Foods to Avoid for Erectile Dysfunction: Worst Foods for Sexual Health
Written by Dr. Pranitha Bangera

Dr. Pranitha Bangera is a gold-medalist healthcare professional with an elite foundation in clinical training and patient care. A researcher at heart, she specializes in creating high-impact, research-driven medical content that empowers readers through accessible patient education. Dr. Bangera focuses on the intersection of digital health and clinical communication, specifically within the fields of sexual health and mental well-being. Her work is dedicated to making complex medical innovations understandable and trustworthy for a global audience.
•
October 10, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Quick Read
A poor diet can lead to both erectile dysfunction (ED) and heart disease, as both are linked to unhealthy blood flow and damaged blood vessels. Diets high in saturated fats, salt, and sugar can cause heart disease, high blood pressure, and insulin resistance — all of which lower nitric oxide levels and restrict blood flow to the penis. Over time, this combination weakens erections and harms overall sexual wellness. Chronic inflammation from processed and fried foods also plays a major role by damaging the endothelium (the inner lining of blood vessels) and reducing its flexibility. Studies show that following a Mediterranean diet — rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, fish, and olive oil — can improve cardiovascular function, boost nitric oxide, and support long-term sexual health. Pairing this with regular exercise, stress management, and other lifestyle changes can help protect your heart and naturally improve your erections. If you’re unsure where to start, contact a registered dietitian for personalized nutrition advice. And if ED symptoms persist, it’s best to consult a doctor for evaluation and proper treatment.
It’s no secret that what you eat affects how you feel, but did you know it can also affect the quality of your erections? Erectile dysfunction (ED) isn’t just about age or stress, but it’s also closely linked to what’s on your plate. Certain foods that cause impotence can reduce blood flow, harm blood vessels, and disrupt the delicate hormonal balance needed for healthy erections. Let’s explore the science behind this connection and how a few smart dietary changes can protect your sexual health.
Allo asks
Do you think your diet affects your sexual performance?
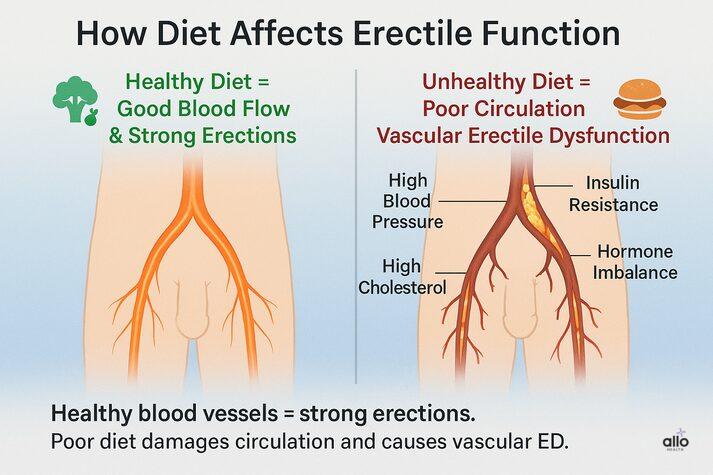
How Diet Affects Erectile Function
An unhealthy diet can damage the inner lining of your blood vessels, making them stiff and less flexible. Since erections depend on good blood flow and healthy vessels, this damage reduces circulation to the penis. Over time, it can make erections weaker or harder to maintain. This is a condition known as vascular erectile dysfunction. A poor diet can also lead to health problems that interfere with the body systems needed for erections, such as:
- High Blood Pressure
- High Cholesterol
- Insulin Resistance
- Hormone Imbalance
All of these conditions are associated with an increased risk of developing ED in men.
