Amitriptyline, Sex Drive and Erectile Dysfunction: Uses, Dosage and Sexual Side Effects
Written by Dr. Pranitha Bangera

Dr. Pranitha Bangera is a gold-medalist healthcare professional with an elite foundation in clinical training and patient care. A researcher at heart, she specializes in creating high-impact, research-driven medical content that empowers readers through accessible patient education. Dr. Bangera focuses on the intersection of digital health and clinical communication, specifically within the fields of sexual health and mental well-being. Her work is dedicated to making complex medical innovations understandable and trustworthy for a global audience.
•
November 18, 2025
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.

Quick Read
Amitriptyline can affect sex drive, mostly because it raises serotonin and lowers dopamine, the chemical that drives sexual desire and motivation. This shift, along with sedation and changes in arousal signals, can reduce libido or make it harder to get and maintain an erection. Some people, however, notice improved sex drive as their depression lifts. These effects are usually dose-related, temporary, and often improve with dose adjustments or time. If sexual changes bother you, a healthcare provider can guide you toward safe, effective solutions.
Amitriptyline is a well-known tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) used for conditions like chronic pain, neuropathic pain, and migraine headaches. But some people worry about sexual side effects, and have one question: how does amitriptyline affect sex drive and cause erectile dysfunction? Amitriptyline increases serotonin, which can lower dopamine, the chemical that drives desire and sexual motivation. It also affects brain chemicals needed for arousal and healthy blood flow to the penis. These changes, combined with sedation and fatigue, can reduce sex drive and make it harder to get or maintain an erection. In this article, we will look at how amitriptyline affects sex drive and erections, whether dosage influences risk, and what solutions are safe if these sexual side effects occur.
Allo asks
How has amitriptyline affected your sex drive?
Does Amitriptyline Affect Sex Drive?
Yes, amitriptyline can affect sex drive. It increases serotonin and helps stabilise your mood, but higher levels of serotonin in your brain can reduce dopamine, the chemical tied to sexual desire. [1] This leads to lower arousal and delayed orgasm. Many people also feel sedated or fatigued on amitriptyline, especially in the beginning, and this naturally lowers interest in sexual activity. On the flip side, some individuals actually notice an increase in libido as their depression improves due to the drug, since depression itself is a major cause of low sex drive. [1] Ultimately, amitriptyline can raise or lower sex drive depending on your dosage, the condition being treated, treatment duration, and whether you’re taking other medications.
Does Amitriptyline Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Yes, amitriptyline can cause erectile dysfunction (ED) in some men, and the evidence for this is fairly consistent across studies:
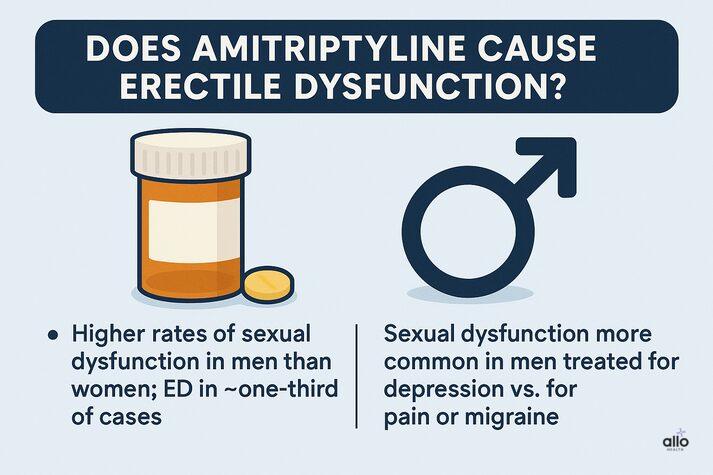
- A study found that overall sexual dysfunction occurred in rates that were much higher in men than in women, within which roughly one-third of cases involved erectile dysfunction and another third involved low libido (sex drive). [1]
