexual function
- Performing mental rituals to neutralize intrusive thoughts
- Watching pornography only to “test” if arousal still works
While these actions may feel like short-term fixes, they actually reinforce the OCD cycle, increasing anxiety and further worsening erectile dysfunction.
5. Low Self-Esteem and Depression
OCD can lead to feelings of inadequacy or self-doubt, especially in intimate settings. Low self-esteem and the high overlap between OCD and depression can both reduce sexual desire and directly contribute to erectile dysfunction
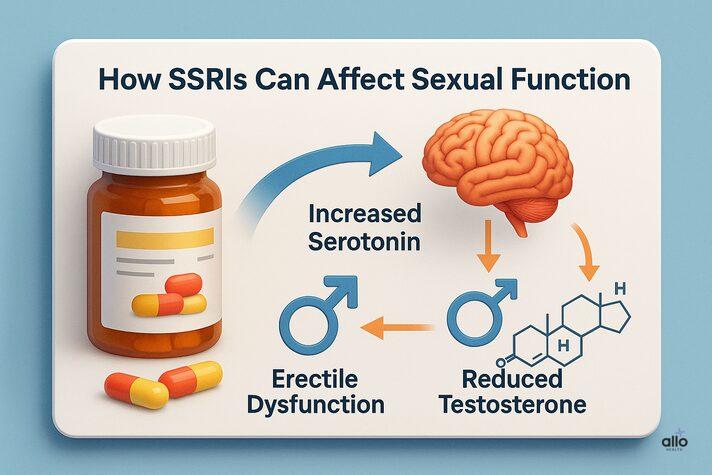
Can OCD Medication Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Yes, OCD medications and erectile dysfunction can be connected. The most common medicines prescribed for OCD are Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), which are known to cause sexual side effects in some people.
In fact, research[2] shows that 30% to 50% of patients taking SSRIs experience some form of sexual dysfunction. These side effects may include:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased libido
- Difficulty reaching orgasm
- Delayed ejaculation
These effects are dose-dependent, meaning they are more likely to occur when the medication dose is higher. Since OCD often requires higher doses for effective treatment, managing these side effects can be challenging.
A study[3] found that sexual dysfunction was common even among men with OCD who were not on medication. While the direct link wasn’t very strong, hormonal and psychological factors may also play a role.
If you’re taking medication for OCD and notice changes in your sexual health, it’s important to talk to a qualified sexologist or psychiatrist.

Diagnosing the OCD-ED Link: When to Seek Help
If persistent intrusive thoughts or anxiety from OCD are beginning to affect your sex life, and you’ve been experiencing erectile dysfunction for more than three months, it’s time to speak with a doctor.
You should consider seeking help if:
- ED appears suddenly, worsens, or is accompanied by the loss of morning erections.
- You have underlying health conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or high blood pressure.
- Intrusive thoughts or anxiety are interfering with intimacy or your relationship.
- ED symptoms began after starting a new psychiatric medication, especially SSRIs, which are known to affect sexual function.
During diagnosis, doctors may:
- Ask about your OCD symptoms, anxiety patterns, medication history, and stress levels.
- Conduct a physical examination and order blood tests to check hormone levels and rule out other causes.
Psychological ED linked to OCD often fluctuates with stress and is usually accompanied by performance anxiety, avoidance behaviors, or intrusive sexual thoughts. Understanding these patterns helps doctors tailor treatment, whether through therapy, medication adjustments, or a mix of both.

Treatment Options for OCD-Related Erectile Dysfunction
Addressing the underlying psychological and medical factors is crucial for treating ED related to OCD.
1. Therapy For OCD
A) Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) Therapy
ERP is considered the gold-standard treatment for OCD and has shown strong results in improving sexual function affected by anxiety or obsessive thoughts.[4] It works by:
- Gradually exposing patients to thoughts, images, or situations that trigger sexual obsessions, without using avoidance as an escape.
- Preventing compulsive responses, teaching the person to tolerate anxiety without performing rituals.
- Encouraging habituation, where repeated exposure to feared thoughts naturally reduces anxiety over time.
- Building inhibitory learning, where patients realize that not performing compulsions does not lead to catastrophic outcomes.
B) Cognitive Behavioral Sex Therapy (CBST)
CBST combines traditional cognitive-behavioral therapy with targeted sexual health interventions.[5] It helps men with OCD-related ED through:
- Cognitive restructuring to challenge negative beliefs about sexual performance and masculinity.
- Sensate-focus exercises that shift attention from performance worries to pleasurable sensations.
- Mindfulness practices to reduce anxiety and stay present during intimacy.
- Communication training with partners to strengthen emotional connection and comfort.
2. Medication Adjustment
When OCD medications, especially SSRIs, cause sexual side effects, doctors may:
- Adjust the dosage to minimize symptoms.
- Switch to a different SSRI that may have fewer sexual side effects.
- Add a second medication to counteract ED symptoms.
- Explore non-SSRI antidepressants when appropriate.
Any medication changes should only be made under professional supervision
3. Couple Communication
Open communication between partners plays a vital role in recovery. Relationship stress can worsen both OCD and ED, so couples therapy or sex therapy can help by:
- Reducing misunderstandings and emotional distance.
- Addressing intimacy concerns together.
- Building trust, patience, and mutual reassurance.
When OCD is well-managed, sexual health usually improves too. The mind and body recover together.
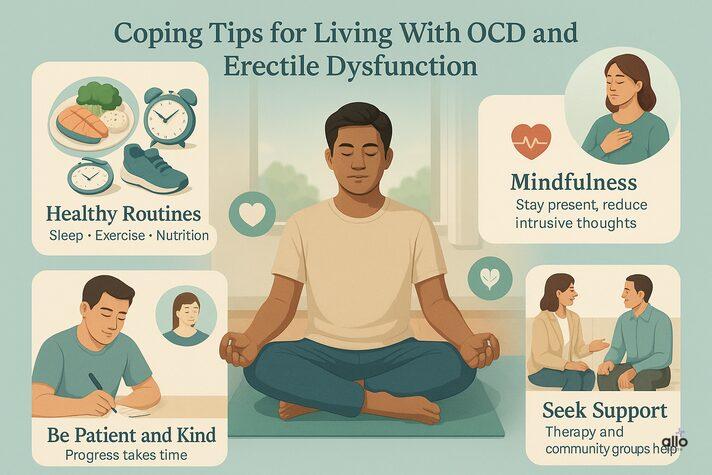
Coping Tips for Living With OCD and Erectile Dysfunction
Living with OCD and ED can be difficult but manageable through consistent self-care and mental relaxation.
1. Maintain Healthy Routines
Keep a regular sleep schedule, exercise daily, and eat balanced meals. Avoid alcohol, smoking, and excess caffeine. These habits help reduce anxiety and support better sexual health.
2. Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness helps you stay present during intimacy. Focus on sensations instead of fears. Try short breathing or meditation sessions each day to calm intrusive thoughts and build control.
3. Be Patient and Kind to Yourself
Progress takes time. Don’t blame yourself for setbacks. Appreciate small improvements and stay positive through the process.
4. Continue Therapy and Seek Support
Stay consistent with therapy or join support groups. Talking openly with professionals or peers helps relieve stress and improve confidence.
Key Takeaway
OCD and erectile dysfunction are closely linked through anxiety, intrusive thoughts, and the effects of medications. The most important step is to have an open and honest conversation with your doctor about your thoughts, mental health, and sexual difficulties. With the right care, therapy, and communication, managing OCD often leads to better mental balance and stronger, healthier sexual performance.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."