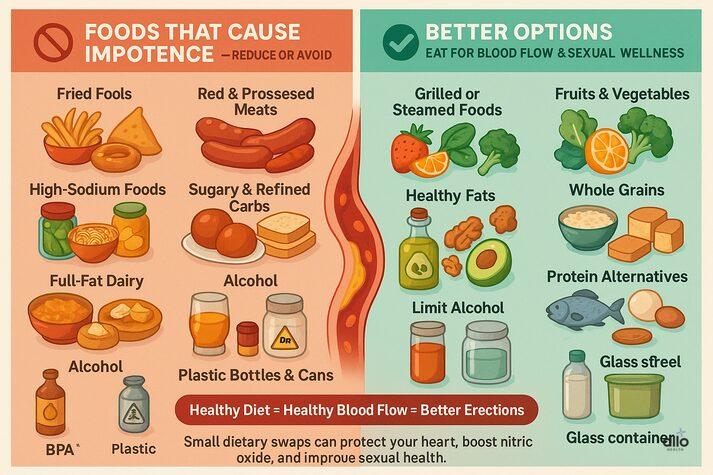
Foods To Avoid For Erectile Dysfunction
When we talk about foods that cause impotence, it’s not just about one type of meal. It’s about how your eating habits affect your heart (cardiovascular system) and blood vessels in the long run. Here are some common foods that can increase the risk of erectile dysfunction:
1. Fried Foods
Fried foods like French fries, chicken strips, fried chicken, mozzarella sticks, egg rolls, and fried fish, as well as popular Indian snacks like samosas, pakoras, bhature, puris, kachoris, and jalebis, are among the biggest culprits when it comes to foods that cause impotence. They’re loaded with saturated fats and trans fats. These can clog arteries, reduce nitric oxide levels, and damage the lining of your blood vessels (endothelium). This limits blood flow to the penis and leads to weaker or shorter-lasting erections.[1] Better option: Swap fried foods for grilled, steamed, or baked alternatives. Use olive oil, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, to support vascular health and improve blood circulation.
2. Red and Processed Meats
A diet heavy in red meat (like beef, lamb, pork, mutton, or dishes such as mutton kebabs and beef curries) and processed meats (like sausages, salami, and bacon) increases the risk of high cholesterol and heart disease. These foods are high in saturated fats, which cause fatty layers to form inside your arteries, including those that supply blood to your penis. [2] This can block healthy blood flow. Studies have linked high consumption of red meat with poorer cardiovascular health and lower sexual function in men. [3] Better option: Choose lean protein sources like fish, chicken, or plant-based alternatives. There are some diets that help with ED, like the Mediterranean diet, which includes more fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, and has been proven to improve sexual health.
3. High-Sodium and Processed Foods
About 70% of the salt we eat comes from processed foods like pizza, canned soups, frozen meals, fast food, and salty Indian favorites such as pickles, papads, instant noodles, chips, and packaged snacks. A diet high in salt (sodium chloride) raises blood pressure and damages the cardiovascular system, which directly impacts erectile function. [4] High blood pressure can cause ED by stiffening arteries and reducing nitric oxide availability. Better option: Opt for fresh, whole foods seasoned with herbs or lemon instead of salt. This helps lower sodium intake and maintain vascular endothelial health, crucial for strong erections.
4. Sugary Foods and Refined Carbs
Excess sugar-sweetened beverages, pastries, and candies might satisfy your cravings, but they wreak havoc on your blood flow and hormone levels. The same goes for sugary Indian desserts like gulab jamun, rasgulla, halwa, laddoos, and other mithai, as well as refined carbs such as white bread, bakery biscuits, and maida-based items like naans, samosas, and momos. High sugar intake causes insulin resistance, promotes chronic inflammation, and damages the blood vessels. [5] It can also lead to testosterone deficiency, further reducing sexual function. [6] According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), excess sugar increases the risk of diabetes, digestive diseases, and kidney disease. [7] All of these conditions can increase the risk of ED. Better option: Replace sugary snacks with flavonoid-rich foods such as lemon, berries, dark chocolate, and nuts. These can boost nitric oxide and enhance circulation.
5. Alcohol
While a glass of wine might help you unwind, too much alcohol can quickly turn from a relaxant to a performance killer. Excessive drinking lowers testosterone, raises estrogen, and harms penile tissues by causing blood vessel damage. [8] Over time, heavy alcohol use leads to nerve damage [9] and resistance to ED medications. [10] Better Option: Drink in moderation. For most men, having less than one or two drinks a day can protect sexual wellness.
6. Full-Fat Dairy
Whole milk, cheese, butter, and cream, along with rich Indian dishes like parathas soaked in ghee, butter chicken, paneer butter masala, and malai koft, are high in saturated fats, which can increase bad cholesterol (LDL) in the body.[11] This "bad" cholesterol narrows vessels and restricts blood circulation. Better option: Choose low-fat or plant-based alternatives like Greek yogurt or almond milk.
7. Hormone-Disrupting Foods
Certain foods, such as mint [12] and soy[13], may affect hormone balance in men if consumed in large amounts, though the scientific evidence is still mixed. [14] Better option: It’s best to enjoy these in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Include more zinc-rich items like pumpkin seeds, lentils, and nuts, as these help support healthy testosterone levels naturally.
