Buspirone and Erectile Dysfunction: Can Anxiety Medicine Affect Your Performance?
Written by Dr. Pranitha Bangera

Dr. Pranitha Bangera is a gold-medalist healthcare professional with an elite foundation in clinical training and patient care. A researcher at heart, she specializes in creating high-impact, research-driven medical content that empowers readers through accessible patient education. Dr. Bangera focuses on the intersection of digital health and clinical communication, specifically within the fields of sexual health and mental well-being. Her work is dedicated to making complex medical innovations understandable and trustworthy for a global audience.
•
November 24, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.

Quick Read
If you’re wondering whether buspirone causes erectile dysfunction, the short answer is reassuring, it rarely does. Most research shows that buspirone has a low risk of sexual side effects and, in many cases, can actually improve erections and libido, especially when sexual problems are caused by SSRIs. It works by balancing brain chemicals like serotonin and dopamine and supporting nerve signaling involved in arousal. If ED does occur while taking buspirone, it’s usually temporary and manageable with simple steps like reviewing medications, addressing anxiety, and, if needed, adding ED medication. Remember, help is available, and both anxiety and sexual function can improve together with the right support.
When you search for “buspirone erectile dysfunction,” you’re usually looking for one thing: clarity. If you’re taking buspirone for anxiety, it’s natural to worry about how this medication might affect your erections. Anxiety itself can reduce sexual arousal, and adding medication into the mix can often cause confusion. Buspirone rarely causes erectile dysfunction. Most studies show it has a low risk of sexual side effects and may actually help certain people, especially those dealing with sexual problems caused by SSRIs and other antidepressants. By balancing brain chemicals like serotonin and dopamine, buspirone can support healthier arousal signals, libido, and even erectile function. In this article, we’ll explore whether buspirone causes ED, how it may improve sexual function, what the research says, how it compares to other psychiatric medications, and practical steps to manage or prevent ED while taking it. Let’s break this down in a clear, calm, and doctor-friendly way.
Allo asks
If you're taking Buspirone, have you noticed any sexual changes?
Does Buspirone Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Buspirone rarely causes erectile dysfunction, and most studies show it does not negatively affect sexual function. Researchers also couldn’t confirm whether buspirone was actually responsible, because factors like underlying anxiety disorders, major depressive disorder, other medications, and even stress or relationship concerns can independently trigger sexual dysfunction.
How Does Buspirone Support Erectile Function?
1. Helps Reverse SSRI-Induced Sexual Dysfunction
Buspirone can reverse sexual side effects caused by SSRIs and other antidepressants.[1]These medicines often lower sex drive, make arousal difficult, or cause erection and orgasm problems. Adding buspirone can help ease these issues without stopping the antidepressant itself. It works by gently balancing serotonin, a brain chemical that often becomes “too active,” and can shut down sexual desire and arousal, which is the main cause of SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction. Over time, buspirone helps bring these signals back to normal, making sexual response more natural again. Unlike medications like sildenafil or tadalafil that act directly on blood flow, buspirone works on the brain’s sexual-arousal pathways, which is why it may be particularly useful for people whose ED is connected to SSRIs or anxiety rather than circulation.
2. Improves Sexual Response
Buspirone affects dopamine, the “motivation and pleasure” chemical, and helps boost signals that are important for sex drive, arousal, and getting or maintaining an erection. [2]
3. Boosts Nerve Communication
Buspirone also affects another set of signals in the body called alpha-adrenergic pathways. In simple terms, this helps the nerves involved in arousal communicate better. When these signals flow smoothly, it supports healthier erections and a more natural sex drive. [3]
4. Boosts Arousal Signals
Unlike medications such as sildenafil or tadalafil, which directly improve blood flow, buspirone works at a central nervous system level, helping reset the brain’s sexual-arousal pathways. For people experiencing SSRI-related ED, this is often more helpful than switching antidepressants, especially when mental health treatment still needs to continue. [1]

