Hormonal Imbalance and Erectile Dysfunction: Understanding the Link
Written by Dr. Pranitha Bangera

Dr. Pranitha Bangera is a gold-medalist healthcare professional with an elite foundation in clinical training and patient care. A researcher at heart, she specializes in creating high-impact, research-driven medical content that empowers readers through accessible patient education. Dr. Bangera focuses on the intersection of digital health and clinical communication, specifically within the fields of sexual health and mental well-being. Her work is dedicated to making complex medical innovations understandable and trustworthy for a global audience.
•
November 10, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Quick Read
Hormonal imbalance is a common but often overlooked cause of erectile dysfunction. Key hormones like testosterone, prolactin, estradiol, and thyroid hormones directly affect sexual desire, blood flow, and erection quality. When these hormone levels are off balance, men may experience low libido, fatigue, mood changes, or weaker erections. The good news is that with simple blood tests, medical evaluation, and lifestyle changes, most hormone-related ED cases are highly treatable and reversible.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) isn’t always about blood flow or performance anxiety. Sometimes, the real cause starts deeper, at the hormonal level. Hormonal imbalance affects millions of men worldwide, quietly influencing everything from mood to energy to sexual function. Hormones play a key role in maintaining healthy erections by controlling sexual desire, nerve sensitivity, and blood vessel relaxation. When these hormone levels become imbalanced, the body’s natural rhythm of sexual function can be disrupted. In this article, we’ll explore how hormonal imbalance can lead to erectile dysfunction, which hormones are most involved, what symptoms to watch for, and what you can do to restore balance and improve your sexual health.
Allo asks
Which hormone do you think affects sexual function the most?
Can Hormonal Imbalance Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
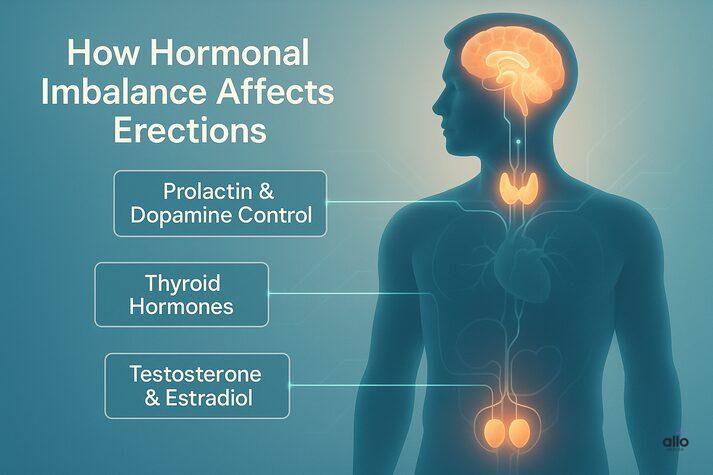
Yes, hormonal imbalance can cause erectile dysfunction. Around 30% of men with ED are found to have underlying hormonal or metabolic issues.[1] These hormones act as the body’s chemical messengers, and when they’re off, erections may not occur as easily or as firmly as before. Let’s look at the main sex hormones involved in erectile function:
1. Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone responsible for libido, energy, and erection quality. Low testosterone levels reduce nitric oxide production in penile tissue, a key step for proper blood flow and erection. [2] When testosterone levels drop below 300 ng/dL, men often experience lower sexual desire, fewer spontaneous erections, fatigue, and mood changes.
2. Estradiol
Men also produce estradiol, a form of estrogen created from testosterone. Too much estradiol or an unfavorable estradiol-to-testosterone ratio can disrupt erectile function by reducing penile rigidity and nitric oxide activity. [3] This imbalance is especially common as men age and testosterone declines naturally.
3. Prolactin
When prolactin levels rise, they suppress dopamine, the brain chemical that drives sexual desire and arousal. [4] High prolactin can disturb the brain’s hormone control center (the pituitary gland), which then makes less of the hormones (like luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone) that are needed to produce testosterone.[5]
4. Thyroid Hormones
Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can affect erection quality. Low thyroid hormones reduce metabolism and testosterone availability, while high thyroid levels may trigger anxiety, which interferes with normal erections. [6] Together, these hormones form a delicate network managed by the endocrine system. When one hormone shifts, others often follow, impacting sex drive, mood, and physical arousal.
