Back Pain (Lower Back) and Erectile Dysfunction: Link Between and Effects
Written by Dr. Deepali Anand

Dr. Deepali is a medical writer and healthcare professional with a background in clinical surgery and patient care. Having transitioned from active clinical practice to medical communications, she specializes in bridging the gap between complex clinical data and patient education. Dr. Deepali is dedicated to creating evidence-based content that is grounded in scientific rigor and empathy, ensuring that sensitive topics like sexual wellness and mental health are accessible and empowering for every reader.
•
September 27, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.

Quick Read
Yes, lower back pain and erectile dysfunction are closely connected, with research showing that around 77% of men with lower back issues experience some degree of ED. This happens because nerves in the lower spine (especially S2-S4 region) control sexual function, and when compressed by conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis, they can disrupt the signals needed for erections. The connection also involves reduced blood flow, hormonal imbalances from chronic pain stress, and psychological factors like anxiety and depression. The good news is that both conditions can be effectively treated together through a combination of medical interventions (from physical therapy to specialized ED treatments), lifestyle changes (exercise, stress management), and open communication with healthcare providers and partners. Early treatment is key- don't ignore symptoms like pelvic numbness or sudden erection changes, as addressing spinal health often improves sexual function too.
Back pain and erectile dysfunction are two problems that might not seem connected at first, but for many men, they are. Lower back pain can affect the nerves, blood flow, and even hormones that play a role in sexual function. It can also take a toll on your confidence and relationships.
In this article, we’ll explore the link between lower back pain and erectile dysfunction, explain why it happens, highlight the warning signs you shouldn’t ignore, and share medical as well as lifestyle treatments.
Can Back Pain Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Yes, back pain and erectile dysfunction are more closely linked than many people realize. The connection can be direct, such as when nerves in the lower spine are compressed, or indirect, through the effects of chronic pain on the body and mind.
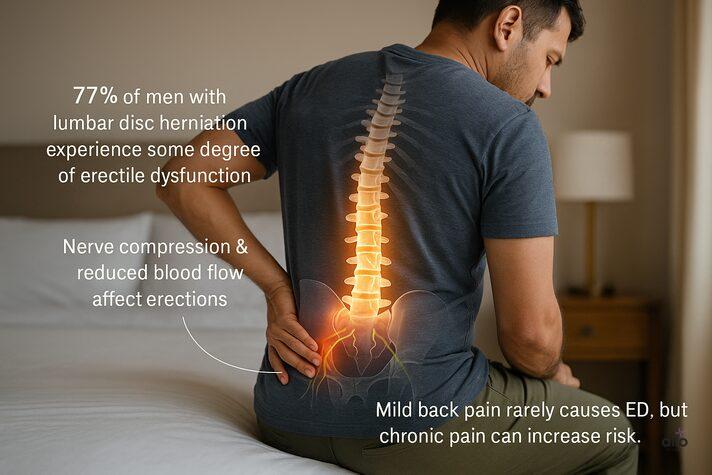
Research[1] shows that around 77% of patients with lower back issues, like lumbar disc herniation, experience some degree of erectile dysfunction. Other studies also highlight a strong relationship between spinal health, sexual function, and overall sexual health.
That said, it’s important to remember: not every back pain automatically leads to erectile problems. Mild back pain rarely affects erections. However, long-term or chronic lower back pain may signal underlying nerve compression or injury, which can contribute to erectile dysfunction over time.
According to Allo Health, nearly 1 in 2 men experience erectile dysfunction, which is based on our internal clinical data of more than 2.5 lakh patients who have visited our clinics.
Let’s take a closer look at how lower back pain and erectile dysfunction are connected.
Allo asks
Have you ever noticed a change in your sexual performance while dealing with back pain?
Back Pain and Erectile Dysfunction: The Connection
1. Nerve Compression and Damage
This is the most direct link between back pain and erectile dysfunction. The nerves in the lower back, especially the S2–S4 region, play a vital role in sexual arousal and erections.[2]
When these nerves are compressed or inflamed due to conditions like a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease, the signals from the brain to the penis can get disrupted. This makes it harder to achieve or maintain an erection.
