Metoprolol and Erectile Dysfunction: Side Effects & How to Manage them
Written by Dr. Sharon Kumar

With a strong academic background in dentistry and clinical exposure, Dr. Sharon who has studied at PDM Dental College, brings a valuable blend of medical knowledge and communication skills to health content writing. She is passionate about creating clear, compassionate, and evidence-based content on topics such as general wellness, sexual health, oral care, and patient education. Her goal is to make complex medical information easy to understand, relatable, and genuinely helpful for readers seeking clarity on their health concerns. Dr. Sharon believes in the power of well-researched, empathetic content to educate and empower people to make better health decisions. Whether it’s writing about preventive care or breaking down myths in sexual wellness, her content always balances science with sensitivity.
•
September 6, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Quick Read
Metoprolol and erectile dysfunction are often linked because this beta-blocker, commonly used for high blood pressure, angina, and heart failure, can sometimes affect sexual health. Many men wonder, does metoprolol cause impotence, or can metoprolol cause erectile dysfunction? Research shows metoprolol may increase the risk of ED by reducing blood flow and not supporting nitric oxide release, which is important for erections. The sexual side effects of metoprolol vary; some men notice erection problems or lower libido, while others do not. If ED becomes a concern, talk to your doctor about alternatives or treatments to protect both heart and sexual health.
Many men taking beta-blockers like metoprolol worry about the connection between this medication and erectile dysfunction. Metoprolol and erectile dysfunction are common concerns because sexual side effects can impact quality of life. While metoprolol is effective for treating heart conditions and hypertension [1], it can sometimes lead to ED. Understanding the relationship, why these side effects happen, and how to manage or prevent them can help men maintain both their heart health and sexual well-being. This article provides a clear explanation and practical advice for anyone concerned about metoprolol and erectile dysfunction.
Does Metoprolol Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Many men prescribed metoprolol often ask, Does metoprolol cause erectile dysfunction or impotence? Metoprolol is a beta-blocker commonly used to treat hypertension, angina [2], and heart failure[4]. Like other beta-blockers, metoprolol can affect sexual function, and erectile dysfunction (ED) is reported as a possible side effect. Studies show that men taking metoprolol may experience a mild to moderate increase in the risk of ED compared to those not on the medication [3]. It’s important to note that cardiovascular disease itself is a significant cause of erectile dysfunction. The connection between metoprolol and erectile dysfunction is influenced by multiple factors, including psychological stress, underlying heart conditions, and other medications. While metoprolol may contribute to ED, it is not always the sole cause. Recognizing this helps avoid unnecessary anxiety and encourages a balanced approach to treatment.
Allo asks
If you’re taking metoprolol, have you noticed any changes in your sexual function?
Why Does Metoprolol Affect Sexual Function?
Understanding how metoprolol causes sexual side effects can clarify why some men experience ED while taking this medication. Metoprolol works on some sensors (beta-1 adrenergic receptors) present in the heart, which reduces heart rate and blood pressure.
Erectile dysfunction with metoprolol doesn’t mean your sex life is over. It just means we need to find the right balance, whether that’s adjusting your dose, switching medications, or adding supportive treatments.
But, this action can also lead to decreased blood flow, including to the penile tissues, impairing the ability to achieve or maintain an erection. Metoprolol does not promote nitric oxide (NO) release, which is a key molecule that facilitates penile blood vessel relaxation and erection. Beta-blockers like nebivolol, which stimulate NO release, are less likely to cause sexual dysfunction. Metoprolol's lack of this effect can result in decreased erectile function. Psychological factors also play a role. Fear of side effects or concerns about heart health can create anxiety, which itself may cause or worsen ED. The "Hawthorne effect," where the expectation of ED leads to its occurrence, has been observed with beta-blockers, including metoprolol.[3]
What Are the Sexual Side Effects of Metoprolol?
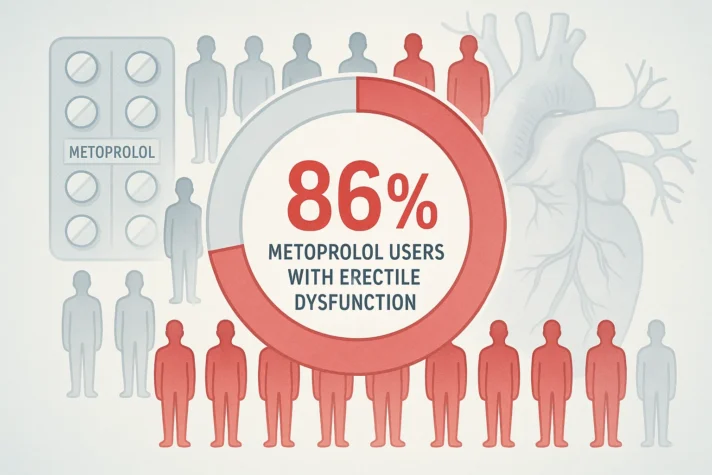
The most commonly reported sexual side effect of metoprolol is erectile dysfunction. Some men may also notice a reduction in libido or difficulties with ejaculation, although these are less common. Research shows that about 86% of men taking metoprolol experience erectile dysfunction, highlighting that this beta-blocker may increase the risk of ED.[3] The severity varies between individuals and may depend on dosage, duration of use, and overall health. If sexual side effects interfere with quality of life, it is crucial to discuss them with a healthcare professional. Do not stop or alter your medication without medical guidance, as uncontrolled blood pressure or heart conditions can have serious consequences.
