Blood Thinners and Erectile Dysfunction: Side Effects Explained
Written by Dr. Sharon Kumar

With a strong academic background in dentistry and clinical exposure, Dr. Sharon who has studied at PDM Dental College, brings a valuable blend of medical knowledge and communication skills to health content writing. She is passionate about creating clear, compassionate, and evidence-based content on topics such as general wellness, sexual health, oral care, and patient education. Her goal is to make complex medical information easy to understand, relatable, and genuinely helpful for readers seeking clarity on their health concerns. Dr. Sharon believes in the power of well-researched, empathetic content to educate and empower people to make better health decisions. Whether it’s writing about preventive care or breaking down myths in sexual wellness, her content always balances science with sensitivity.
•
October 10, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Quick Read
Blood thinners don’t directly cause erectile dysfunction (ED), but they can sometimes play an indirect role. These medications prevent blood clots and improve circulation, which supports overall heart health, but they don’t necessarily increase blood flow to the penis. In rare cases, side effects like bleeding, anemia, or poor circulation can contribute to ED. On the other hand, by keeping blood vessels clear, blood thinners may indirectly help manage conditions that lead to erectile problems. If you experience ED while on blood thinners, consult your doctor to identify the cause and explore safe, effective treatment options.
Many men taking blood thinners start to wonder, could these medications be affecting my erections? It’s an understandable concern. After all, blood flow is at the heart of every healthy erection, and blood thinners literally change how your blood behaves. These medications are vital for preventing heart attacks, strokes, and blood clots, but when it comes to sexual health, things can get a bit confusing. Some worry that blood thinners might cause erectile dysfunction, while others wonder if they might help by improving circulation. The truth isn’t so black and white, but it depends on your health, the type of blood thinner, and what’s happening inside your blood vessels. In this article, we’ll break down how blood thinners work, their possible side effects, and what they really mean for your erections and sexual performance.
Allo asks
Have you ever noticed any changes in your erections or sexual performance after starting blood thinners?
Do Blood Thinners Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Blood thinners don’t directly cause erectile dysfunction (ED), but they might indirectly play a role in certain cases. These medications work by preventing blood clots, making the blood less sticky, and targeting the proteins responsible for clotting. While this helps reduce the risk of serious conditions like strokes [1] and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) [2], there is no strong evidence showing that blood thinners themselves directly lead to ED. But many men on blood thinners worry about their sexual health due to potential side effects. Some medications, like blood pressure drugs, can lower blood flow, which is important for getting and keeping an erection. But ED is often more closely linked to other health problems, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and mental health issues like stress. In fact, some medications used to treat these conditions, including certain blood pressure medicines and antidepressants, can affect sexual function more than blood thinners do.
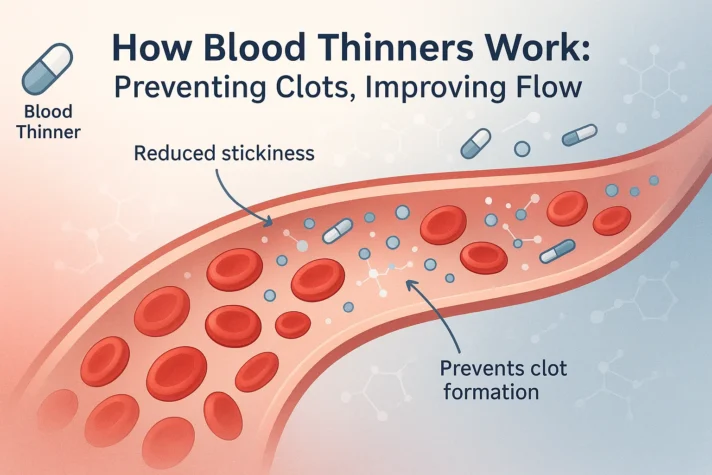
How Blood Thinners Impact Sexual Health
Blood thinners work by interfering with the body's natural clotting process, making it harder for blood to clot. This helps prevent serious conditions like
- Pulmonary Embolism [3] - A serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot blocks one or more arteries (blood vessels) in the lungs.
- Systemic Embolism [4]- When something like a blood clot, air bubble, or fat particle travels through the bloodstream and blocks a blood vessel somewhere in the body, stopping normal blood flow.