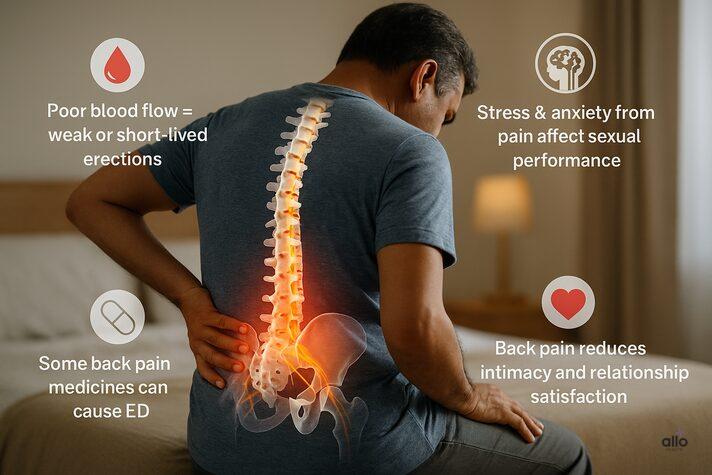
2. Blood Flow
Healthy blood flow is essential for an erection. But lower back pain, inflammation, muscle spasms, or stiffness can affect blood circulation. Poor circulation often leads to weaker or short-lived erections.
3. Hormonal Imbalances
Chronic back pain raises cortisol, the body’s main stress hormone. High cortisol levels over time can lower testosterone production. Since testosterone is key to sex drive, energy, and overall well-being, reduced levels may increase the risk of erectile dysfunction.
4. Psychological Factors
The constant discomfort of chronic back pain can affect mental health. Anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem often follow, which can reduce sexual desire and performance.
Research[3] shows that men with lower back pain and erectile dysfunction may experience:
- Depression is linked with greater sexual dysfunction.
- Fear of pain during movement leads to less sexual activity.
- Worry about pain affecting erections.
- Lower life satisfaction impacts intimacy and relationships.
5. Physical Discomfort
Back pain can make certain sexual positions uncomfortable or even impossible. This physical limitation reduces sexual activity and can cause frustration or dissatisfaction for both partners.
6. Medication Side Effects
Some medications prescribed for back pain, such as gabapentin or strong painkillers, may also affect sexual performance. These side effects can further contribute to erectile dysfunction.
Back pain doesn’t always cause erectile dysfunction, but when it’s chronic or involves nerve pressure, the chances increase. That’s why addressing back problems early is just as important for your overall health as it is for your sexual well-being.
Specific Back Pain Conditions Affecting Erectile Function
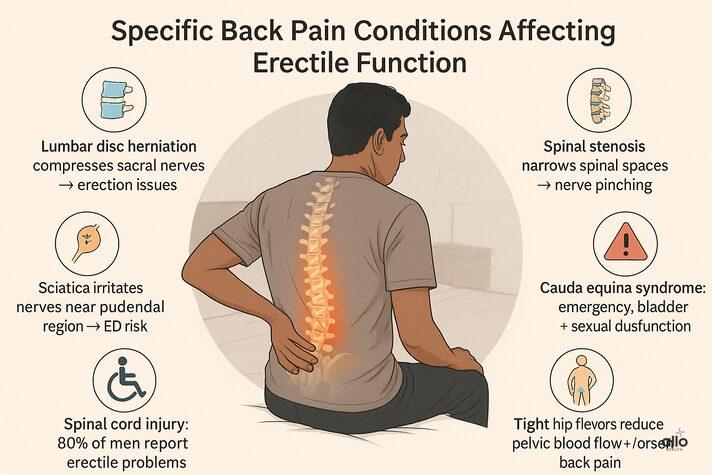
Lumbar Disc Herniation
Herniated discs, especially at the L4–L5 and L5–S1 levels, are strongly linked to back pain and erectile dysfunction.
When a disc slips or protrudes, it can press on nearby nerves and blood vessels, disrupting both blood flow and nerve signals needed for erections.
Studies[4] show that men with centrally herniated discs have a higher risk of erectile dysfunction compared to those with laterally herniated discs.
Spinal Cord Injury
Spinal cord injuries have a major impact on sexual health, and the exact effects depend on where the injury occurs[5]:
- Reflexogenic erections: These are erections triggered by touch or direct physical stimulation. They rely on the sacral nerves (S2–S4), located in the lower spine.
- Psychogenic erections: These are erections triggered by mental or emotional arousal (like fantasies or attraction). They depend on the thoracolumbar region (T11–L2), which is higher up in the spine.
Research shows that about 80% of men with spinal injuries have erection problems. In addition, around 84% report having sex less often because of the combined challenges of lower back pain and erectile dysfunction.