- In another study, it was noted that sexual dysfunction was seen more in men treated for depression, in comparison to those taking amitriptyline for non-depressive conditions such as pain or migraine. [2]
How Does Amitriptyline Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
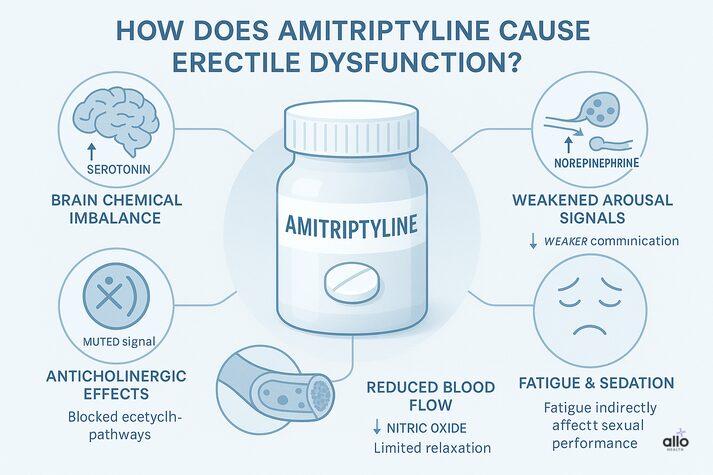
1. Brain Chemical Imbalance
Amitriptyline increases serotonin levels to stabilise mood, but as mentioned before, this can reduce dopamine. Low dopamine is closely linked to decreased erections. When dopamine signalling drops, the brain’s arousal pathways become less responsive, making it harder to initiate or maintain an erection. [1]
2. Weakens Arousal Signals
Norepinephrine is a chemical your body uses to help you feel alert, aroused, and ready for sexual activity. It also supports healthy blood flow to the penis, all of which helps you maintain a firm erection. Amitriptyline causes your body to "pull back" norepinephrine too quickly (norepinephrine reuptake), and this can weaken the signals that tell the penile blood vessels to relax. When those blood vessels don’t relax properly, the penis doesn’t get enough blood flow, and erections can become softer or harder to maintain. [3] Amitriptyline also has strong anticholinergic effects, meaning it blocks acetylcholine, an important chemical for arousal and erection. This can disrupt arousal signals from the brain and reduce the natural swelling that happens during arousal (Penile tumescence). [4]
4. Reduces Blood Flow
Nitric oxide is a molecule that tells penile blood vessels to relax and allow more blood to enter the penis. Amitriptyline can interfere with how nitric oxide functions, and this can affect blood vessel relaxation. [1] Lower NO = reduced blood flow = weaker erections.
5. Causes Fatigue and Mood Changes
Amitriptyline commonly causes drowsiness, fatigue, and mental slowing, especially in the first few weeks. These effects may not directly cause ED, but they indirectly affect sexual arousal, interest, and sexual satisfaction. When your energy is low or your mood fluctuates, sexual activity naturally becomes less of a priority.
What Dose of Amitriptyline Causes ED?
Erectile Dysfunction from amitriptyline is usually dose-related and reversible. A study noted that sexual side effects tended to lessen over 2–8 weeks of continued treatment and decreased further with dose reductions over time. [1] Here’s a simple table that helps you understand how different doses of amitriptyline affect the risk of sexual side effects:
Dose
Common Uses
Risk
Low doses (5–25 mg)
Neuropathic pain, chronic tension-type headache
Very low risk
Moderate doses (50–100 mg)
Depression
High Risk
High doses (100–150 mg+)
Severe depression, some chronic pain cases
Most sexual side effects occur in this range
Elderly patients taking amitriptyline for depression or chronic pain tend to be more sensitive to its effects and may experience sexual side effects even at very low doses.
How to Manage ED Caused by Amitriptyline
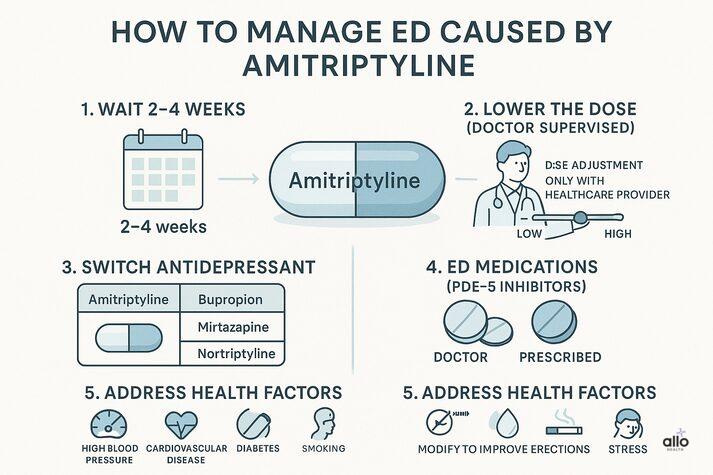
1. Wait 2–4 weeks
Many sexual side effects improve as your body adjusts.
2. Lower the dose (if medically safe)
Lowering the maintenance dose often improves:
- Erections
- Sex drive/ Libido
- Energy levels
Never do this without consulting your healthcare provider.