8. Foods Stored in Plastic or Canned Containers
The way food is stored can also affect your sexual health. Many plastic bottles, food containers, and canned goods contain Bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical that can act as an endocrine disruptor, interfering with hormone balance and potentially contributing to erectile dysfunction over time.[15] Better option: Store food in glass or stainless steel containers and try to limit your use of plastics and canned foods whenever possible.
You don’t need to give up all your favorite foods, but you do need balance. Limiting processed foods and eating more fruits and grains can help with ED.
Can A Healthy Diet Fix ED?
Changing your diet and avoiding foods that cause ED can definitely help. A healthy diet supports your heart, boosts energy, and can make a real difference in your overall sexual wellness. However, diet alone can’t always fix erectile dysfunction. Since ED can have many causes, physical, hormonal, or psychological, only a doctor can identify the root problem and recommend the right treatment. This might include medications, therapy, or other medical procedures. So, while eating better is a great first step, make sure to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment if your symptoms persist.

Conclusion
Foods that cause impotence don’t just affect your sex life, but can they impact your overall health. A diet high in fried, salty, or sugary foods can slow blood flow, lower nitric oxide, and weaken erections over time. Making small, consistent changes can help. Switching to a Mediterranean-style diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can all boost circulation and support better sexual health. If you’re unsure where to start, talk to a registered dietitian for simple, practical meal changes. And if erectile dysfunction persists, don’t wait, but see a doctor for personalized treatment and support.
Disclaimer
The following blog article discusses food and diet-related information for general educational purposes. However, it is important to note that the information provided is not intended as personalized dietary advice and should not be considered a substitute for professional guidance from a registered dietitian or qualified healthcare professional. Before making any significant changes to your diet or nutrition plan, it is recommended to consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional. Dietary changes can have a significant impact on your overall health and well-being. It is important to approach any changes to your diet in a balanced and sustainable manner, ensuring that you meet your nutritional needs and avoid any potential nutrient deficiencies. Rapid or extreme changes in dietary patterns can be detrimental to your health and may require professional guidance. It is crucial to note that any specific dietary recommendations or guidelines mentioned in this article may not be appropriate for individuals with specific medical conditions, allergies, or intolerances. A registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide individualized advice, including modifications or alternative food choices to accommodate your unique circumstances. The information provided in this article may not encompass all possible dietary considerations or account for the latest research and nutritional guidelines.
Most Asked Questions
Can the food I eat really cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes. Diet plays a major role in blood flow, heart health, and hormone balance, all of which are essential for erections. Foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats can reduce circulation and increase the risk of ED.
What are the worst foods for erectile dysfunction?
Fried foods, red and processed meats, salty snacks, sugary desserts, refined carbs, and alcohol are some of the worst offenders. They can damage blood vessels and lower nitric oxide levels, which are needed for strong erections.
Can reducing fried and fatty foods reverse ED?
In many cases, yes, especially if ED is linked to poor circulation or heart health. Improving your diet and lifestyle can help restore normal erectile function over time.
Can Indian foods cause ED?
Yes, certain Indian foods like deep-fried snacks (samosas, pakoras), heavy ghee-based curries, sugary sweets, and processed meats can raise cholesterol and blood pressure, which increase ED risk.
How long does it take to see improvement if I change my diet?
It varies from person to person, but some men notice improvements in energy, mood, and erection quality within a few weeks of consistent diet and lifestyle changes.
Sources
- 1.
Eating, Diet, & Nutrition for Erectile Dysfunction
- 2.
Saturated Fat
- 3.
Association of Diet With Erectile Dysfunction Among Men
- 4.
About Sodium and Health
- 5.
Excessive intake of sugar: An accomplice of inflammation
- 6.
Sugar-sweetened beverage intake and serum testosterone levels in adult males
- 7.
Diabetes
- 8.
Alcohol’s Effects on Male Reproduction
- 9.
Alcoholic Neuropathy
- 10.
Influence of Alcohol on Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors Use in Middle- to Old-Aged Men
- 11.
What's the deal with dairy and heart health?
- 12.
Spearmint herbal tea has significant anti-androgen effects
- 13.
Effect of Soy Protein on Testosterone Levels
- 14.
Effects of soy on fertility: Current evidence and controversies
- 15.
Bisphenol A: an endocrine disruptor with widespread exposure and multiple effects