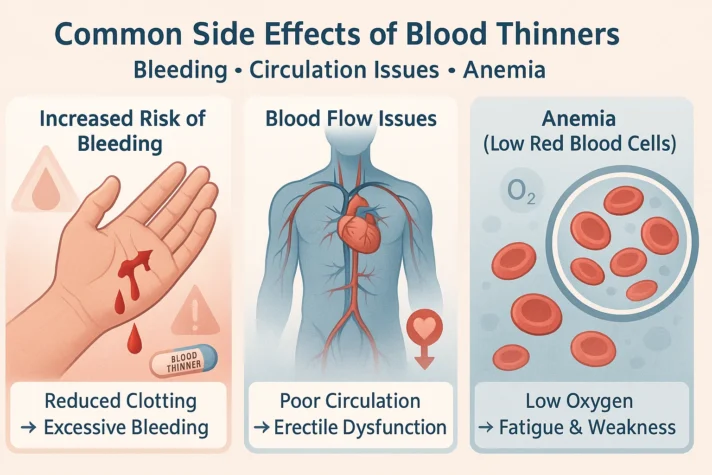
But it can also cause some side effects, including:
1. Increased risk of Bleeding
- Blood thinners reduce clotting, so even minor injuries or trauma can lead to excessive bleeding. In rare cases, internal bleeding or bleeding in the genital area can occur, which could affect sexual performance and function.
- The FDA has warned about a condition called spinal or epidural hematoma [5], which can happen during certain procedures like spinal taps or injections when on blood thinners.
“Blood thinners don’t directly damage your ability to have an erection they simply change how your blood clots. Most men who notice ED while on them usually have other underlying issues like heart disease or stress.”
2. Blood flow issues
- For men with heart disease or other circulatory problems, blood thinners help prevent clots but may not improve blood flow to the penis.
- Poor circulation, also known as endothelial dysfunction, can contribute to erectile dysfunction (ED). Healthy blood vessels are key to good sexual function.
3. Anemia
- Blood thinners can cause bleeding, leading to anemia, which is a low red blood cell count.
- This can reduce oxygen levels in the blood and may affect energy levels and sexual function.
While these effects exist, there’s no solid evidence that blood thinners directly cause ED. Suppose ED does occur while using blood thinners. In that case, other factors might be to blame, such as age, existing health conditions like metabolic syndrome or multiple sclerosis, nerve damage, hormone imbalances, an enlarged prostate, venous leaks, genetic factors, or mental health issues.
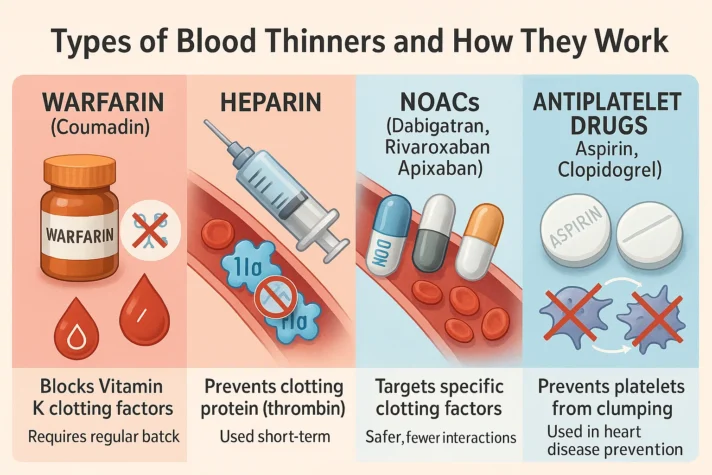
Common Blood Thinners and Their Side Effects
There are several types of anticoagulating agents, and each one can have different side effects. The most commonly prescribed blood thinners include:
1. Warfarin (Coumadin)
- Warfarin is an older blood thinner that prevents blood clots by blocking vitamin K-dependent clotting factors.
- It can cause bleeding, bruising, and allergic reactions.
- There is no direct link between Warfarin and erectile dysfunction (ED). If ED occurs, it’s more likely due to some other conditions like cardiovascular/heart disease, rather than the medication itself.
- Patients taking Warfarin must undergo regular blood tests to monitor their clotting levels.
2. Heparin
- Heparin is used for short-term treatment in hospitals and is injected into the body. There is a protein called thrombin that causes the blood to clot. Heparin prevents the blood from clotting.
- The main side effect is bleeding.
- Erectile dysfunction is not a common side effect of Heparin.
3. Novel Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs)
- NOACs, such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban, target specific blood-clotting factors and are often preferred over Warfarin for their lower risk of interactions.