Sciatica
Sciatica-related ED happens when the sciatic nerve is irritated or compressed. Since this nerve runs close to the pudendal nerves (which control erections), the condition can directly contribute to sexual dysfunction.[6]
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of spaces within the spine. This narrowing can pinch the spinal cord and surrounding nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and sometimes sexual problems, including erectile dysfunction.
Cauda Equina Syndrome
This is a rare but serious medical emergency. Cauda equina syndrome occurs when the bundle of nerves at the base of the spine is compressed.[7] It can cause:
- Severe lower back pain
- Numbness around the buttocks or groin
- Loss of bladder and bowel control
- Sexual dysfunction
Hip Flexor Dysfunction
Tight hip flexor muscles are an often-overlooked cause of both lower back pain and erectile dysfunction.[8]These muscles run from the lower spine through the groin into the hip. Prolonged sitting or poor posture can make them tight and cause muscle strain, leading to:
- Compression in the groin area
- Reduced blood flow to pelvic structures
- Postural changes that worsen back pain
- Disrupted nerve signals linked to erections

Overlapping Signs of Lower Back Pain and Erectile Dysfunction You Shouldn’t Ignore
Sometimes the symptoms of back pain and erectile dysfunction overlap. If you notice these warning signs, they may point to a deeper connection between your back and sexual health:
- Numbness or tingling in the pelvic or thigh region.
- Weakness in the lower legs or pelvic muscles.
- Pain in the lumbar or pelvic area during sexual activity.
- Bladder control issues or sudden incontinence.
- Muscle spasms in the lower back and pelvic area.
- Loss of reflexes or reduced sensation during sex.
- Reduced sensation in the genital region or penis.
- Sudden loss of erection, especially after back pain worsens.
In such cases, it’s important to consult a doctor to rule out serious conditions.
Treatment Options for Back Pain and Erectile Dysfunction
Successful treatment often requires a dual approach: treating the spinal condition while also addressing the sexual dysfunction directly.
Treatment For Back Pain Management
Studies[9] show that 68-99% of men can regain significant improvement in both spinal health and sexual function with coordinated care
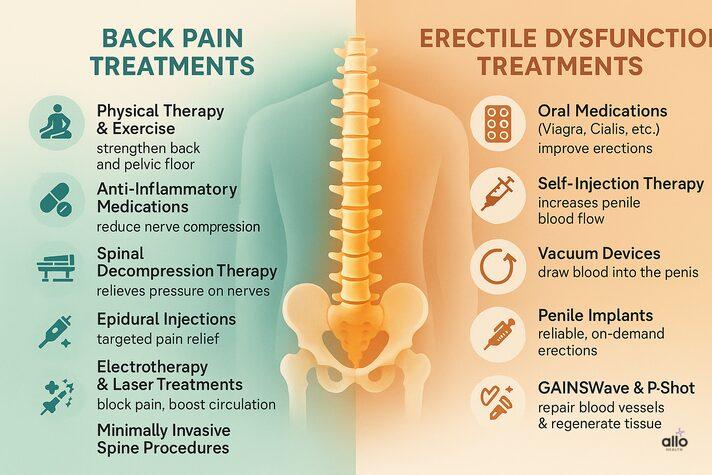
Conservative Options (non-surgical):
- Physical therapy strengthens the core, stretches tight hip flexors, and improves posture.
- Anti-inflammatory medications reduce swelling and nerve compression.
- Spinal decompression therapy relieves pressure on spinal nerves.
- Epidural injections targeted pain relief for severe back pain.
Advanced Options:
- Matrix Electroanalgesia System – computer-controlled electrical stimulation that blocks pain signals and boosts blood circulation, even to the genitals.[10]
- MLS Robotic Laser Therapy – stimulates natural healing and reduces inflammation.[11]
- Minimally invasive procedures – like percutaneous laser disc decompression to reduce nerve pressure.
Medical Treatments for Erectile Dysfunction
For men with spinal cord injuries, lower back pain, and erectile dysfunction, specific ED therapies can help:
- Oral medications – PDE5 inhibitors like sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, and avanafil.
- Penile-injection therapy – self-injection medicines are injected directly into the erectile tissue to improve blood flow.
- Vacuum erection devices – external penis pumps that draw blood into the penis.
- Hormone therapy – testosterone replacement for men with low hormone levels.
