High Triglycerides and Erectile Dysfunction: The Cholesterol Connection
Written by Dr. Pranitha Bangera

Dr. Pranitha Bangera is a gold-medalist healthcare professional with an elite foundation in clinical training and patient care. A researcher at heart, she specializes in creating high-impact, research-driven medical content that empowers readers through accessible patient education. Dr. Bangera focuses on the intersection of digital health and clinical communication, specifically within the fields of sexual health and mental well-being. Her work is dedicated to making complex medical innovations understandable and trustworthy for a global audience.
•
December 8, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.

Quick Read
High triglycerides don’t just affect your blood report; they can quietly damage blood vessels, hormones and metabolism in ways that increase the risk of erectile dysfunction. When triglycerides stay high for long periods, they stiffen the tiny penile arteries, reduce nitric oxide release and contribute to metabolic syndrome, all of which weaken erections over time. The good news is that triglyceride-related ED is often reversible with early lifestyle changes, better metabolic control and the right medical treatment. If you’re experiencing ED and have high triglycerides, it’s worth getting a proper check-up so you can support your heart health and sexual health together.
Many men first discover high triglycerides through a routine blood test, without realising how strongly this change in metabolism can affect blood flow, heart health and, over time, sexual function. In fact, high triglycerides impotence is becoming an increasingly recognised pattern in men. High triglycerides can contribute to ED in several ways. They damage the delicate lining of blood vessels, slow down nitric oxide release (the chemical signal that triggers an erection), and stiffen the tiny penile arteries that need to open quickly for good blood flow. Over time, this reduces circulation to the penis, disrupts hormonal balance and increases the likelihood of erection difficulties, especially the blood-flow–related ED. In this article, we’ll break down how high triglycerides develop, why they increase the risk of erectile dysfunction, what the science says, and the steps men can take to improve their triglyceride levels, protect their vascular health and strengthen their erections.
Allo asks
What do you think is the biggest contributor to ED?
Does Having High Triglycerides cause Impotence?
Having high triglyceride levels in your blood doesn’t guarantee that you may develop erectile dysfunction (impotence), but they significantly raise the risk, especially for blood-flow–related (arteriogenic) ED. But what does having high triglycerides even mean? Having high triglycerides simply means there is too much fat circulating in your blood. Your body produces triglycerides from the extra calories you eat, especially sugars, refined carbs and fatty foods. When these levels stay high for a long time, they start to affect your blood vessels, metabolism and overall heart health. Large studies comparing men with ED to a Non-ED group consistently find much higher rates of triglycerides in those with ED, and this link remains significant even after adjusting for age and other demographic characteristics like BMI and smoking. [1] In one study, nearly 80% of men with ED had average triglyceride levels clearly higher than in the Non-ED group. [1] Another study of nearly 4,000 men with sexual complaints found that higher triglyceride levels were a key factor linked specifically to arteriogenic ED (ED caused by impaired penile blood flow). [2]
How Does Having High Triglycerides Cause ED?
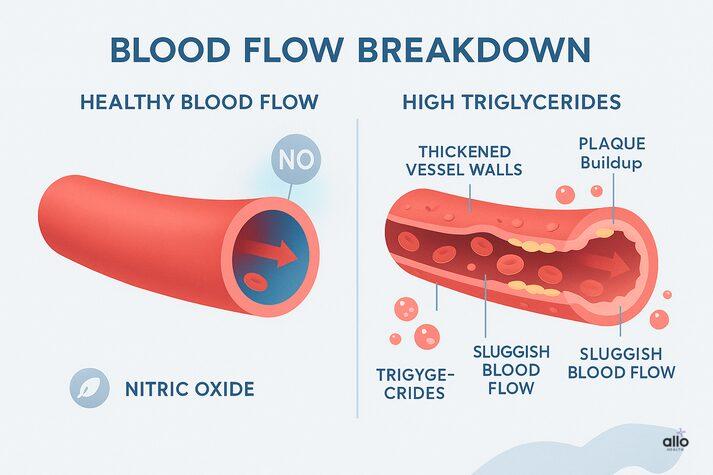
To understand how high triglycerides lead to ED, it helps to remember that a healthy erection depends on healthy blood flow. The penis relies on tiny arteries and a healthy vessel lining to open up quickly and let blood rush in, to fill the erectile tissue of the penis, making the penis firm and erect. When triglycerides stay high for long periods, they start to damage these blood vessels, making them stiffer and impairing the release of nitric oxide, the chemical that triggers an erection. Over time, this can slow blood flow, narrow the penile arteries, and disrupt the hormonal balance the body needs for healthy erections. Let's look at this in detail:
1. Damage to the Blood Vessel Lining
The endothelium is the thin, active lining inside all your blood vessels. It produces nitric oxide, which:
- Relaxes the penile arteries
- Allows rapid blood inflow
- Helps trap blood inside the penis to maintain an erection
High triglycerides interfere with this system and cause endothelial dysfunction, meaning the vessel lining simply isn’t working as well as it should. [3] This creates several problems:
- High triglycerides increase inflammatory activity, which damages vessel cells.
