Lexapro and Erectile Dysfunction: A Complete Guide
Written by Dr. Sharon Kumar

With a strong academic background in dentistry and clinical exposure, Dr. Sharon who has studied at PDM Dental College, brings a valuable blend of medical knowledge and communication skills to health content writing. She is passionate about creating clear, compassionate, and evidence-based content on topics such as general wellness, sexual health, oral care, and patient education. Her goal is to make complex medical information easy to understand, relatable, and genuinely helpful for readers seeking clarity on their health concerns. Dr. Sharon believes in the power of well-researched, empathetic content to educate and empower people to make better health decisions. Whether it’s writing about preventive care or breaking down myths in sexual wellness, her content always balances science with sensitivity.
•
October 23, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.

Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a topic many men avoid discussing, but it’s more common than most realize, especially for those who are managing depression or anxiety with medication. If you’re one of the many men taking antidepressants like Lexapro (escitalopram), you might have noticed some unexpected side effects, one of them being ED. While these medications can be life-changing for mental health, they can sometimes cast a shadow on your sex life, leaving you feeling frustrated or self-conscious. Let’s dive into how SSRIs, like Lexapro, might be affecting your sexual health and what you can do about it.
The Connection Between Antidepressants and Sexual Problems
Lexapro is a type of serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that helps balance brain chemistry. It works by preventing serotonin from being absorbed back into nerve cells too quickly. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter, a chemical that helps transmit signals in the brain and throughout the nervous system. This increase in serotonin helps improve mood and reduce anxiety symptoms. However, the same process that helps with depression can sometimes interfere with sexual function and erectile function. Sexual dysfunction is one of the most commonly reported adverse events with antidepressant use. Studies show that sexual side effects occur in many people taking SSRIs. These problems can include low libido or sexual desire, difficulty with sexual arousal, delayed orgasm, and erectile dysfunction. For some men, these issues can be mild, while for others, they can impact their ability to enjoy sexual intercourse. The sexual response cycle involves multiple stages: desire, arousal, orgasm, and resolution. Antidepressant medication can disrupt any of these stages. When serotonin levels rise too high, they can interfere with the body's natural signals that trigger sexual desire and erectile function.
Why SSRIs Cause Sexual Side Effects
Several factors contribute to sexual dysfunction when taking SSRIs:
Serotonin's Impact on Sexual Function
- While serotonin helps regulate mood, too much can dampen sexual desire and interfere with the physical responses needed for sexual intercourse.
- High serotonin levels can block dopamine, a neurotransmitter important for sexual thoughts and motivation.
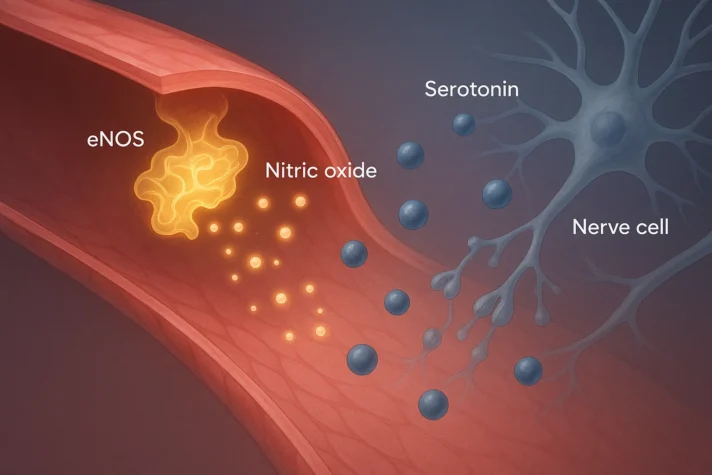
Nitric Oxide and Blood Flow
- Erections depend on nitric oxide, a molecule that helps blood vessels relax and allows blood to flow into the penis.
- SSRIs can affect nitric oxide synthase, the enzyme responsible for producing nitric oxide.
- This disruption can make it harder to achieve and maintain erections.
- Research shows that endothelial nitric oxide synthase plays a crucial role in erectile function, and when this system is disrupted, ED can result.[1]
- Some people feel numbness in the genital area, called genital anesthesia [2]. They may also have other strange sensations. These make sexual activity less enjoyable or harder.
