Can a Herniated Disc Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Written by Dr. Deepali Anand

Dr. Deepali is a medical writer and healthcare professional with a background in clinical surgery and patient care. Having transitioned from active clinical practice to medical communications, she specializes in bridging the gap between complex clinical data and patient education. Dr. Deepali is dedicated to creating evidence-based content that is grounded in scientific rigor and empathy, ensuring that sensitive topics like sexual wellness and mental health are accessible and empowering for every reader.
•
September 6, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Quick Read
Yes, herniated discs, especially at the L4-L5 and L5-S1 levels, can cause erectile dysfunction by compressing the nerves that control sexual function. The most effective treatment takes a dual approach: addressing the disc problem itself through physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or procedures such as epidural injections and microdiscectomy, while also treating ED directly with options like PDE5 inhibitors (Viagra, Cialis), vacuum devices, or penile injections when needed. With prompt, coordinated care between spine specialists and urologists, studies demonstrate that 68–99% of men regain significant improvement in both spinal health and sexual function, often returning to their previous quality of life.
Herniated disc erectile dysfunction treatment is a topic that raises an important but often overlooked question: what happens when back problems start affecting your sex life?
If you’re dealing with a herniated disc, you might already know it can cause more than just back pain. For many men, nerve compression, reduced blood flow, and constant discomfort can lead to erectile dysfunction.
In this article, we’ll explore how a herniated disc can impact erections, what tests doctors use to confirm the link, and most importantly, the range of treatment options, from spine care to ED therapies that can help you recover both your mobility and your sexual health.
Can a Herniated Disc Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Yes, a herniated disc can cause erectile dysfunction, especially when it occurs in the lower lumbar spine**(lumbar disk herniation)** at the L4-L5 and L5-S1 levels (sometimes even referred to as L4-L5 erectile dysfunction).
Research[1] suggests that up to 77% of patients with lumbar disc herniation experience some form of erectile dysfunction. This happens because a herniated disc can affect erections both directly and indirectly. The bulging or protruding disc may press on nearby nerves, triggering symptoms that vary depending on its exact location. The risk becomes even greater in conditions like cauda equina syndrome, where the bundle of nerves at the base of the spine (the cauda equina) is compressed. This can affect bladder, bowel, and sexual function. Let’s break down this connection in more detail.
Allo asks
If you’ve experienced both back pain and erectile dysfunction, what worries you the most?
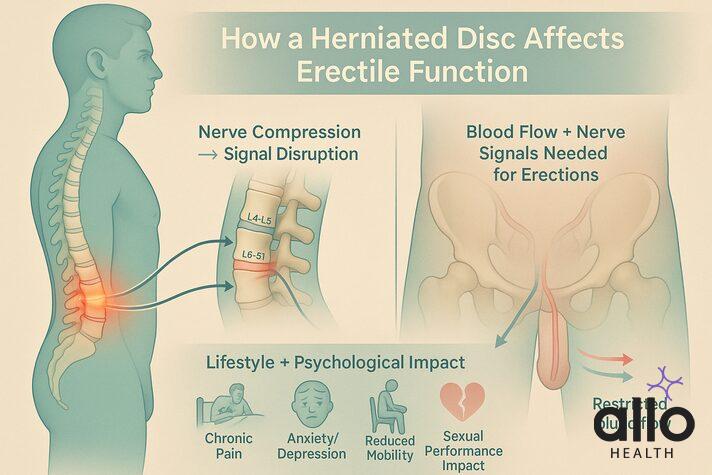
The Link Between a Herniated Disc and Erectile Dysfunction
Nerve Compression and Erectile Function
- A herniated disc can come into contact with nearby spinal nerves, leading to irritation or compression.[2]
- Spinal nerves in the lumbar and sacral regions (S2–S4, L4–L5, and L5–S1) are particularly important, as they carry the signals that control erections.
- Compression of these nerves disrupts the “brain-to-penis” communication needed for an erection.
- The pudendal nerves, which control sensation and function in the pelvic region, can also be directly affected.
- In severe cases, compression of the cauda equina nerve bundle, which is responsible for bladder, bowel, and sexual function, may lead to significant erectile problems.
Blood Flow and Circulation
- Inflammation and muscle spasms triggered by a herniated disc can limit blood circulation to the pelvic area.
- Since erections depend on healthy blood flow, this restriction can directly affect erectile performance.