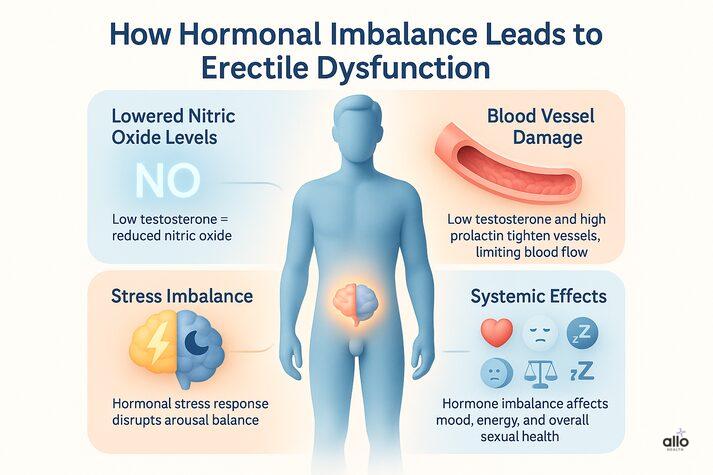
How Does Hormonal Imbalance Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
1. Lowered Nitric Oxide Levels:
Testosterone regulates nitric oxide synthase (NOS), an enzyme that creates nitric oxide. Low testosterone means less nitric oxide and weaker erections. [2]
2. Impact On Blood Vessels:
Low testosterone can harm the inner walls of the penis’s blood vessels, which reduces blood flow and flexibility. Too much prolactin or thyroid hormone can also make the blood vessels tighter, making it harder to get or keep an erection.
3. Impaired Stress Regulation:
Getting aroused needs a balance between the body’s “alert” and “relaxed” systems. Testosterone helps keep things calm and relaxed for arousal, but high prolactin or thyroid problems can cause more stress and anxiety, making it harder to get an erection. [7]
4. Systemic Effects:
Hormonal imbalances can also contribute to fatigue, low mood, irritability, and reduced confidence, all of which indirectly affect sexual performance. Moreover, conditions like heart disease, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, often tied to hormonal shifts, can cause ED.
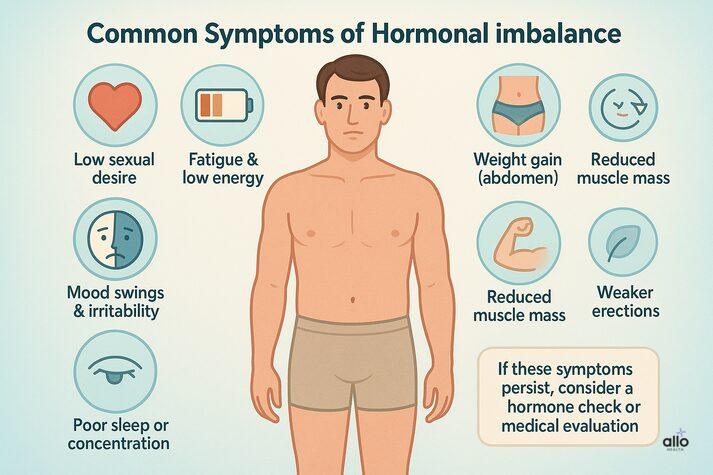
What Are the Symptoms of Hormonal Imbalance?
Hormonal changes may develop slowly, making them easy to overlook. Common symptoms include:
- Low sexual desire or reduced arousal
- Fewer or weaker erections (including morning erections)
- Fatigue and low energy
- Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen
- Mood swings, depression, or irritability
- Decreased muscle mass
- Thinning hair or dry skin
- Poor sleep or low concentration
If you experience these signs along with erectile difficulties, it’s worth requesting blood tests to check hormone levels. A thorough medical history and physical examination help identify whether the cause lies in the hormones, the blood vessels, or the nervous system.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical advice if:
- You experience persistent ED lasting more than three months
- Your sexual desire has noticeably decreased
- You notice other symptoms like unexplained fatigue or weight changes
- You have existing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or high blood pressure
How to Manage Hormonal Imbalance That Causes ED
The treatment depends on identifying the specific hormonal cause. The aim is to restore balance, improve sexual function, and enhance overall health.
1. Testosterone Therapy
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can restore libido, mood, and erection quality. However, TRT should be prescribed only after proper testing, as it doesn’t help men with normal hormone levels.