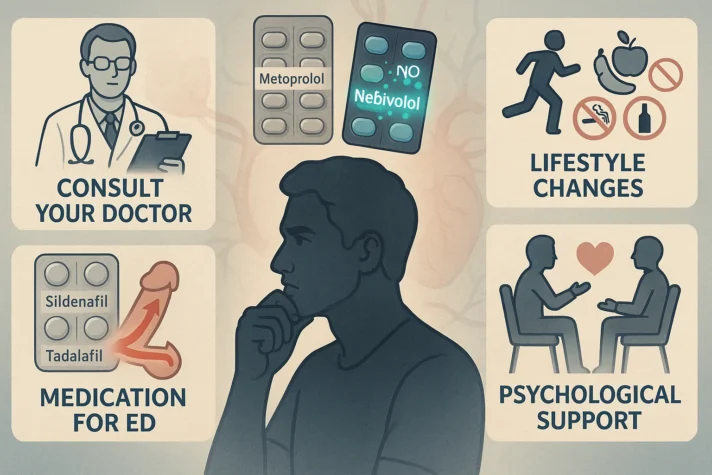
How to Manage Erectile Dysfunction Caused by Metoprolol
Managing ED related to metoprolol involves several strategies:
1. Consult Your Doctor
Always start here. Your healthcare provider can evaluate your symptoms and may adjust your treatment.
2. Switch Beta-Blockers
Some beta-blockers have fewer sexual side effects. Nebivolol, for example, has been shown to have a lower risk of ED due to its ability to increase nitric oxide release and promote vasodilation.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Exercise, a healthy diet, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol intake improve both cardiovascular and sexual health. Stress management techniques like meditation or therapy may also help.
4. Medication for ED
Drugs such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), or vardenafil (Levitra) can improve erectile function. These medications increase blood flow to the penis and may be prescribed if lifestyle changes and medication adjustments do not help.
5. Psychological Support
Counseling or sex therapy may be beneficial if anxiety or depression contributes to ED.
Are There Alternatives to Metoprolol with Fewer Sexual Side Effects?
Yes. When erectile dysfunction becomes a concern, switching to a beta-blocker with a better sexual side effect profile is an option. Research comparing beta-blockers shows:
- Nebivolol has the lowest risk of erectile dysfunction. It improves endothelial function by increasing nitric oxide release, supporting better blood flow.
- Carvedilol and atenolol have a moderate risk.
- Metoprolol and bisoprolol show slightly higher risk, with bisoprolol having the highest risk among them.
Discuss these alternatives with your healthcare provider. The goal is to control your heart condition while maintaining sexual health.
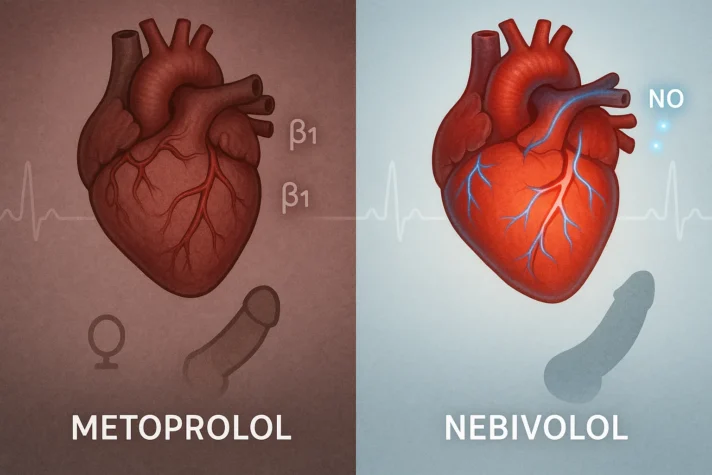
Metoprolol vs Nebivolol
Feature
Metoprolol
Nebivolol
What it is
A beta-1 blocker that slows down the heart and lowers blood pressure
A beta-1 blocker that also helps blood vessels relax by releasing nitric oxide
Main Uses
High blood pressure, chest pain (angina), irregular heartbeats, heart failure
High blood pressure, sometimes used in heart failure
ED Incidence (Study Data)
About 85.96% of users reported ED
About 83.87% of users reported ED
ED Risk Trend
Slightly higher chance of ED
Slightly lower chance of ED
Why the Difference?
Only blocks beta-1 receptors, which may reduce sexual performance in some men
Adds nitric oxide effect, which improves blood flow and may protect against ED
Other Side Effects
Tiredness, dizziness, cold hands/feet, sexual dysfunction
Headache, fatigue, but generally fewer complaints about sexual side effects