- Triglyceride-rich particles in the blood can become “rusted” or damaged. [3] These behave like irritating sludge moving through narrow pipes, gradually wearing down and injuring the delicate inner lining.
- When the lining is inflamed or damaged, it struggles to release enough NO to trigger or maintain an erection.
Because the penile arteries are extremely small, only 1–2 mm wide, they are often the first place where this kind of damage shows up. That’s why ED is recognised as an early sign of cardiovascular disease. [4]
2. Narrowing of the Arteries
High triglycerides also speed up the buildup of fatty plaque inside the arteries. This process is called atherosclerosis. [1] Over time:
- The arteries slowly clog
- The vessel walls harden
- Blood flow becomes more restricted
Even a small amount of narrowing can significantly affect the tiny penile arteries. When the blood can’t flow in strongly or quickly enough, getting or maintaining an erection becomes much more difficult.
3. Trouble with Overall Metabolism
High triglycerides rarely appear alone; they’re usually part of a bigger picture known as metabolic syndrome, which includes [5]:
- Increased waist circumference
- Higher blood pressure
- Raised fasting blood glucose
- Low HDL (“good cholesterol”)
A major part of metabolic syndrome is insulin resistance, which creates chronic, low-grade inflammation throughout the body. This inflammatory environment continues to damage:
- The endothelial lining
- The smooth muscle inside the penis (needed for strong erections)
Over time, this combination weakens the body’s ability to produce and maintain erections. [5]
4. Hormonal Changes
High triglycerides and metabolic syndrome are also linked to changes in testosterone, the male hormone responsible for sexual desire. [6]
- Men with high triglycerides are more likely to have low testosterone and other altered hormonal parameters.
- Low testosterone levels reduce libido, weaken spontaneous erections, and affect the health of penile tissue.
Is ED from High Triglycerides Permanent?
ED associated with high triglycerides and metabolic factors is often at least partially reversible, especially when addressed early. [7] ED is more likely to improve when:
- High triglycerides and metabolic syndrome are recognised early
- Lifestyle changes lead to meaningful reductions in weight and waist circumference
- Blood pressure and blood glucose are controlled
- Smoking and excessive alcohol use are reduced or stopped
- Low testosterone (if present) is correctly evaluated and treated in line with guidelines
ED may be less reversible if:
- There is long-standing, advanced atherosclerosis of the penile arteries
- Diabetes, severe metabolic syndrome or long-term smoking have already caused nerve and vascular damage
- No changes are made to diet, exercise or risk factors
Even in these cases, symptomatic treatment with ED medication like Viagra can still improve the quality of sex life.
When to See A Doctor
Consider seeing a doctor if:
- ED persists for more than 3 months
- You notice ED developing earlier than expected (for example, in your 30s or early 40s)
- You already know you have high triglycerides, high cholesterol or high blood glucose
- You have a strong family history of early heart disease or stroke
- You have other features of metabolic syndrome, such as increasing waist circumference, high blood pressure or fatty liver
A typical evaluation may include:
- Fasting lipid profile (including triglycerides)
- Fasting blood glucose
- Blood pressure, BMI and waist circumference
- Basic hormonal parameters, such as morning total testosterone.
When triglycerides are high, the tiny penile arteries struggle long before the larger ones do, so ED is often the body’s early warning sign, not a failure.
Is ED from High Triglycerides and High Cholesterol the Same?
Now, when we talk about fat in the blood, there is a more common term we are all familiar with: cholesterol. Many people assume cholesterol and triglycerides are the same thing, but they actually play very different roles in the body:
Triglycerides
Cholesterol
What it is
A type of fat used for energy storage
A waxy substance used to make hormones, cells, and vitamin D
Where it comes from
Extra calories, especially sugars and refined carbs
Made by the liver + found in foods like meat, eggs, dairy
What high levels mean
Often linked to insulin resistance and metabolic problems
Increases artery clogging and plaque buildup
How it damages blood vessels
Causes inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and stiffens arteries
Causes atherosclerosis—plaque that narrows and hardens arteries
Impact on erections
Poor nitric oxide release
Inflammation
Hormonal changes
Blocked arteries
Reduced blood flow
Now that we understand the difference between ED caused by cholesterol and ED caused by triglycerides, let's look at how to manage the latter in detail.
How to Manage ED from High Triglycerides?
Treating high triglycerides in men with ED is about reducing overall cardiovascular risk and protecting erectile function in the long run.
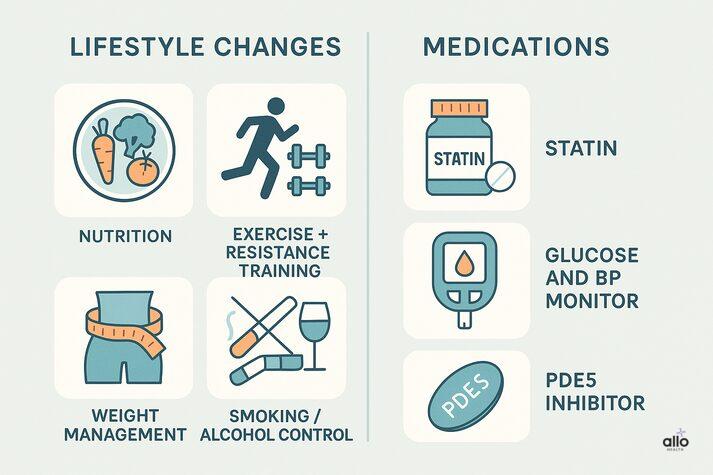
1. Lifestyle changes
Nutrition
- Reduce sugary drinks, white flour products, sweets and deep-fried snacks.