Pain, Stress, and Psychological Impact
- Chronic pain from disc herniation can create psychological barriers to sexual activity.[3]
- Pain and limited mobility may make certain positions uncomfortable, reducing desire and confidence.
- The fear of worsening back pain during sex, combined with stress, anxiety, or depression, often worsens sexual desire and erectile dysfunction.
Reduced Mobility and Lifestyle Changes
- A herniated disc can lead to reduced mobility, forcing men into a more sedentary lifestyle.
- This inactivity can lower blood flow, reduce cardiovascular fitness, and negatively affect erectile function.
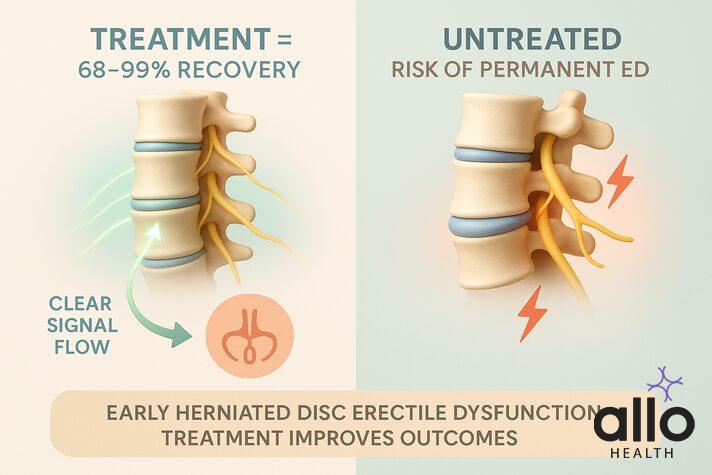
Can a Herniated Disc Really Cause Permanent ED?
In many cases, erectile dysfunction caused by a herniated disc improves once the underlying nerve compression is treated.
Studies[4] show that 68.4% to 99% of patients experience improvements in sexual and erectile function after appropriate treatment.
Another major study[5] found that 77% of men with erectile dysfunction due to disc herniation improved within 3 months after surgery.
But, untreated or long-standing nerve damage may cause persistent erectile dysfunction. That’s why timely diagnosis and herniated disc erectile dysfunction treatment is so important, the earlier the intervention, the better the outcome.
When a herniated disc presses on the nerves in your lower spine, it can interrupt the signals needed for an erection. The good news is, once that pressure is relieved, whether through therapy, injections, or surgery many men see their sexual function impro__ve."__
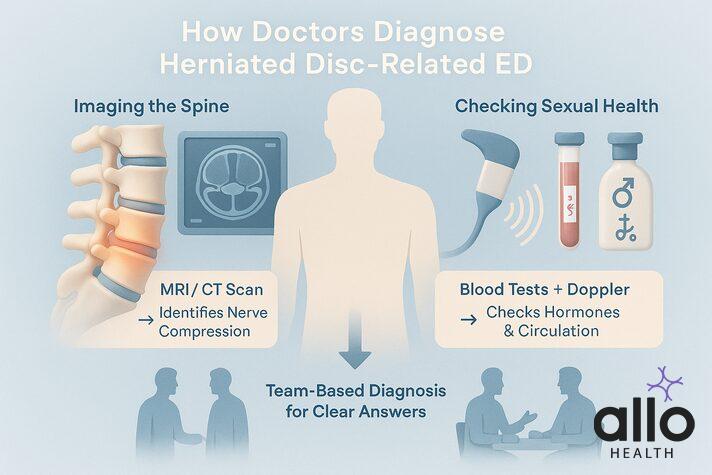
Diagnosing the Connection
Figuring out if your erectile dysfunction is linked to a herniated disc isn’t always straightforward. That’s why doctors take a thorough, team-based approach.
Imaging the Spine
Your spine specialist may order an MRI scan or CT scan to see exactly where the disc is pressing and whether it’s affecting the nerves that control erections, especially those in the lower spine.
Checking Sexual Health
A urologist will look at the other side of the equation. This usually means blood tests for hormones, diabetes, and heart health, plus a penile Doppler ultrasound to check blood flow.
Putting It All Together
When these experts compare notes, the picture becomes clearer. The spine specialist understands the back, the urologist focuses on sexual health, and sometimes a psychologist is added to address the stress that comes with chronic pain.
Together, they can figure out whether your herniated disc is the main culprit or not.