3. Switch to a gentler antidepressant
If sexual symptoms persist even after the body has otherwise adjusted to the medication, the doctor can prescribe an alternative antidepressant with fewer sexual side effects, like:
- Bupropion (often boosts libido)
- Mirtazapine
- Nortriptyline
- Agomelatine
- Moclobemide
4. ED Medications
ED medications (PDE-5 inhibitors) like sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil, and vardenafil can help restore erectile rigidity and improve sexual satisfaction.
5. Address other contributors
ED can worsen if you have:
- High blood pressure
- Cardiovascular disease
- Diabetes
- Vascular disease
- Smoking, stress, and alcohol use
Treating these improves outcomes.
A few simple lifestyle habits can make a surprisingly big difference, especially when you’re managing a mental health condition and also dealing with sexual symptoms that may come from the medication.
How to Improve Sex Drive and Prevent ED While Taking Amitriptyline
1. Watch for early warning signs
If you notice reduced sex drive or weaker erections in the first few weeks, let your doctor know early. Small adjustments to levels of amitriptyline or timing often reverse these effects quickly.
2. Start with the lowest effective dose
Many conditions, like nerve pain, chronic tension-type headache, and migraine headaches, respond well to low doses (such as 10–25 mg). Lower doses reduce the risk of adverse effects, including sexual problems.
3. Support healthy blood flow
Regular exercise, quitting smoking, and maintaining a balanced weight keep your blood vessels healthier. Better circulation naturally supports erection quality, libido, and overall sexual activity.
4. Prioritise sleep and energy
Amitriptyline can be sedating. If you feel too drowsy, talk to your healthcare provider about adjusting timing. Night-time dosing usually works best and helps maintain good sleep without daytime fatigue, which is important for sex drive.
5. Strengthen emotional intimacy
Sexual arousal isn’t only physical. Stress, anxiety, and emotional overload can lower sexual desire. Slowing down, communicating with your partner, and building comfort often help revive libido.
6. Avoid alcohol
Alcohol can worsen blood pressure changes and make you more drowsy/depressed ( CNS-depressant effects), which can cause erectile dysfunction. Keeping alcohol minimal supports both mood stability and sexual performance.
7. Avoid combining with other antidepressants
Coadministration with medications like MAO inhibitors or serotonergic drugs can boost serotonin levels. This causes a condition called serotonin syndrome, which can be dangerous. It can also have sexual effects.
8. Protect heart health
Good erectile function depends on strong cardiovascular health. Managing blood pressure, cholesterol, and lifestyle factors helps keep blood flow steady, which directly supports erection quality and libido.
9. Mental Health Support
Taking care of your mental health is just as important as managing medication side effects. Psychotherapy for ED can help you understand what’s affecting your desire, improve communication with your partner, and reduce performance pressure. Techniques like CBT, mindfulness, and stress-management therapy often improve both mood and sexual satisfaction.

Conclusion
Amitriptyline can affect sex drive and cause erectile dysfunction. These sexual problems are usually dose-related, often temporary, and mostly reversible. There are many ways to manage these side effects, from adjusting your dose to switching medications, improving lifestyle habits, or using phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors when appropriate. If you notice changes in your sexual health, don’t be embarrassed to talk to a sexual health expert. With the right guidance, you can protect both your mental health and your sexual wellbeing.
Disclaimer
The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only. The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog.
Most Asked Questions
Does amitriptyline lower sex drive?
Yes, it can. Amitriptyline increases serotonin, and higher serotonin may reduce dopamine, the chemical that drives sexual desire. This can temporarily lower sex drive, especially in the first few weeks.
Can amitriptyline cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes, some men experience weaker erections or difficulty maintaining them. This happens because amitriptyline affects arousal signals and blood flow to the penis. The good news is that this side effect is usually reversible.
Are sexual side effects from amitriptyline permanent?
In most cases, no. Studies show that sexual side effects often improve within 2–8 weeks or after adjusting the dose. If symptoms persist, your doctor can switch you to a medication with fewer sexual side effects.
Does the dose of amitriptyline affect sexual side effects?
Yes. Low doses (5–25 mg) used for pain rarely cause issues. Moderate to high doses (50–150 mg) used for depression have a higher risk of low libido and ED.
Why does amitriptyline cause sexual problems?
Amitriptyline alters brain chemicals like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. These chemicals regulate sexual desire, arousal, and blood flow, so changes can affect libido and erection quality.