- Penile implants – a surgical penile prosthesis that allows reliable, on-demand erections.
Specialized and Advanced ED Therapies
- GAINSWave Therapy – uses acoustic waves to repair blood vessels and improve penile blood flow.
- P-Shot (Priapus Shot) – platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection to regenerate tissue.[12]
- Bioidentical hormone pellets – restore hormonal balance to support sexual function.
Emerging Treatments
Sacral Neuromodulation (SNS):
- Stimulates the sacral nerve pathways (S2–S4) that control erections.
- Helps restore balance between excitatory and inhibitory signals in the nervous system.
- Studies show men improved from moderate to mild erectile dysfunction after treatment.[13]

4 Practical Tips for Men Living With Back Pain and ED
1. Safe Sex Positions for Men with Back Pain
- Use cushions or sex pillows for extra support; they can make almost any position more comfortable.
- Experiment with new roles, positions, and props until you and your partner discover what feels best.
2. Exercises for Back Pain and Erectile Dysfunction
- Try yoga poses for ED and back pain like Cobra, Bridge, Pelvic Tilt, and Butterfly. They increase flexibility, improve pelvic circulation, and relax tight muscles.
- Practice deep breathing exercises to slow your heart rate, calm your mind, and reduce pain sensations.
- Focus on consciously relaxing your body to ease tension and reduce performance anxiety.
3. Lifestyle Changes
- Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and manage stress.
- Avoid movements or activities that worsen your back pain.
4. Partner communication tips
- Set aside judgment-free times to talk, ideally outside the bedroom.
- Share specific examples of what helps you (e.g., “Using a pillow supports my back,” or “It helps when you check in during sex.”).
- Work together, try new positions, switch roles, or take turns leading.
- Build closeness in other ways too - words, hugs, and shared activities can be just as intimate as sex.
Bottom Line
There is a clear connection between back pain and erectile dysfunction. Lower back pain and erectile dysfunction are closely linked through nerves, blood flow, hormones, and psychological factors, and these should never be ignored.
If you notice sexual changes while dealing with back pain, it’s important to see a doctor for a proper evaluation of both. The good news is that with the right diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan, most men can manage their back pain and still enjoy a healthy, satisfying sex life.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Can back pain really cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes. Chronic or severe back pain, especially in the lower back, can press on nerves or affect blood flow that’s essential for erections. Not every back pain leads to ED, but persistent pain may increase the risk.
Will treating my back pain improve my erectile dysfunction?
In many cases, yes. Studies show that when men receive proper treatment for spinal issue like physical therapy, medication, or minimally invasive procedure, their sexual function often improves too.
What are the warning signs that back pain and ED are connected?
Watch for numbness or tingling in the pelvic area, weakness in the legs, pain during sex, bladder control issues, or sudden loss of erections. These signs suggest the nerves in your lower back may be involved.
What treatments are available for erectile dysfunction linked to back pain?
Treatment usually involves two parts: managing the spinal problem (physical therapy, medications, or surgery if needed) and addressing ED directly (oral medications, vacuum devices, hormone therapy, or penile implants).
When should I see a doctor about back pain and erectile dysfunction?
If your erections suddenly weaken after a back injury, or if you notice numbness, bladder issues, or severe ongoing pain, it’s important to see a doctor right away. These could be signs of a nerve-related problem that needs prompt care.
Sources
- 1.
Sexual disability in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain—a multicenter retrospective analysis
- 2.
The Impact of Sacral Neuromodulation on Sexual Dysfunction
- 3.
Sexual disability in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain—a multicenter retrospective analysis
- 4.
Erectile Dysfunction in Patients with Lumbar Herniated Disc
- 5.
Effect of lumbar spinal stenosis and surgical decompression on erectile function
- 6.
Sciatica
- 7.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8055459/
- 8.
Tight Hip Flexors Can Cause Lower Back Pain, Knee Pain and Foot Pain
- 9.
The implications of surgery on sexual dysfunction in patients with lumbar disc herniation with cauda equina syndrome: a systematic review
- 10.
Use of electroanalgesia and laser therapies as alternatives to opioids for acute and chronic pain management
- 11.
The Remarkable Healing Power of MLS Laser Therapy
- 12.
The P-Shot - Using Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) to Treat Erectile Dysfunction and enhance erectile quality
- 13.
The Impact of Sacral Neuromodulation on Sexual Dysfunction