ED Risk: Buspirone vs Other Psychiatric Drugs
Below is a quick comparison of how likely different anxiety and depression medications are to cause erectile dysfunction and where buspirone fits in:
Medication
ED Risk
SSRIs (e.g., fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline)
Very High
SNRIs (venlafaxine, duloxetine)
High
Tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline)
High
Buspirone
Low
How to Manage ED Caused by Buspirone
If you notice erection changes after starting buspirone, try not to panic; these symptoms are usually temporary and can be managed with the right approach.
1. Talk to your Healthcare Provider
The first and most important step is to talk to your healthcare provider. They may review all the medications you’re taking, adjust your dose, or change the timing of your doses.
2. Address Underlying Conditions
Sometimes erectile dysfunction has nothing to do with buspirone at all and may be linked to anxiety, depression, diabetes, blood pressure medicines, or hormone imbalances. Managing your anxiety is a key part of improving sexual function. When anxiety is under better control, arousal, erections, and overall sexual well-being naturally improve as well. This can be supported through cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), biofeedback therapy, lifestyle changes, regular exercise, and better sleep routines. Your doctor may run blood tests to check hormones, blood sugar, or heart health. These tests help make sure there isn’t another medical issue contributing to the problem.
3. Add ED Medication
If needed, your doctor might add a PDE5 inhibitor such as sildenafil (Viagra) or tadalafil (Cialis). These medications directly improve blood flow to the penis and can work even if the underlying issue is related to anxiety or medication side effects.

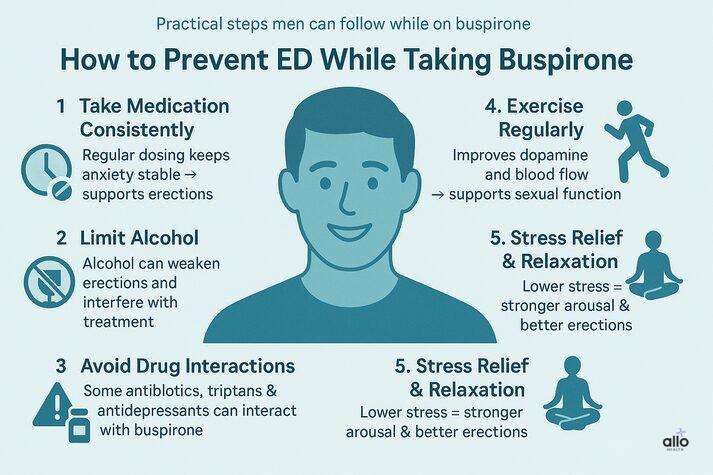
How to Prevent ED While Taking Buspirone
1. Take your medication consistently
Irregular dosing can worsen anxiety symptoms, indirectly affecting erections.
2. Limit alcohol
Alcohol is a major cause of ED and interferes with anxiety treatment.
3. Avoid Combining Certain Drugs
Some drugs like macrolide antibiotics, triptans, and certain antidepressants can interact with buspirone and increase side effects.
4. Exercise regularly
Regular exercise is one of the simplest and most effective ways to support sexual health. Moving your body helps boost dopamine while also improving overall blood flow. Better circulation and healthier dopamine levels work together to enhance arousal, erection quality, and overall sexual function.
5. Stress Relief
Breathing exercises, stretching, therapy, and mindful routines can reduce stress-related ED.
Conclusion
Buspirone does not typically cause erectile dysfunction. In fact, it is one of the few anxiolytic drugs with minimal sexual side effects, no dependence, or long-term sexual harm. Its most meaningful role in sexual health is as a treatment for SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction, where multiple clinical trials show improvements in libido, erections, orgasm, and overall sexual function. If ED persists, don't hesitate to speak to a sexual health expert. You’re not alone, and with the right support, both your anxiety and your sexual health can improve together.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Can buspirone cause erectile dysfunction?
Buspirone very rarely causes erectile dysfunction. Most studies show it has a low risk of sexual side effects compared to many antidepressants. If ED happens after starting buspirone, it’s often due to anxiety, stress, or another medication rather than buspirone itself.
Can buspirone help with sexual problems caused by antidepressants?
Yes. Buspirone is sometimes prescribed alongside SSRIs to improve low libido, arousal problems, delayed ejaculation, or ED. Many people notice improvement within the first few weeks.
Does buspirone reduce sex drive or libido?
A small number of people may notice temporary changes in libido, but this is uncommon. For many, buspirone has no negative effect on sex drive and in people whose libido dropped after starting SSRIs, it may actually help restore it.
If I get ED while taking buspirone, should I stop the medication?
No, don’t stop buspirone on your own. ED is often caused by anxiety, stress, hormones, or other medicines rather than buspirone. Talk to your doctor first so they can adjust the dose or timing, or suggest other solutions.
Can I take Viagra or Cialis while on buspirone?
Usually yes, and doctors often recommend PDE5 inhibitors like sildenafil or tadalafil if needed. These medications safely support erections while buspirone continues to manage anxiety. Always ask your healthcare provider before combining medications.
Sources
- 1.
Effect of buspirone on sexual dysfunction in depressed patients treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- 2.
Therapeutic doses of buspirone block D3 receptors in the living primate brain
- 3.
Post-Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Sexual Dysfunctions (PSSD): Clinical Experience with a Multimodal Approach