- These medications are generally safer with fewer bleeding problems, but any medication affecting blood flow can contribute to ED, though this is rare.
- Doctors prescribe these for patients with conditions like atrial fibrillation or artificial heart valves to help prevent blood clots. Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm problem where the heart’s chambers (atria) beat irregularly.
4. Antiplatelet Drugs (Thienopyridine Derivatives)
- Medications like aspirin and clopidogrel work by preventing blood platelets from sticking together, which stops blood clots from forming.
- While these drugs don’t directly cause ED, they may lead to issues with circulation or bleeding, which could affect sexual performance.
- They are often given to people with heart conditions to reduce the risk of clots.
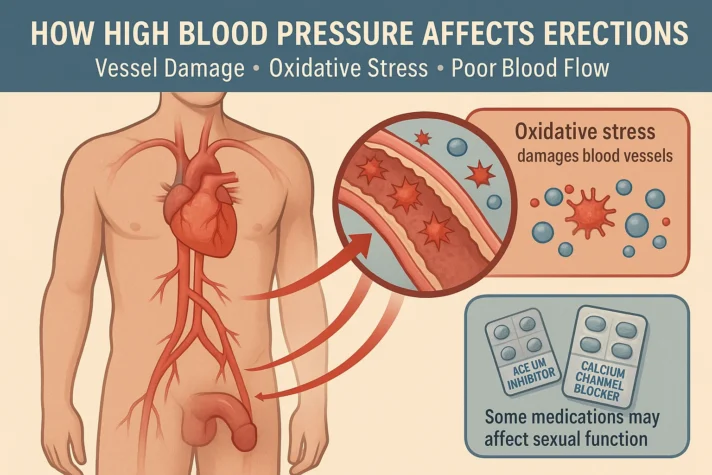
The Role of Blood Pressure and ED
High blood pressure itself is a major contributor to erectile dysfunction because it damages blood vessels over time, leading to
- Oxidative stress - It refers to an imbalance between free radicals (unstable molecules) and antioxidants (molecules that neutralize free radicals) in the body.
- Reduced blood flow to the penis
Some prescription high blood pressure medications, including ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers, can also affect sexual function. But controlling blood pressure is essential for better health and reducing your risk of heart disease and stroke.
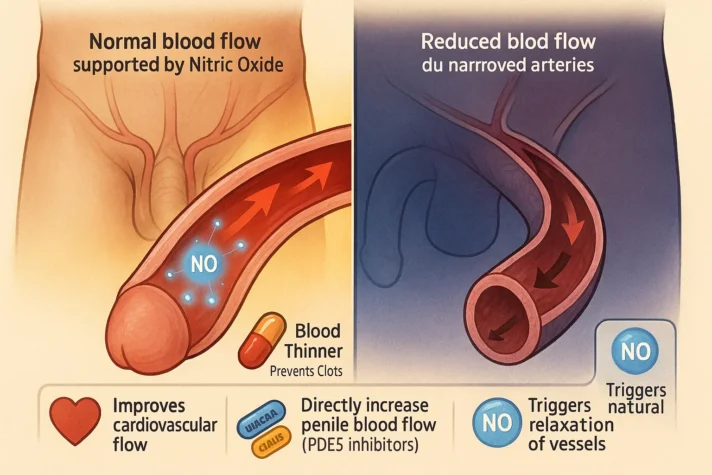
Do Blood Thinners Help with Erectile Dysfunction?
- While blood thinners do not directly help erectile dysfunction, improving blood flow is an essential part of treating ED.
- There is a connection between certain types of blood thinners and ED management, but this should not be confused with the primary use of blood thinners.
- Erectile dysfunction is often caused by reduced blood flow to the penis, which is sometimes linked to cardiovascular or heart issues.
- In this case, blood thinners may help manage the actual cause, which may indirectly improve ED.
- The body's natural ability to achieve an erection depends on nitric oxide, which helps relax blood vessels and allows blood to flow into the penis in response to nerve impulses.
- However, other medications are more commonly prescribed for erectile dysfunction, such as PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., Viagra, Cialis). These medications specifically increase blood flow to the penis and have proven to be effective in treating ED.
Managing Erectile Dysfunction While on Blood Thinners
If you are experiencing erectile dysfunction while taking blood thinners, it is important to first consult with your healthcare provider or a specialist like those at Lazare Urology. They can help determine the cause of your ED, whether it is related to the blood thinners, your underlying health conditions, or other factors. Here are some common treatments for ED that may be appropriate for individuals on blood thinners:
1. Oral Medications
- The most common pills for ED are PDE5 inhibitors.