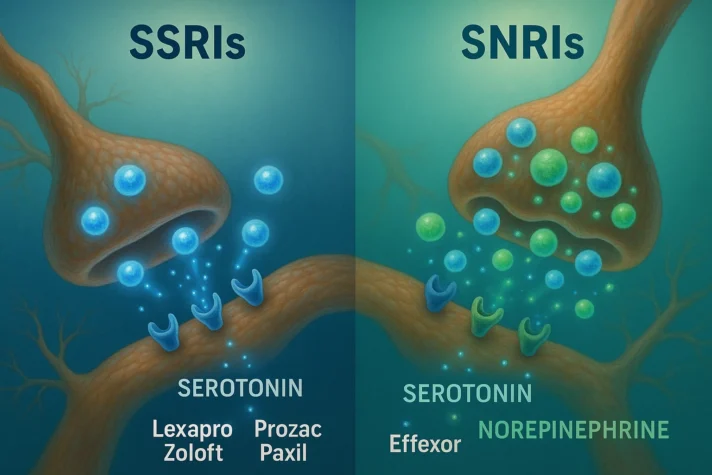
Comparing Different Antidepressant Types with Lexapro
Not all antidepressants affect sexual function the same way. Understanding the differences can help you and your doctor make better decisions:
- SSRIs: These include Lexapro, Prozac, Zoloft, and Paxil. They're effective for depression but have higher rates of sexual side effects.
- Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) [3] are medications, such as Effexor [4] and Cymbalta [5]. They affect both serotonin and norepinephrine. They may cause similar sexual problems as SSRIs.
- Tricyclic antidepressants: These older medications can also cause sexual dysfunction, though they work differently from SSRIs.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) [6]: Another older class of antidepressants that can affect sexual function and require dietary restrictions.
- Bupropion (Wellbutrin): This medication works differently as a psychoactive substance [7] and typically causes fewer sexual side effects. Many doctors consider it when patients experience sexual problems with other antidepressants.
Experiencing ED with Lexapro?
If you're experiencing erectile dysfunction while taking Lexapro, it's important to identify whether the medication is the cause. Take note of your sexual history before starting the medication and compare it to your current experience. Did the problems start after beginning antidepressant use? Have they gotten worse with time? Common signs include:
- Reduced sexual desire or interest
- Difficulty getting or maintaining an erection
- Delayed orgasm or inability to climax
- Decreased sensitivity during sexual activity
- Less frequent sexual thoughts
Sometimes, depression itself can cause these problems, making it tricky to determine if the medication or the condition is responsible. A thorough discussion with your doctor can help clarify the situation.
How Doctors Treat SSRI-Related Erectile Dysfunction
When you discuss erectile dysfunction with your healthcare provider, they'll review your complete medical history and consider various options:
1. Dose Adjustment
Sometimes lowering the dose can reduce sexual side effects while still providing mental health benefits. This approach requires careful monitoring to ensure your depression or anxiety doesn't return.
2. Drug Holiday
Some doctors suggest temporarily stopping the medication on weekends or before planned sexual activity. However, this isn't suitable for everyone and can cause withdrawal symptoms or mood changes. Never try this without medical supervision.
3. Switching Medications
Your doctor might recommend trying a different antidepressant medication with fewer sexual side effects. This process, called drug cessation and transition, should be done gradually under medical supervision to avoid withdrawal symptoms or worsening mental health.
4. Adding Medications
In some cases, doctors prescribe additional medications to counteract sexual side effects. Viagra, Cialis, or similar drugs can help with erectile dysfunction by improving blood flow. These work by affecting different pathways than SSRIs, including some that involve NADPH oxidase [8] and reactive oxygen species regulation in blood vessels.
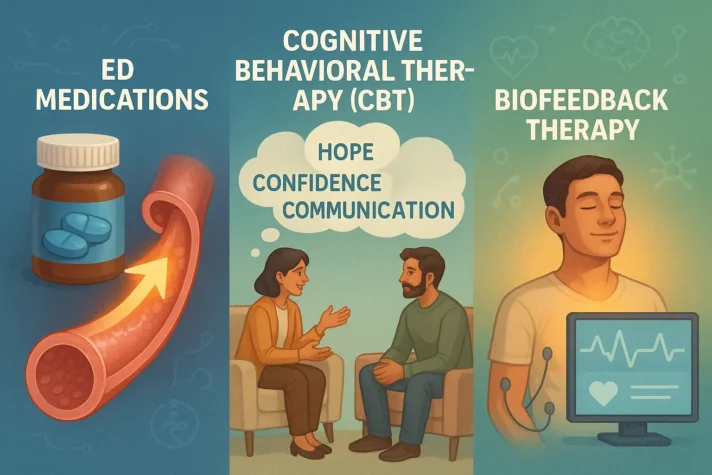
Treatment Options for ED
Several approaches can help manage erectile dysfunction while continuing antidepressant treatment: Medical Treatments- ED medications work by enhancing blood flow to the penis. They're generally safe when used as directed, though they can interact with some medications. Your doctor will check for potential interactions before prescribing them. Talking therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), can help with both depression and sexual concerns. Sex therapy specifically focuses on sexual problems and can teach techniques to improve intimacy despite medication side effects. The approach looks at biological, psychological, and social factors that affect your sexual health. It recognizes that mental health, relationships, and physical health are all connected. Biofeedback Therapy: This technique helps you become more aware of your body's responses and learn to control certain physical functions, which may improve sexual function.