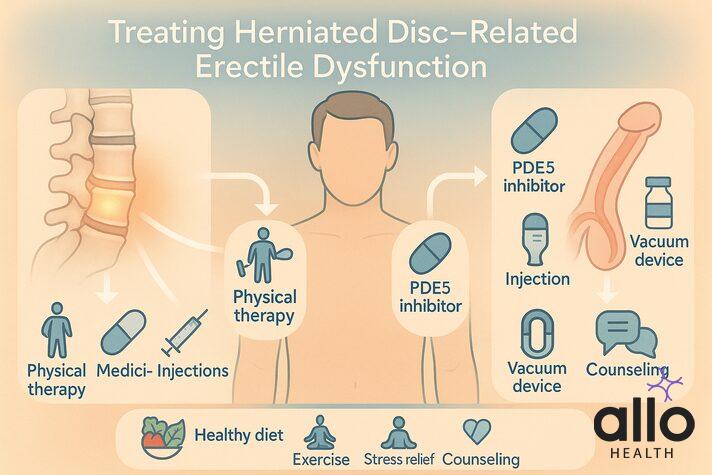
Treatment Options: Managing Herniated Disc-Related Erectile Dysfunction
If your herniated disc is affecting your sexual health, the good news is that there are plenty of treatment options. The best approach is to treat both the underlying spine issue and the erectile dysfunction itself, often at the same time.
Treating the Herniated Disc (Root Cause)
Conservative Treatments
- Most men start with non-surgical care, and often that’s all that’s needed. Physical therapy is the foundation; it strengthens your core, improves posture, and eases pressure on the nerves.
- Over-the-counter anti-inflammatories like ibuprofen can calm swelling, while medications such as gabapentin target nerve pain relief more directly.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
- If pain and nerve pressure don’t improve, epidural steroid injections can bring targeted relief.
- For tougher cases, procedures like Percutaneous Laser Disc Decompression (PLDD) can shrink the bulging disc with minimal downtime, often as an outpatient procedure.
Surgical Interventions
- When nothing else works, microdiscectomy is usually the go-to surgery. It’s a minimally invasive surgical treatment that removes just the portion of the disc pressing on the nerve.
- Many men notice their sexual function improving within weeks, with full recovery in about 6–12 weeks.
Treating Erectile Dysfunction Directly
First-Line Medications
- PDE5 inhibitors such as Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra remain highly effective, even for spine-related ED.
Advanced Treatment Options
- If pills don’t work, there are reliable alternatives. Vacuum erection devices create an erection without medication. Penile injections like alprostadil are very effective and act quickly.
- For more severe or long-term ED, penile implants provide a permanent solution, with high satisfaction rates for both patients and partners.
Specialized Therapies
- Emerging treatments such as low-intensity shock wave therapy for ED are being studied for nerve-related ED. These therapies may improve blood flow and even encourage nerve repair over time.
Combined Care Approach
Treating the disc first (if surgery is needed) and then adjusting ED treatments as your recovery progresses can be ver beneficial
Lifestyle Medicine
- Lifestyle changes play a big role. Safe exercise routines can strengthen your back and improve erections.
- A heart-healthy diet supports blood flow, which benefits both your spine and your sexual function.
- Stress management through meditation or counseling helps break the cycle of pain and performance anxiety.
Psychological Support
- Chronic back pain plus sexual problems can take a toll on confidence and relationships.
- Counseling or sex therapy can make a huge difference, addressing performance anxiety, depression, or relationship stress alongside medical treatments.
- Most men with herniated disc–related ED improve significantly once the right treatment plan is in place. With patience and a tailored approach, you can get both your back and your sexual health back on track.
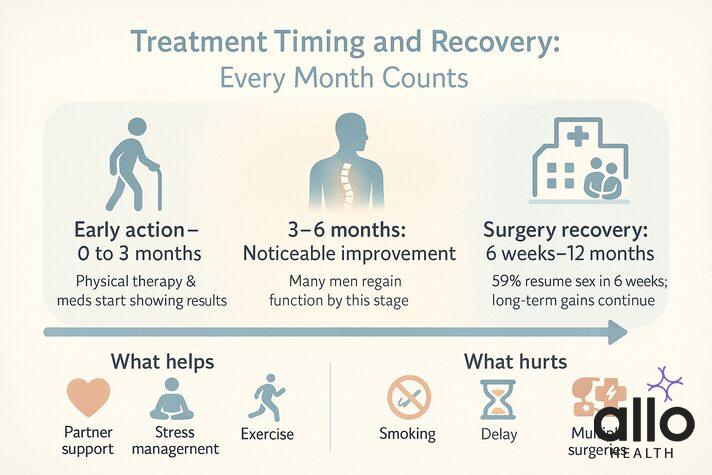
Treatment Timing and Recovery
With spine-related ED, early action makes a big difference. Research shows that waiting more than 9-12 months can lower the chances of full recovery, so don’t delay seeking help.