- Increase vegetables, fruits, whole grains, pulses, nuts and seeds.
- Choose healthy fats (like olive, mustard or groundnut oil) instead of repeated high-temperature frying.
Movement and Exercise
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week.
- Add 2–3 sessions of resistance training to support muscle mass and insulin sensitivity.
Weight Management
- Even a 5–10% body-weight reduction, particularly around the abdomen, can substantially improve triglyceride levels
Smoking and Alcohol
- Stopping smoking is one of the fastest ways to improve endothelial function.
- Reduce alcohol intake, especially binge drinking, which can cause big spikes in triglycerides. [7]
2. Medications
Your doctor may consider:
- Statins to reduce LDL and improve endothelial function. Some research suggests modest improvement in ED or in response to ED medication when appropriate statin therapy is used.
- Glucose-lowering and blood pressure medications, if diabetes or hypertension are part of the picture.
- ED itself is typically treated with PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil). These help with erections directly, while triglyceride- and risk-factor control address the underlying disease process. [8]
How to Prevent ED Caused by High Triglycerides?
You can reduce your risk of developing ED due to high triglyceride levels by:
1. Monitoring numbers early
Check triglycerides, cholesterol and blood glucose periodically, especially if there is a family history of heart disease or diabetes.
2. Watching your waistline
An increasing waist circumference is a simple visual cue that metabolic syndrome may be developing, even before lab reports look “very abnormal.”
3. Protecting endothelial health
Avoid smoking, manage blood pressure and prioritise sleep and stress management. All of these protect the endothelium and reduce the chance of endothelial dysfunction.
4. Acting promptly when ED appears
Don’t ignore ED or treat it only as a psychological issue. In many men, it is the first “red flag” that metabolic and vascular stress is building up.
5. Combining symptom relief and risk control
It’s perfectly reasonable to use PDE5 inhibitors for symptom relief, but ideally, they should be combined with strategies to normalise triglycerides and other cardiometabolic factors.
Conclusion
High triglycerides are far more significant than a small note on your lab report. Along with blood glucose, waist circumference and other metabolic markers, they sit at the centre of endothelial dysfunction, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, atherosclerosis and even changes in testosterone levels. For many men, ED is the earliest sign that this whole vascular–metabolic system is under stress. The good news is that this pattern is highly modifiable. With the right mix of lifestyle changes, targeted medications and ED-specific treatment when needed, it’s possible to lower triglycerides, protect blood vessel health, reduce long-term heart risk and strengthen erections. If a man has both ED and high triglycerides, the most important next step is to get a thorough check-up and a clear plan that supports his heart, hormones and sexual health together.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Is the ED caused by high triglycerides reversible?
Often, yes. If addressed early with diet, exercise, weight loss and appropriate medication, improvements in triglyceride levels can also improve erectile function. Long-standing arterial damage may be harder to reverse.
How do high triglycerides affect blood flow to the penis?
They promote inflammation, stiffen the arteries and interfere with nitric oxide release. All of these reduce the ability of penile arteries to open quickly and stay open during an erection.
Are high triglycerides and high cholesterol the same problem when it comes to ED?
No. High triglycerides mainly cause metabolic and endothelial issues, while high cholesterol mainly causes plaque buildup in arteries. Both can lead to ED but through slightly different pathways.
Can improving my triglyceride levels improve my erections?
Many men notice better erections when their triglycerides improve because overall circulation, hormone balance and metabolic health get better. This may also make ED medications work more effectively.
What triglyceride level is considered “too high” for erectile health?
Generally, triglycerides above 150 mg/dL are considered elevated. However, even moderately high levels can contribute to endothelial dysfunction and reduced penile blood flow.
Sources
- 1.
Dyslipidemia as a risk factor for erectile dysfunction
- 2.
Is Dyslipidemia A Risk Factor for Developing Erectile Dysfunction?
- 3.
High Triglycerides Predicts Arteriogenic Erectile Dysfunction and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Subjects With Sexual Dysfunction
- 4.
Erectile Dysfunction Is a Hallmark of Cardiovascular Disease: Unavoidable Matter of Fact or Opportunity to Improve Men’s Health?
- 5.
A higher TyG index is related with a higher prevalence of erectile dysfunction in males between the ages 20-70 in the United States, according to a cross-sectional research
- 6.
High Triglycerides Predicts Arteriogenic Erectile Dysfunction and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Subjects With Sexual Dysfunction
- 7.
Erectile dysfunction, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular risks: facts and controversies
- 8.
Association of high LDL concentrations with erectile dysfunction from a Mendelian randomization study