Lifestyle Changes That Help ED
Besides medical treatments, you can make lifestyle changes to improve sexual function.
Regular Exercise
Exercise programmes improve blood flow throughout the body, including to the genital area. Physical activity also boosts mood and energy, which can enhance sexual desire. Even moderate activity like walking or swimming can make a difference.
Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains (like breakfast cereal with whole grains), and lean proteins supports overall health and erectile function. Some foods may help with blood vessel health and nitric oxide production.
Stress Management
Stress worsens both depression and sexual problems. Techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help manage stress.
Adequate Sleep
Poor sleep affects mood, energy, and sexual function. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.

“Limit alcohol use and avoid recreational drugs. These substances can make erectile dysfunction worse and can interact dangerously with antidepressants.”
Understanding Post-SSRI Sexual Dysfunction (PSSD)
In rare cases, some people experience persistent sexual dysfunction even after stopping SSRIs. This condition, called PSSD, is not fully understood. Symptoms can include ongoing erectile dysfunction, low libido, genital anesthesia, or difficulty with orgasm. While uncommon, it's important to be aware that this possibility exists. Research is ongoing to understand why PSSD occurs in some individuals and how to treat it. If you experience persistent sexual problems after drug cessation, inform your healthcare provider. They can help rule out other causes and discuss potential treatments.
Important Safety Considerations for Lexapro
While managing sexual side effects, don't ignore serious symptoms that require immediate attention: Serious Allergic Reaction: Seek emergency help if you experience swelling, difficulty breathing, or a severe rash. Unusual Bleeding: Blood in your pee, blood in your vomit, or bleeding from the gut requires urgent medical review. Vaginal Bleeding: If you're female or have a female partner experiencing unusual vaginal bleeding, consult a doctor. Serotonin Syndrome [9]: This rare but serious condition occurs when serotonin levels become dangerously high. Symptoms include agitation, confusion, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, dilated pupils, and muscle rigidity. Some people rarely have unusual sexual symptoms. These include orgasmic hypersexuality, sexual obsession, or big changes in sexual behavior. Report these to your doctor immediately.

Conclusion
Taking Lexapro or other antidepressants can cause erectile dysfunction. This is hard to deal with. However, there are solutions. The key is open communication with your healthcare providers and a willingness to explore different options. Your mental health matters, but so does your sexual health and overall quality of life. Remember that finding the right balance may take time. Some people need to try several approaches before finding what works best. Be patient with yourself and stay engaged with your healthcare team throughout the process. With the right support and treatment adjustments, many men successfully manage both their mental health and sexual function. You deserve to feel good both emotionally and physically.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Can Lexapro cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes, Lexapro, an SSRI, can cause sexual side effects, including erectile dysfunction (ED). This happens because it affects serotonin levels, which can interfere with sexual desire and the ability to achieve an erection.
How can I tell if Lexapro is causing my erectile dysfunction?
If you notice changes in your sexual function after starting Lexapro, such as reduced libido, difficulty maintaining an erection, or delayed orgasm, it could be related to the medication. A discussion with your doctor can help confirm the cause.
What can I do about ED caused by Lexapro?
Your doctor may adjust your dosage, switch medications, or suggest medications like Viagra to help manage ED. Counseling or sex therapy can also help address the psychological aspects of ED.
Are there any antidepressants that don’t cause sexual dysfunction?
While many antidepressants, particularly SSRIs, can lead to sexual side effects, medications like Bupropion (Wellbutrin) are often considered to cause fewer sexual problems. Discussing options with your doctor can help you find a suitable alternative.
Is erectile dysfunction caused by Lexapro permanent?
ED caused by Lexapro is usually reversible once the medication is adjusted or switched. However, in rare cases, some individuals may experience persistent sexual dysfunction even after stopping the medication (Post-SSRI Sexual Dysfunction or PSSD).
Sources
- 1.
Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Keeps Erection Regulatory Function Balance in the Penis
- 2.
Genital anaesthesia persisting six years after sertraline discontinuation
- 3.
New Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors and Their Anesthetic and Analgesic Considerations
- 4.
Venlafaxine
- 5.
Cymbalta
- 6.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI)
- 7.
psychoactive substance
- 8.
NAD(P)H Oxidase
- 9.
Serotonin Syndrome