Recovery Timeline
- Surgery: About 59% of men resume sexual activity within 6 weeks, with continued improvements over time.[6]
- Conservative care: Physical therapy and medications often show results within 3–6 months, with full recovery possible in that window.
- Age Factor: Younger men with mild ED usually recover best.
- Severity of ED: Patients with mild ED and L4-L5 disc herniation usually show best recovery rates.Those with more serious ED may also need extra help, such as penile rehab or advanced urology treatments, alongside spinal care.
What Helps
Better outcomes are linked to tackling the problem early, having a supportive partner, staying active, and following treatment consistently.
What Hurts
Smoking, long-standing pain (over a year), and prior spinal surgeries can make recovery harder,but many men still improve with the right care.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help right away if erectile dysfunction suddenly appears alongside back pain, numbness, or bladder and bowel problems. These can signal serious nerve or spinal cord issues, and delaying care may cause permanent damage.
Red flags to watch out for are:
- Sudden ED with back pain. This may point to severe nerve compression or spinal cord injury.
- Numbness in the groin, genitals, or inner thighs can hint at possible cauda equina syndrome, a surgical emergency.
- Bladder or bowel problems, leaking urine, or losing bowel control are strong warnings of nerve damage.
The Bottom Line
Herniated disc disease can play a real role in erectile dysfunction, but the outlook is often positive. With early recognition, timely treatment, and coordinated care between spine and sexual health specialists, most men see meaningful improvements in both back health and sexual function. Understanding the connection is the first step toward getting the right help and reclaiming quality of life.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Can L4-L5 nerve damage cause ED?
Yes. The L4-L5 and L5-S1 levels in the lower spine are closely linked to the nerves that control erections. If a herniated disc at these levels compresses or irritates those nerves, it can interfere with the signals between your brain and penis, leading to erectile dysfunction. The good news is that with proper treatment, many men regain normal function.
How to quickly heal a herniated disc?
There’s no instant fix, but starting the right treatment early speeds recovery. Most men do well with conservative care—physical therapy, gentle exercises, anti-inflammatory medications, and rest. For persistent cases, injections or minimally invasive procedures may help. Surgery is only needed if symptoms are severe or not improving,
What will the ER do for a herniated disc?
If you go to the emergency room with sudden severe back pain, leg weakness, loss of bladder/bowel control, or erectile dysfunction, doctors will act quickly. They may order an urgent MRI or CT scan to check for nerve compression. If a serious condition like cauda equina syndrome is found, emergency surgery may be recommended to prevent permanent damage.
Is heat bad for a herniated disc?
Not necessarily. Heat therapy can actually relax tight muscles and ease pain in many cases. However, if there’s swelling or inflammation, alternating between heat and cold may work better. It’s best to check with your doctor or physical therapist for the safest approach for your specific condition.
Does erectile dysfunction from a herniated disc go away on its own?
In many cases, yes,once the nerve pressure is treated, erectile function improves. Some men notice recovery within weeks, while others may take several months. If ED persists, treatments like PDE5 inhibitors (Viagra, Cialis), vacuum devices, or other therapies can help. The key is not to ignore symptoms and to seek medical care early.
Sources
- 1.
Impact of Acute Lumbar Disk Herniation on Sexual Function in Male Patients
- 2.
Physiology of Penile Erection and Pathophysiology of Erectile Dysfunction
- 3.
Impact of Acute Lumbar Disk Herniation on Sexual Function in Male Patients
- 4.
An Unappreciated Correlation : Surgical Treatment of Lumbosacral Disc Disease and Erectile Dysfunction
- 5.
Lumbar disk herniation: what are reliable criterions indicative for surgery?
- 6.
Impact of Acute Lumbar Disk Herniation on Sexual Function in Male Patients