2. Dopamine Agonists
If the patient has high prolactin levels, medications like cabergoline or bromocriptine help normalize prolactin and improve erectile function.
3. Treating Thyroid Disorders
Balancing thyroid hormones with appropriate medication (thyroxine for hypothyroidism or anti-thyroid drugs for hyperthyroidism) usually resolves associated erectile or libido issues.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Many hormonal fluctuations are linked to daily habits. Try:
- Regular exercise to improve blood pressure, circulation, and testosterone
- A nutritious diet rich in zinc, vitamin D, and healthy fats
- Adequate sleep to optimize hormone secretion
- Limiting alcohol, smoking, and stress
- Maintaining a healthy weight and managing high cholesterol
5. Combination Treatments
In men unresponsive to PDE-5 inhibitors, combining them with testosterone therapy often improves outcomes. Devices like vacuum erection pumps or penile implants may also help in complex cases.

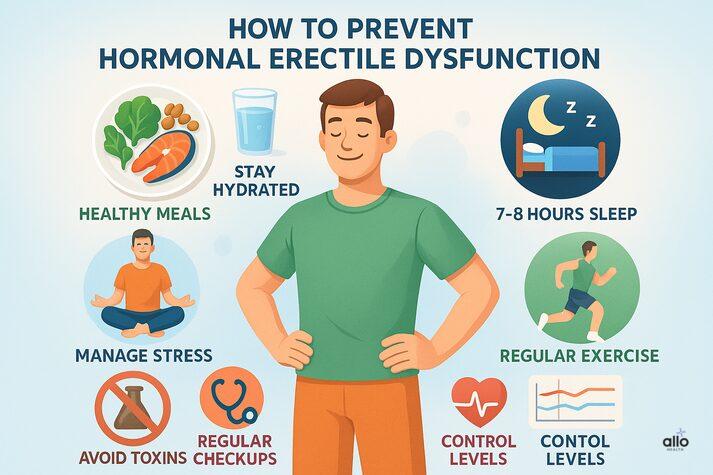
How to Prevent Hormonal Erectile Dysfunction
While some hormonal changes are natural with aging, many can be minimized by lifestyle choices and regular health checkups:
- Keep a balanced diet and stay hydrated
- Get 7–8 hours of sleep daily
- Manage stress through mindfulness, yoga, or breathing exercises
- Avoid environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (like BPA)
- Exercise regularly to support blood circulation and sex hormone production
- Control blood pressure, sugar, and cholesterol levels
Conclusion
Hormonal imbalance and erectile dysfunction are closely intertwined, yet often underdiagnosed. Low testosterone, high prolactin, or thyroid issues can each quietly affect a man’s sexual function long before other symptoms appear. Hormonal ED is highly treatable once the cause is identified. Through proper blood tests, medical evaluation, and a few lifestyle modifications, most men can regain healthy erectile function and overall vitality.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Which hormones affect erections the most?
The key hormones include testosterone, estradiol (a form of estrogen), prolactin, and thyroid hormones. These work together to control libido, mood, nerve sensitivity, and blood flow to the penis.
How do I know if my erectile dysfunction is hormone-related?
If your ED is accompanied by low sex drive, fatigue, mood swings, weight gain, or hair loss, it could be hormone-related. A simple blood test can confirm if your hormone levels are out of balance.
Can low testosterone alone cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes, but not always. Mildly low testosterone may not cause ED by itself, but when levels drop significantly, it can reduce sexual desire, energy, and the ability to get or maintain erections.
Can thyroid problems cause erectile dysfunction?
Absolutely. Both hypothyroidism (low thyroid function) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can affect sexual performance by changing metabolism, mood, and blood vessel response.
Is hormonal erectile dysfunction reversible?
In most cases, yes. Once the underlying hormone imbalance is identified and treated — through medication, hormone therapy, or lifestyle changes — sexual function usually improves significantly.
Sources
- 1.
A comprehensive review of metabolic syndrome affecting erectile dysfunction
- 2.
Testosterone, Endothelial Health, and Erectile Function
- 3.
Images Download Cite Share Favorites Permissions ORIGINAL ARTICLE Estradiol is an independent risk factor for organic erectile dysfunction
- 4.
Effect of prolactin on penile erection
- 5.
Hyperprolactinemia
- 6.
The Impact of Thyroid Disease on Sexual Dysfunction in Men
- 7.
The association between subclinical hypothyroidism and erectile dysfunction