- These include sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra).
- These medications work by increasing blood flow to the penis and are often effective in treating ED.
- But caution should be taken, as these medications can interact with blood thinners, increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Your doctor will need to carefully evaluate whether these medications are safe for you.
2. Penile Injections
- For men who cannot take oral medications, penile injections like Trimix or Caverject may be an option.
- These interventional techniques are directly administered into the penis to produce an erection.
- While these medications do not pose a risk of interaction with blood thinners, they can cause other side effects, such as pain or priapism (a prolonged erection), so they must be used under medical supervision.
3. Penis Pumps (Vacuum Pump)
- A penis pump, also called a vacuum pump, is a mechanical device that creates a vacuum around the penis, which draws blood into the area, causing an erection.
- This method does not interact with blood thinners and can be an effective solution for men who prefer non-invasive treatments.
4. Penile Implants
- In severe cases where other treatments fail, penile implants may be considered.
- This surgical option involves inserting a device into the penis to help achieve and maintain an erection.
- Implants are typically reserved for men who have not responded to other forms of treatment.
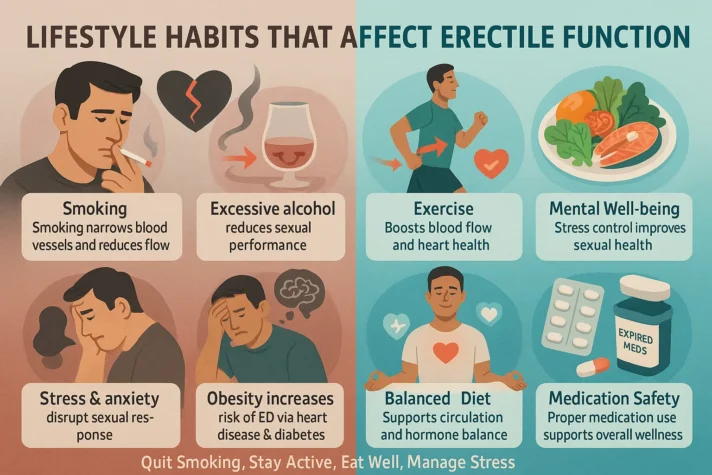
Lifestyle Factors that Impact ED
It's also important to address any lifestyle factors that might be contributing to erectile dysfunction, including:
- Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the penis.
- Being overweight or obese can raise the risk of ED. This happens because it can cause heart disease, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and hormone imbalance.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with sexual performance and lead to ED.
- Stress and Anxiety: Mental health plays a key role in sexual health. Emotional issues like stress, depression, and anxiety can all make ED worse.
- Lack of Exercise: Regular exercise can improve blood flow, strengthen your heart, and contribute to better health overall.
Changing your lifestyle can help improve sexual health. You should also manage your medicines properly. This includes safely disposing of expired drugs.
Conclusion
Blood thinners themselves do not directly cause erectile dysfunction. However, they can contribute to ED in certain cases, particularly by affecting blood flow or increasing the risk of bleeding. Erectile dysfunction often results from many factors. These include health problems like heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or mental stress. If you're experiencing ED while on blood thinners, it's essential to consult your healthcare provider to identify the cause and explore the most appropriate treatment options. Remember that better health through lifestyle changes and proper medical care can significantly improve your sexual function and overall quality of life.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Should I stop my blood thinner if I develop ED?
Never stop a prescribed blood thinner on your own; it could increase your risk of blood clots, heart attack, or stroke. Talk to your doctor about alternative medications or treatments for ED.
Can lifestyle changes improve ED while on blood thinners?
Absolutely. Regular exercise, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol, and managing stress can significantly improve blood flow and sexual function, even if you’re taking blood thinners.
What’s the difference between anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs?
Anticoagulants (like warfarin or apixaban) stop proteins that form clots, while antiplatelet drugs (like aspirin or clopidogrel) prevent platelets from sticking together. Both can reduce the risk of clots, but don’t directly cause ED.
Is it safe to use penis pumps or implants while on blood thinners?
Generally, yes, but always consult your doctor first. Devices like vacuum pumps are non-invasive and safe, but surgical options like implants require special precautions to avoid bleeding.
What should I do if I experience ED while on blood thinners?
Discuss it with your doctor. They can help identify whether your ED is medication-related or due to another condition and suggest safe, effective treatment options.


